Difference between revisions of "R-3S"
Inceptor57 (talk | contribs) (Some historical information I found) |
(→Comparison with analogues: add comparison table) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| link = R-3R | | link = R-3R | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | [[File:R-3S.png|thumb|right|x250px]] | |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
<!-- ''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.'' --> | <!-- ''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.'' --> | ||
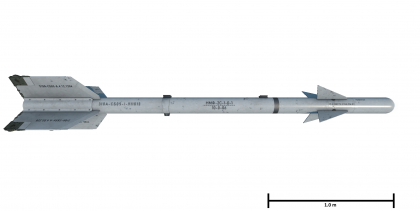
| − | [[File:R-3S.png|thumb| | + | [[File:WeaponImage R-3S.png|thumb|left|420px|The R-3S missile (scale is approximate)]] |
| + | {{Break}} | ||
The '''R-3S''' (K13A, AA-2A 'Atoll') is a Soviet [[Air-to-air_missiles#Infrared_homing_.28heat-seeking.29_missiles|infrared homing air-to-air missile]], it was introduced in [[Update 1.85 "Supersonic"]]. It is an improved version of the original R-3 missile, which was itself a reverse-engineered [[AIM-9B]]. In-game the R-3S performs similarly to the AIM-9B, but is slightly worse in some respects. | The '''R-3S''' (K13A, AA-2A 'Atoll') is a Soviet [[Air-to-air_missiles#Infrared_homing_.28heat-seeking.29_missiles|infrared homing air-to-air missile]], it was introduced in [[Update 1.85 "Supersonic"]]. It is an improved version of the original R-3 missile, which was itself a reverse-engineered [[AIM-9B]]. In-game the R-3S performs similarly to the AIM-9B, but is slightly worse in some respects. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
<!-- ''List out vehicles that are equipped with the weapon.'' --> | <!-- ''List out vehicles that are equipped with the weapon.'' --> | ||
| − | + | {{Navigation-Start|Vehicles equipped with this weapon}} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Jet fighters'''}}{{Specs-Link|mig-17_cuba}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-19pt}} | |
| − | + | {{Navigation-Line|MiG-21}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_f13}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_pfm}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_s}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_smt}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_bis}} | |
| − | + | {{Navigation-Line| }}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_bis_lazur}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_sps_k}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_mf}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_mf_hungary}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_bis_sau_hungary}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig-21_bis_sau}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig_21_bis_finland}} | |
| − | + | {{Navigation-Line|MiG-23}}{{Specs-Link|mig_23m}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig_23mf_germany}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig_23mf_hungary}} | |
| − | + | ||
| + | {{Navigation-End}} | ||
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| − | ''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the missile.'' | + | <!--''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the missile.''--> |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | ||
| + | ! colspan="2" | Missile characteristics | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Mass''' || 75 kg | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Guidance''' || IR | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Aspect''' || Rear-aspect | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Lock range (rear-aspect)''' || 3.5 km | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Launch range''' || 9 km | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Maximum speed''' || 1.7 M | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Maximum overload''' || 10 G | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Missile guidance time''' || 21 secs | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Explosive mass''' || 8.8 kg TNTeq | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
=== Effective damage === | === Effective damage === | ||
| Line 29: | Line 54: | ||
=== Comparison with analogues === | === Comparison with analogues === | ||
''Give a comparative description of missiles that have firepower equal to this weapon.'' | ''Give a comparative description of missiles that have firepower equal to this weapon.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{AIM-9 Comparison Table}} | ||
== Usage in battles == | == Usage in battles == | ||
| − | ''Describe situations when you would utilise this missile in-game (vehicle, pillbox, base, etc)'' | + | <!-- ''Describe situations when you would utilise this missile in-game (vehicle, pillbox, base, etc)'' --> |
| + | It is one of the first air-to-air missiles in the game, it is therefore really rudimentary in its operation. It can only lock on the target if it is right behind it, it will also not be able to lock if the target is in in front of the sun. Any curve tighter than 9G will be enough for the missile to miss the target: only fire if the target is distracted or running away. The missile's speed is also not very high, limited to only Mach 1.7. This means a limited range at low altitude, but it can be circumvented at high altitudes since the higher the less atmospheric air to cause drag on the missile, translating into a greater range and manoeuvrability. | ||
=== Pros and cons === | === Pros and cons === | ||
| − | ''Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.'' | + | <!-- ''Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.'' --> |
'''Pros:''' | '''Pros:''' | ||
| − | * | + | * Able to reach out and attack non-manoeuvring aircraft |
'''Cons:''' | '''Cons:''' | ||
| Line 49: | Line 77: | ||
<!-- ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' --> | <!-- ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' --> | ||
| − | The origin of the '''R-3''' missile has many stories, but it starts in 1954 with Matus Ruvimovich Bisnovat's OKB-4 (renamed 1967 as GMKB ''Vympel''), which was specialized in the development of air-to-air missiles. Bisnovat's OKB-4 soon received a captured and intact [[AIM-9B Sidewinder]] from China.<ref name="GordonAAMpg1">Gordon 2004, p.24</ref> The Chinese reportedly obtained the Sidewinder either as an unexploded missile launched by a Taiwanese F-86,<ref name="LaiDragon">Lai 2016</ref> or in a crashed fighter wreckage that carried the missile.<ref name="GordonAAMpg1"/> Either way, OKB-4 was instructed to reverse-engineer the missile into a working design for Soviet aircraft. | + | The origin of the '''R-3''' missile has many stories, but it starts in 1954 with Matus Ruvimovich Bisnovat's OKB-4 (renamed 1967 as GMKB ''Vympel''), which was specialized in the development of air-to-air missiles. Bisnovat's OKB-4 soon received a captured and intact [[AIM-9B Sidewinder]] from China.<ref name="GordonAAMpg1">Gordon 2004, p.24</ref> The Chinese reportedly obtained the Sidewinder either as an unexploded missile launched by a Taiwanese F-86,<ref name="LaiDragon">Lai 2016</ref> or in a crashed fighter wreckage that carried the missile.<ref name="GordonAAMpg1" /> Either way, OKB-4 was instructed to reverse-engineer the missile into a working design for Soviet aircraft. |
| − | By 1959, OKB-4 has reproduced the missile and tested their design on a Mikoyan SM-9/3T (a variant of the [[MiG-19S_(Germany)|MiG-19S]] for testing purposes) and the Ye-6T (likewise variant of the [[MiG-21F-13|MiG-21]]). The conclusion of the tests allowed OKB-4's missile to move towards production and service as the '''R-3S''' (''S'' - ''sereeynaya'' (Production)). The missile was also known by the name ''K-13'', or under its NATO designation ''AA-2 Atoll''.<ref name="GordonAAMpg1"/> | + | By 1959, OKB-4 has reproduced the missile and tested their design on a Mikoyan SM-9/3T (a variant of the [[MiG-19S_(Germany)|MiG-19S]] for testing purposes) and the Ye-6T (likewise variant of the [[MiG-21F-13|MiG-21]]). The conclusion of the tests allowed OKB-4's missile to move towards production and service as the '''R-3S''' (''S'' - ''sereeynaya'' (Production)). The missile was also known by the name ''K-13'', or under its NATO designation ''AA-2 Atoll''.<ref name="GordonAAMpg1" /> |
The missile would first arm the MiG-21F-13 , and would go on to arm many other variants of the MiG-21 family and other Soviet fighter aircraft. It would later be improved in the [[R-3R]] and [[R-13M]] missile. | The missile would first arm the MiG-21F-13 , and would go on to arm many other variants of the MiG-21 family and other Soviet fighter aircraft. It would later be improved in the [[R-3R]] and [[R-13M]] missile. | ||
| Line 60: | Line 88: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ||
| + | |||
* ''reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;'' | * ''reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;'' | ||
* ''references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.'' | * ''references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.'' | ||
| Line 66: | Line 95: | ||
<!--''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | <!--''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | ||
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
| − | |||
* ''other literature.''--> | * ''other literature.''--> | ||
| − | ; | + | |
| + | === References === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Citations | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
;Bibliography: | ;Bibliography: | ||
| + | |||
* Gordon, Yefim. ''Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War II.'' Midland Publishing, 2004. | * Gordon, Yefim. ''Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War II.'' Midland Publishing, 2004. | ||
* Lai, Benjamin. ''The Dragon's Teeth: The Chinese People's Liberation Army - Its History, Traditions, and Air Sea and Land Capability in the 21st Century.'' Casemate Publishers, 14 July 2016. | * Lai, Benjamin. ''The Dragon's Teeth: The Chinese People's Liberation Army - Its History, Traditions, and Air Sea and Land Capability in the 21st Century.'' Casemate Publishers, 14 July 2016. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:53, 22 October 2024
| This page is about the infrared homing missile R-3S. For the semi-active radar homing version, see R-3R. |
Contents
Description
The R-3S (K13A, AA-2A 'Atoll') is a Soviet infrared homing air-to-air missile, it was introduced in Update 1.85 "Supersonic". It is an improved version of the original R-3 missile, which was itself a reverse-engineered AIM-9B. In-game the R-3S performs similarly to the AIM-9B, but is slightly worse in some respects.
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
| Vehicles equipped with this weapon | |
|---|---|
| Jet fighters | MiG-17AS · MiG-19PT |
| MiG-21 | MiG-21F-13 · MiG-21PFM · MiG-21S (R-13-300) · MiG-21SMT · MiG-21bis |
| ◊MiG-21 "Lazur-M" · ◄MiG-21 SPS-K · ◊MiG-21MF · ◔MiG-21MF · ◔MiG-21bis-SAU · ◊MiG-21bis-SAU · ▄MiG-21bis | |
| MiG-23 | MiG-23M · ◊MiG-23MF · ◔MiG-23MF |
General info
| Missile characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Mass | 75 kg |
| Guidance | IR |
| Aspect | Rear-aspect |
| Lock range (rear-aspect) | 3.5 km |
| Launch range | 9 km |
| Maximum speed | 1.7 M |
| Maximum overload | 10 G |
| Missile guidance time | 21 secs |
| Explosive mass | 8.8 kg TNTeq |
Effective damage
Describe the type of damage produced by this type of missile (high explosive, splash damage, etc)
Comparison with analogues
Give a comparative description of missiles that have firepower equal to this weapon.
- AIM-9B FGW.2 Sidewinder - A European-licensed version of the AIM-9B with their own improvements; however the performance in-game are quite similar.
- R-3S/PL-2 - Infamous as a reverse-engineered variant of the AIM-9B, the R-3 missile shares many of its in-game performances with the AIM-9B, only falling slightly short in locking and launching range.
- Shafrir - Shares in-game performance values despite their design differences
- Rb24 - Licensed-produced version of the AIM-9B for the Swedish, and as such shares in-game performance values.
| Missile | Guidance | Lock range (rear-aspect)(km) |
Launch range (km) |
Maximum speed (Mach) |
Maximum overload (g) |
Mass (kg) |
TNT Equivalent (kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Aspect | Time | Uncaged seeker | Radar slaving | ||||||||
| |
AIM-9B Sidewinder | IR | Rear | 20 | |
|
4 | 10 | 1.7 | 10 | 72 | 7.62 |
| |
AIM-9C Sidewinder | SARH | Front | 60 | |
|
9 | 18 | 2.5 | 18 | 95 | 4.69 |
| |
AIM-9D Sidewinder[note 1] | IR | Rear | 20 | |
|
5.5 | 18 | 2.5 | 18 | 88 | 4.69 |
| |
AIM-9E Sidewinder[note 2] | IR | Rear | 20 | |
|
5.5 | 18 | 2.8 | 10 | 76 | 7.62 |
| |
AIM-9G Sidewinder | IR | Rear | 60 | |
|
5.5 | 18 | 2.5 | 18 | 88 | 3.53 |
| |
AIM-9H Sidewinder | IR | Rear | 60 | |
|
5.5 | 18 | 2.5 | 18 | 88 | 3.53 |
| |
AIM-9J Sidewinder[note 3] | IR | Rear | 40 | |
|
5.5 | 18 | 2.5 | 20 | 76 | 7.62 |
| |
AIM-9L Sidewinder | IR | All | 60 | |
|
11 | 18 | 2.5 | 30 | 84 | 4.58 |
| |
AIM-9M Sidewinder | IR | All | 60 | |
|
11 | 18 | 2.5 | 30 | 84 | 4.58 |
| |
AIM-9P Sidewinder | IR | Rear | 40 | |
|
5.5 | 18 | 2.5 | 20 | 76.93 | 7.62 |
| |
AIM-9P4 Sidewinder | IR | All | 40 | |
|
11 | 18 | 2.5 | 20 | 76.93 | 7.62 |
| |
AIM-9B FGW.2 Sidewinder | IR | Rear | 20 | |
|
5.5 | 10 | 1.7 | 10 | 72 | 7.62 |
| |
Shafrir | IR | Rear | 20 | |
|
7 | 10 | 1.7 | 11 | 65 | 7.62 |
| |
RB24 | IR | Rear | 20 | |
|
4 | 10 | 1.7 | 10 | 72 | 7.62 |
| |
R-3S | IR | Rear | 21 | |
|
9 | 10 | 1.7 | 10 | 75 | 8.8 |
| |
PL-2 | IR | Rear | 21 | |
|
9 | 10 | 1.7 | 10 | 75 | 8.8 |
Usage in battles
It is one of the first air-to-air missiles in the game, it is therefore really rudimentary in its operation. It can only lock on the target if it is right behind it, it will also not be able to lock if the target is in in front of the sun. Any curve tighter than 9G will be enough for the missile to miss the target: only fire if the target is distracted or running away. The missile's speed is also not very high, limited to only Mach 1.7. This means a limited range at low altitude, but it can be circumvented at high altitudes since the higher the less atmospheric air to cause drag on the missile, translating into a greater range and manoeuvrability.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Able to reach out and attack non-manoeuvring aircraft
Cons:
- Poor tracking
- Very low launch overload limit
- Low in-flight G-overload
History
The origin of the R-3 missile has many stories, but it starts in 1954 with Matus Ruvimovich Bisnovat's OKB-4 (renamed 1967 as GMKB Vympel), which was specialized in the development of air-to-air missiles. Bisnovat's OKB-4 soon received a captured and intact AIM-9B Sidewinder from China.[1] The Chinese reportedly obtained the Sidewinder either as an unexploded missile launched by a Taiwanese F-86,[2] or in a crashed fighter wreckage that carried the missile.[1] Either way, OKB-4 was instructed to reverse-engineer the missile into a working design for Soviet aircraft.
By 1959, OKB-4 has reproduced the missile and tested their design on a Mikoyan SM-9/3T (a variant of the MiG-19S for testing purposes) and the Ye-6T (likewise variant of the MiG-21). The conclusion of the tests allowed OKB-4's missile to move towards production and service as the R-3S (S - sereeynaya (Production)). The missile was also known by the name K-13, or under its NATO designation AA-2 Atoll.[1]
The missile would first arm the MiG-21F-13 , and would go on to arm many other variants of the MiG-21 family and other Soviet fighter aircraft. It would later be improved in the R-3R and R-13M missile.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;
- references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.
External links
References
- Citations
- Bibliography
- Gordon, Yefim. Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War II. Midland Publishing, 2004.
- Lai, Benjamin. The Dragon's Teeth: The Chinese People's Liberation Army - Its History, Traditions, and Air Sea and Land Capability in the 21st Century. Casemate Publishers, 14 July 2016.