Difference between revisions of "P-51C-10"
Colok76286 (talk | contribs) |
(→Offensive armament: Updated) |
||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
The '''''{{PAGENAME}}''''' is armed with: | The '''''{{PAGENAME}}''''' is armed with: | ||
| − | * 4 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine guns, wing-mounted ( | + | * 4 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine guns, wing-mounted (280 rpg outer + 350 rpg inner = 1,260 total) |
| − | As mentioned earlier, the P-51C-10's armament is not its strong suit. Four mid-war M2 Brownings do not provide much burst mass and the most reliable way of dispatching enemy aircraft is to set them on fire. For this purpose, the Universal belt has a good content of M8 AP-I rounds. While they do not have tracers like the M20 API-T rounds and have a lower fire chance than the M23 Incendiary rounds enjoyed by the P-51D Mustangs, they will still do good work against more fragile aircraft like [[Bf 109 (Family)|Bf 109s]]. Tougher targets like [[Fw 190 (Family)|Fw 190s]] can shrug off quite a few incoming rounds. Attackers, twin-engined fighters, and bombers with defensive armament tend to be durable and are also challenging to approach and destroy. Focus on knocking out defensive gunners and igniting engines for best results, though these targets are more easily dealt with by friendly [[P-61C-1|P-61 Black Widows]] and [[P-63 (Family)|P-63 Kingcobras]]. The ammunition supply of 300 rounds per gun is good, allowing for some spray-and-pray. | + | As mentioned earlier, the P-51C-10's armament is not its strong suit. Four mid-war M2 Brownings do not provide much burst mass and the most reliable way of dispatching enemy aircraft is to set them on fire. For this purpose, the Universal belt has a good content of M8 AP-I rounds. While they do not have tracers like the M20 API-T rounds and have a lower fire chance than the M23 Incendiary rounds enjoyed by the P-51D Mustangs, they will still do good work against more fragile aircraft like [[Bf 109 (Family)|Bf 109s]]. Tougher targets like [[Fw 190 (Family)|Fw 190s]] can shrug off quite a few incoming rounds. Attackers, twin-engined fighters, and bombers with defensive armament tend to be durable and are also challenging to approach and destroy. Focus on knocking out defensive gunners and igniting engines for best results, though these targets are more easily dealt with by friendly [[P-61C-1|P-61 Black Widows]] and [[P-63 (Family)|P-63 Kingcobras]]. The ammunition supply of ~300 rounds per gun is good, allowing for some spray-and-pray. |
Since the guns are mounted in the wings, gun convergence should be considered. Anywhere between 400-600 metres should work well, but note that more distant convergence settings will make close range shooting more difficult, especially considering the low volume of fire. | Since the guns are mounted in the wings, gun convergence should be considered. Anywhere between 400-600 metres should work well, but note that more distant convergence settings will make close range shooting more difficult, especially considering the low volume of fire. | ||
| Line 181: | Line 181: | ||
{{main|P-51 (Family)|l1=History of the P-51 Mustang}} | {{main|P-51 (Family)|l1=History of the P-51 Mustang}} | ||
| − | The Rolls-Royce Merlin engine was successfully tested on a P-51 Mustang in late 1942, resulting in production of P-51B Mustangs fitted with the Packard V-1650, a license-produced Merlin. North American | + | The Rolls-Royce Merlin engine was successfully tested on a P-51 Mustang in late 1942, resulting in production of P-51B Mustangs fitted with the Packard V-1650, a license-produced Merlin. North American Aviation's (NAA) plant in Inglewood California was maxing out production of the P-51B so a new plant was opened up in Dallas, Texas, in order to increase production. The Mustangs produced in the Dallas plant were designated as the P-51C even though they were identical in all other regards to the P-51B. It was decided during the P-51B and C production run that the aircraft would no longer leave the factory with an olive drab paint, but would instead leave in the unpainted metal finish. |
Deliveries of the P-51C to the US Army Air Force (USAAF) began in August 1943, much later than those of the P-51B due to the Dallas plant having been in the process of construction when the P-51B entered production at Inglewood. A total of 1,750 P-51C Mustangs were built by NAA during the war. | Deliveries of the P-51C to the US Army Air Force (USAAF) began in August 1943, much later than those of the P-51B due to the Dallas plant having been in the process of construction when the P-51B entered production at Inglewood. A total of 1,750 P-51C Mustangs were built by NAA during the war. | ||
| − | P-51B and C Mustangs began arriving in Europe in August and October of 1943, equipping fifteen fighter groups of the 8th and 9th Air Forces in England as well as the 15th Air Force in Italy. P-51C Mustangs, along with their P-51B brethren, were used by the USAAF 8th Air Force to escort B-17 Flying Fortress bombers on daylight raids across the English Channel; the long range of the P-51B/C Mustang made it ideal for that type of mission. The 9th Air Force used them in the fighter-bomber role. In addition to European operations, P-51C Mustangs were used in the China Burma India Theater (CBI). | + | P-51B and C Mustangs began arriving in Europe in August and October of 1943, equipping fifteen fighter groups of the 8th and 9th Air Forces in England as well as the 15th Air Force in Italy. P-51C Mustangs, along with their P-51B brethren, were used by the USAAF 8th Air Force to escort B-17 Flying Fortress bombers on daylight raids across the English Channel; the long range of the P-51B/C Mustang made it ideal for that type of mission. The 9th Air Force used them in the fighter-bomber role. In addition to European operations, P-51C Mustangs were used in the China Burma India Theater (CBI). Even by the end of the war many of the P-51s still in service with the USAAF were of the P-51B and C models, not having been fully replaced by the P-51D and K models but instead only supplemented. |
In addition to serving with the USAAF, 636 P-51B and C Mustangs were also used by the British Royal Air Force (RAF) during the war, where they were designated as the Mustang Mk III. P-51C Mustangs were also used by the Republic of China Air Force (ROCAF) during the Second World War. | In addition to serving with the USAAF, 636 P-51B and C Mustangs were also used by the British Royal Air Force (RAF) during the war, where they were designated as the Mustang Mk III. P-51C Mustangs were also used by the Republic of China Air Force (ROCAF) during the Second World War. | ||
| Line 193: | Line 193: | ||
* '''P-51C-1-NT''' - Original production model with V-1650-3 engine; 350 built. | * '''P-51C-1-NT''' - Original production model with V-1650-3 engine; 350 built. | ||
| − | * '''P-51C-3-NT''' - Added an 85 gallon fuel tank behind the | + | * '''P-51C-3-NT''' - Added an 85 gallon fuel tank behind the pilot's seat; unknown number converted from P-51C-1-NT. |
* '''P-51C-5-NT''' - Used the more powerful V-1650-7 engine; 450 built. | * '''P-51C-5-NT''' - Used the more powerful V-1650-7 engine; 450 built. | ||
* '''P-51C-10-NT''' - 823 built. | * '''P-51C-10-NT''' - 823 built. | ||
| Line 201: | Line 201: | ||
* '''F-6C-NT''' - Reconnaissance conversion with added cameras, armament retained; 20 converted from P-51C-10-NT. | * '''F-6C-NT''' - Reconnaissance conversion with added cameras, armament retained; 20 converted from P-51C-10-NT. | ||
| − | * '''TP-51C''' - Two-seat trainer conversion; 5 converted during WW2, 1 converted in | + | * '''TP-51C''' - Two-seat trainer conversion; 5 converted during WW2, 1 converted in 2000's. |
== Media == | == Media == | ||
Revision as of 09:46, 28 April 2021
| This page is about the American fighter P-51C-10. For other versions, see P-51 (Family). |
Contents
Description
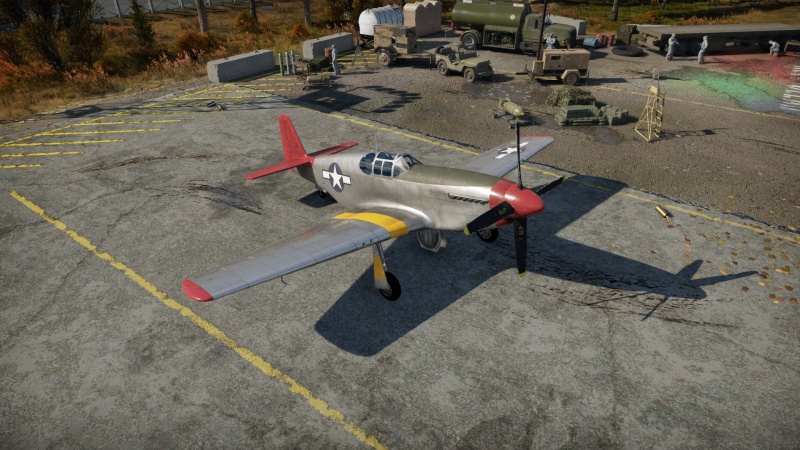
The P-51C-10 Mustang is a rank II American fighter with a battle rating of 3.7 (AB/RB) and 4.0 (SB). It was introduced in Update "Raining Fire".
The P-51C and the essentially identical P-51B were the first production P-51 Mustang models equipped with the famous British Merlin engine, license-produced in the United States as the Packard V-1650. While not quite as famous as the later P-51D series with their bubble canopies, these "razorback" Mustangs were produced in large numbers and served Allied forces well. The vehicle represented in War Thunder is by default painted in the livery of the 332nd Fighter Group, a distinguished all-African-American unit known as the "Red Tails".
The P-51C-10 handles similarly to comparable Merlin-engined Mustangs like the P-51D-5 and P-51D-20-NA and is actually slightly better than them in some respects. Its main weaknesses lie in its armament: four wing-mounted M2 Browning machine guns with mid-war belts leave some to be desired and the suspended ordnance is nothing special. It is still a competitive aircraft overall and offers a good learning opportunity for later USAF propeller fighters. Succeeding the P-51C is the P-47D-22 RE "Razorback" Thunderbolt, which trades general flight performance for better durability, more engine power at extreme altitudes, and most importantly, massively increased firepower.
General info
Flight performance
Unlike its Rank II predecessors, the P-51 and A-36, this plane performs well not only at low altitudes but also above 3,000 metres because of the new Merlin engine and two-stage supercharger instead of one-stage in the Allison powered models. Level speed is exceptionally good at all altitudes compared to the opposition at similar battle ratings. In Realistic Battles, it can reach 610 km/h at sea level and 705 km/h at 7,300 metres of altitude. Acceleration is also above average in level flight. The climb rate is good, especially when compared to the other American planes, and is noticeably better than the P-51D-5 and P-51D-20. At low altitude it is slightly above 20 m/s and the plane can reach 6,000 m alt in about 7 minutes. Diving performance is great as usual, its elevator and other control surfaces do not lock up even at 700-800 km/h IAS and can pull 9G at that speed. Medium and high speed manoeuvrability is good enough to keep up with the Bf 109 G and similar fighters for a while, and the sustained turn rate has been improved over previous Mustangs. Horizontal energy retention is very good, vertical energy retention is good, but manoeuvring energy retention is somewhat below average (but only in RB because of how the instructor controls the plane). Low speed manoeuvrability is still mediocre. The main issue is its rudder, which can lock up above 300 km/h IAS, albeit not to the extent of the P-51D models since the "razorback" fuselage provides better directional stability. The roll rate is not exceptional, veering into poor territory at low speeds.
If using Manual Engine Controls, it is worth mentioning that the Meredith effect is modeled on Mustangs. The cooling system is designed to generate a slight thrust that partially compensates for the aerodynamic drag caused by the radiators. This means that opening up the radiators even to high percentages only causes small effects on energy retention and top speed while keeping the engine nice and cool on WEP settings. This is definitely convenient considering that many contemporary opponents like the Bf 109 F-4 will cook their engines if they run WEP for more than brief periods of time and tend to have draggy radiators.
When flying with full realistic controls, the plane requires some trimming, positive for the elevator (+ 5-7) and rudder or ailerons to the right (but only below 600 km/h IAS) if you want to keep the plane straight in the level flight, when turning the plane tends to roll to the right side. Stall characteristics are very good, with the fuel set to 30 minutes it stalls out only when the elevator deflection reaches 90%. It does have a high stalling speed however, at 175 km/h without flaps and 155 km/h with flaps.
| Characteristics | Max Speed (km/h at 7,300 m) |
Max altitude (metres) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (metres/second) |
Take-off run (metres) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | |||
| Stock | 685 | 666 | 12800 | 22.0 | 22.6 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 300 |
| Upgraded | 734 | 708 | 20.5 | 21.0 | 20.2 | 16.2 | ||
Details
| Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flaps | Take-off flaps | Landing flaps | Air brakes | Arrestor gear |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | X |
| Limits | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wings (km/h) | Gear (km/h) | Flaps (km/h) | Max Static G | |||
| Combat | Take-off | Landing | + | - | ||
| 853 | 287 | 675 | 675 | 275 | ~11 | ~5 |
| Optimal velocities (km/h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons | Rudder | Elevators | Radiator |
| < 500 | < 300 | < 550 | > 400 |
Survivability and armour
The survivability is similar to most other prop fighters. The engine is located in the nose, and the fuel tanks are located behind the pilot's seat and in the wing roots. There is significant armour protection for the pilot, but the pilot is still vulnerable from the top, bottom, and sides. The fuel tanks are also vulnerable, as is the cooling system.
- 38 mm Bulletproof glass - Windshield
- 11.11 mm Steel - Behind pilot's seat
- 6.35 mm Steel - Behind engine, in front of oil cooling system and pilot
- 6.35 mm Steel - In front of upper engine
- Self-sealing fuel tanks
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Offensive armament
The P-51C-10 is armed with:
- 4 x 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine guns, wing-mounted (280 rpg outer + 350 rpg inner = 1,260 total)
As mentioned earlier, the P-51C-10's armament is not its strong suit. Four mid-war M2 Brownings do not provide much burst mass and the most reliable way of dispatching enemy aircraft is to set them on fire. For this purpose, the Universal belt has a good content of M8 AP-I rounds. While they do not have tracers like the M20 API-T rounds and have a lower fire chance than the M23 Incendiary rounds enjoyed by the P-51D Mustangs, they will still do good work against more fragile aircraft like Bf 109s. Tougher targets like Fw 190s can shrug off quite a few incoming rounds. Attackers, twin-engined fighters, and bombers with defensive armament tend to be durable and are also challenging to approach and destroy. Focus on knocking out defensive gunners and igniting engines for best results, though these targets are more easily dealt with by friendly P-61 Black Widows and P-63 Kingcobras. The ammunition supply of ~300 rounds per gun is good, allowing for some spray-and-pray.
Since the guns are mounted in the wings, gun convergence should be considered. Anywhere between 400-600 metres should work well, but note that more distant convergence settings will make close range shooting more difficult, especially considering the low volume of fire.
Suspended armament
The P-51C-10 can be outfitted with the following ordnance:
- Without load
- 2 x 100 lb AN-M30A1 bombs (200 lb total)
- 2 x 250 lb AN-M57 bombs (500 lb total)
- 2 x 500 lb AN-M64A1 bombs (1,000 lb total)
The P-51C-10 has the same suspended ordnance as the A-36 Apache, minus the infamous gunpods. The only loadout worth taking is the twin 500 lb bombs. They drop as a pair and have enough power to take out a target or two if dropped with some precision, though they are certainly less impressive than the twin 1,000 lb bombs carried by later Mustangs with their reinforced hardpoints. Do not engage other fighters while carrying bombs, as they are mounted on the wings and contribute significant amounts of drag, weight, and inertia.
Usage in battles
The P-51C-10 has outstanding performance compared to other planes that can meet in the same bracket (Enduring Confrontation 3, BR 3.7-4.7), level speed is higher at all altitudes than anything that it can face, so it can easily escape from anything when it finds itself in a trouble, climb rate is also very good and allows it to quickly get to the 3,000-5,000 m alt. This plane like all other Mustangs does not overheat when the radiator is set to 90-100%, it also does not slow down the plane, so it can always cruise with enabled WEP which is not limited, always engage other planes with humongous speed advantage and make use of very good mid and high-speed manoeuvrability. Sustained climb rate is worse than that of the Bf 109 F-4 or G-2 by 2-4 m/s, escaping from them by climbing away should be avoided, but still allows the plane to get pretty quick to 3,000-5,000 m alt, also the zoom climb is very good.
One issue that the plane has is quite disappointing armament, sometimes it takes some time to shoot down the enemy fighters and it is even worse against bombers and attackers with higher durability, but attacking with a speed advantage and surprising the enemy should solve it.
The other issue is unsatisfactory turn rate at low speed, engaging other fighters in dogfight should be avoided (instantaneous turn rate is actually good when the plane has lots of energy to spare), especially the Bf 109 F-4, G.55 or Yaks and anything that can turn better than them, the speed advantage should be used instead to beat them.
Because of these points, the preferable tactics for this plane should be Boom and Zoom and other manoeuvres that do not purely depend on turn rate and more on the plane's speed. Dogfighting can work to some extent and against some planes like the Fw 190 A (which does not really stand a chance against the razorback Mustang) but while doing that the player will be forced to sacrifice speed advantage and make the plane vulnerable to attacks from slower planes with far better turn rates.
The plane when it is upgraded can also used as a starter plane in the higher bracket (Enduring Confrontation 4, BR 5.0-6.3) where it should not have any issues with beating tier 4 German, Japanese and Italian fighters, most of them that can be meet there have very similar performance and the P-51C is even better than the D-5 version in some ways.
Manual Engine Control
| MEC elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixer | Pitch | Radiator | Supercharger | Turbocharger | ||
| Oil | Water | Type | ||||
| Not controllable | Controllable Not auto controlled |
Controllable Auto control available |
Controllable Auto control available |
Separate | Not controllable 2 gears |
Not controllable |
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Outstanding Boom & Zoom capability
- Great performance at altitude
- Very fast at all altitudes, especially in a shallow dive
- Very agile at high speeds due to laminar flow wings
- Decent cockpit visibility
- Large fuel capacity (1 hour 45 minutes maximum flight time)
- Fantastic top speed and acceleration
- Very good sustained climb rate
Cons:
- Only four 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine guns with mid-war belts which don't do much damage
- High stall speed and mediocre low speed manoeuvrability
- Not so great at ground pounding, only a few loadout options
- Not very durable
- Roll rate, while not terrible, is not sufficient enough to shake enemy planes off or force overshoots
History
The Rolls-Royce Merlin engine was successfully tested on a P-51 Mustang in late 1942, resulting in production of P-51B Mustangs fitted with the Packard V-1650, a license-produced Merlin. North American Aviation's (NAA) plant in Inglewood California was maxing out production of the P-51B so a new plant was opened up in Dallas, Texas, in order to increase production. The Mustangs produced in the Dallas plant were designated as the P-51C even though they were identical in all other regards to the P-51B. It was decided during the P-51B and C production run that the aircraft would no longer leave the factory with an olive drab paint, but would instead leave in the unpainted metal finish.
Deliveries of the P-51C to the US Army Air Force (USAAF) began in August 1943, much later than those of the P-51B due to the Dallas plant having been in the process of construction when the P-51B entered production at Inglewood. A total of 1,750 P-51C Mustangs were built by NAA during the war.
P-51B and C Mustangs began arriving in Europe in August and October of 1943, equipping fifteen fighter groups of the 8th and 9th Air Forces in England as well as the 15th Air Force in Italy. P-51C Mustangs, along with their P-51B brethren, were used by the USAAF 8th Air Force to escort B-17 Flying Fortress bombers on daylight raids across the English Channel; the long range of the P-51B/C Mustang made it ideal for that type of mission. The 9th Air Force used them in the fighter-bomber role. In addition to European operations, P-51C Mustangs were used in the China Burma India Theater (CBI). Even by the end of the war many of the P-51s still in service with the USAAF were of the P-51B and C models, not having been fully replaced by the P-51D and K models but instead only supplemented.
In addition to serving with the USAAF, 636 P-51B and C Mustangs were also used by the British Royal Air Force (RAF) during the war, where they were designated as the Mustang Mk III. P-51C Mustangs were also used by the Republic of China Air Force (ROCAF) during the Second World War.
P-51C Variants
Combat Variants: 1,750 built
- P-51C-1-NT - Original production model with V-1650-3 engine; 350 built.
- P-51C-3-NT - Added an 85 gallon fuel tank behind the pilot's seat; unknown number converted from P-51C-1-NT.
- P-51C-5-NT - Used the more powerful V-1650-7 engine; 450 built.
- P-51C-10-NT - 823 built.
- P-51C-11-NT - 127 built.
Non Combat Variants
- F-6C-NT - Reconnaissance conversion with added cameras, armament retained; 20 converted from P-51C-10-NT.
- TP-51C - Two-seat trainer conversion; 5 converted during WW2, 1 converted in 2000's.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Other variants in-game
External links
| North American Aviation | |
|---|---|
| Fighters | |
| P-51A | P-51 · P-51A |
| P-51C | P-51C-10 |
| P-51D | P-51D-5 · P-51D-10 · P-51D-20-NA · P-51D-30 |
| P-51H | P-51H-5-NA |
| Twin-engine fighters | F-82E |
| Jet fighters | F-86A-5 · F-86F-2 · F-86F-25 · F-86F-35 · F-100D |
| Strike aircraft | A-36 · PBJ-1H · PBJ-1J |
| FJ-4B · FJ-4B VMF-232 | |
| Bombers | B-25J-1 · B-25J-20 |
| Export/Licence | ▂B-25J-30 · ␗B-25J-30 |
| ▄Mustang Mk IA · F-6C-10-NA · ␗P-51C-11-NT · ␗P-51D-20 · J26 David · J26 · P-51D-20-NA · ␗P-51K | |
| F-86F-30 ▅ · ␗F-86F-30 · F-86F-40 ▅ · F-86F-40 JASDF▅ · ␗F-86F-40 | |
| ◄F-86K · ▄F-86K (Italy) · ▄F-86K (France) | |
| ␗F-100A · ▄F-100D · ␗F-100F | |
| Captured | ▅P-51C-11-NT |
| Canadair Limited license-built the F-86 as the CL-13 for use in Canada and export to Europe. | |
| Fiat license-built the F-86K for the Italian Air Force though another 120 NAA built F-86Ks were also sold to the Italians. | |
| See Also | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries · Canadair Limited · Fiat Aviation |
| USA fighters | |
|---|---|
| P-26 Peashooter | P-26A-33 · P-26A-34 · P-26A-34 M2 · P-26B-35 |
| P-36 Hawk | P-36A · Rasmussen's P-36A · P-36C · ○P-36C · P-36G |
| P-39 Airacobra | P-400 · P-39N-0 · P-39Q-5 |
| P-40 | P-40C · P-40E-1 · P-40E-1 TD · P-40F-10 |
| P-43 Lancer | P-43A-1 |
| P-47 Thunderbolt | P-47D-22-RE · P-47D-25 · P-47D-28 · P-47M-1-RE · ⋠P-47M-1-RE · P-47N-15 |
| P-51 Mustang | P-51 · P-51A (Thunder League) · P-51C-10 · P-51D-5 · P-51D-10 · P-51D-20-NA · P-51D-30 · P-51H-5-NA |
| P-63 Kingcobra | P-63A-5 · P-63A-10 · P-63C-5 · ␠Kingcobra |
| Prototypes | XP-55 |
| F2A Buffalo | F2A-1 · Thach's F2A-1 · F2A-3 |
| BF2C | BF2C-1 |
| F3F | F3F-2 · Galer's F3F-2 |
| F4F Wildcat | F4F-3 · F4F-4 |
| F4U Corsair | F4U-1A · F4U-1A (USMC) · F4U-1D · F4U-1C · F4U-4 · F4U-4B · F4U-4B VMF-214 · F2G-1 |
| F6F Hellcat | F6F-5 · F6F-5N |
| F8F Bearcat | F8F-1 · F8F-1B |
| Other countries | ▃Ki-43-II · ▃Ki-61-Ib · ▃A6M2 · ▃Bf 109 F-4 · ▃Fw 190 A-8 · ▃Spitfire LF Mk IXc |