Difference between revisions of "R-60"
TheDoctorMD (talk | contribs) m (Comparison with analogues and addendum on uncaged seeker function) (Tag: Visual edit) |
Inceptor57 (talk | contribs) (Added history section with sources) |
||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' | + | <!--''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.''--> |
| + | Development at the GMKB Vympel bureau (formerly OKB-4 prior to 1967) on what would be known as the '''R-60''' (also known by the bureau designation ''K-60'' or ''izdeliye 62'') began in the early 1970s. The missile specifications were designed under the requirements for a short-launch range missile capable of high-G turns, high angle speed tracking, in a package of low weight and size for mounting on an aircraft.<ref name="GordonAAM_cite1">Gordon 2004, p.29</ref> In the United States and NATO, the R-60 was designated the ''AA-8'' and ''Aphid'' respectively.<ref name="GordonAAM_cite2">Gordon 2004, p.30</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The missile design's basis was from the [[R-13M|R-13]]. One major design distinction on the R-60 was the addition of small fixed canard surfaces (termed "destabilisers") in front of the rudder to improve their efficiency at high angles of attack.<ref name="GordonAAM_cite1"/> The missile is guided via the Komar (''Mosquito'') IR seeker with an uncooled optical element. The rudder actuators are powered by gases bled from the rocket motor, assisted with a pressure accumulator. Two turbine-driven generators are also present, powered by bleeding the rocket motor gases in order to provide the electrical power for the missile's systems.<ref name="GordonAAM_cite1"/> The missile's solid-fuel rocket motor has a burn time of 3-5 seconds, and a self-destruct timer of 25 seconds should the missile miss.<ref name="GordonAAM_cite2"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Measures to improve the R-60's resistance against electric counter-measures included the development of two different proximity fuses. The Strizh (''Swift'') optical fuse is the active fuse that detonates the missile within 1-5 metres of the target. The second is the Kolibri (''Colibri'') radar proximity fuse with antennas receiving pulsed radio signals. Missiles with the Kolibri installed are designated ''R-60K''.<ref name="GordonAAM_cite2"/> A variant of the R-60 was also produced, designated ''R-60U'' and lacks fins or rudders, with a data recorder installed in the warhead space and a ballast in the rocket motor space. This was intended for training with the missile retained on the pylon while the data recorder captured the pilot's actions to ensure proper preparations and requirements are met before a mock launch was attempted.<ref name="GordonAAM_cite3">Gordon 2004, p.32</ref><ref name="GordonAAM_cite4">Gordon 2004, p.25</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The R-60 missiles production would start in 1973, with deployment in 1975. The missiles are installed onto aircraft via the APU-60-1 single missile rail or the APU-60-2 double missile rail, with the APU-60-1 usually mounted onto the BD3-60-23F1 or BD3-60-23F1 pylons.<ref name="GS_Stinger">GlobalSecurity.org "AA-8 APHID"</ref><ref name="GordonAAM_cite3"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The R-60 would be refined further into the ''[[R-60M]]'' variant. | ||
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| Line 93: | Line 102: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | + | <!--''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' |
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
| − | * ''other literature.'' | + | * ''other literature.''--> |
| + | ;References: | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Bibliography: | ||
| + | * GlobalSecurity.org "AA-8 APHID" ''Global Security'', [https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/russia/aa-8.htm Website]. Accessed 03 Jul. 2021 ([https://web.archive.org/web/20210703202542/https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/russia/aa-8.htm Web Archive]). | ||
| + | * Gordon, Yefim. ''Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War II.'' Midland Publishing, 2004. | ||
{{Missiles}} | {{Missiles}} | ||
[[Category:Suspended armaments]] | [[Category:Suspended armaments]] | ||
Revision as of 20:41, 3 July 2021

Contents
Description
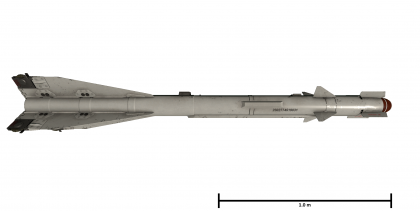
The R-60 is a Soviet infrared homing air-to-air missile, it was introduced in Update 1.85 "Supersonic".
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
| Vehicles equipped with this weapon | |
|---|---|
| Jet fighters | MiG-21bis · ◊MiG-21MF · MiG-21SMT · MiG-23M |
| Strike aircraft | Su-17M2 · Yak-38 · Yak-38M |
| Attack helicopters | Mi-24P · ◊Mi-24P · ◄Mi-24P HFS 80 · Mi-24V |
General info
The R-60, a short range infrared homing missile, is usually most effective at ranges between 600 and 2,200 m (at sea level). The burn time of the R-60's propellant is 3 seconds. Compared to other missiles, the R-60 accelerates slower but for longer when comparing to other missiles (the AIM-9Js fuel last for 2.2 seconds with more force, R-60s having 3 seconds but with less force). The R-60s have better total-force-to-weight ratio when compared to the AIM-9Js. Comparing the AIM-9Js to the R-60s, R-60s have almost half the weight of the AIM-9Js, meaning the R-60s pulls better at lower speeds and higher altitudes.
It is also important to note that this missile can uncage its seeker which allow the user to lead the target before launching. Although there is only a brief window of opportunity to fire as uncaging the seeker only maintains lock for a short period of time before it resets to acquire another target unless slaved to radar.
When compared to the AIM-9Js, the R-60s have double the inner FOV of the seeker head, meaning it is easier to acquire a lock when doing turning engagements, though this comes at the cost of being able to be fooled easier by flares and other countermeasures, since these may come into the view of the missiles (This is also the reason why AIM-9Js are less likely to be fooled by flares when compared to R-60s).
Unlike the heavier missiles (such as AIM-9Js), R-60s will be able to hit targets at extremely close ranges of up to roughly 550 m. This is all due to the very lightweight design on the missile itself.
One major problem of the R-60 is its tendency to almost always be fooled by flares. If the target has flares, even while stalling, the missile will be fooled and follow the flares anyway. It is recommended to only target unaware enemies or those without flares.
Effective damage
Due to the low explosive mass of 1.15 kg of TNT, R-60 requires closer detonation or a direct hit on a target, in order to deal sufficient damage, especially when compared to missiles such as AIM-9J which have almost 5x the explosive mass.
Comparison with analogues
Compared to the most common air-to-air missiles such as AIM-9J or R550 Magic, R-60 tends to have the upper hand in most chasing/dog fighting scenarios due to its extended turning capability possible through the long engine burn time and high G tolerance although this is offset by its distinctly larger seeker FOV and smaller gimbal compared to the AIM-9J and R550 Magic. The smaller gimbal means leading the missile is more difficult compared to its contemporaries.
Usage in battles
Important details:
Every missile greatly performs better when at higher altitudes, this should be used to your advantage as missiles becomes unavoidable when launched at a reasonable range and altitude if the target doesn't deploy countermeasures, missiles accelerate faster, pull harder and reach higher velocities at higher altitudes due to the reduced drag. This comes as a double edge sword however as your missiles perform better, the enemy's missiles do as well which means that you shouldn't put yourself in a position where enemies can engage you while you're engaging a target. Coming in at unexpected angles while being undetected is the best way to utilize R-60s and every other missile.
The higher the speed of which the missile is launched, the faster the missile will reach its optimum manoeuvrability, therefore keeping your speed high and obtaining optimal launch conditions are instrumental to a successful missile kill.
Use of radar slaving may prove to be incredibly useful when leading a target, especially when the dogfight continually changes angles and pointing the nose towards the target may not be possible.
Launching at a target flying away from you:
This is the optimum launch angle against a target. When at sea level, the maximum range in relation of yourself to the target is around 2,200 m, given that the target is flying at the same speed, same direction and not manoeuvring. This changes depending on whether the target is moving slower or faster than you. The slower the target in comparison to you, the further you can launch your missile at the target. The faster the target in comparison to you, the shorter the range is of your missile. Range is also heavily influenced by the altitude of yourself and of the target. The higher the altitude, the less drag and therefore, the longer the range is.
Launching at a target, perpendicular to you:
When the target is flying perpendicular to you, the important factors are giving your missile the optimum launch conditions to be able to pull enough Gs to hit your target. These optimum conditions include; launching your missile at a high speed (preferably above Mach), keeping enough distance between you and the target, as well as leading target as much as you can to reduce the amount of energy the missile has to use to reach the target. If the target is slower, these conditions are easier to fulfill when engaging a target. However, if the target is moving at very high speeds, such attempt at hitting the target will likely result in missing the target and greater launch conditions are required to hit the target.
Once again, higher altitudes greatly improve the performance of the missile, meaning that such angles for a missile towards the target may be impossible at lower altitudes, while being easy for the missile at higher altitudes.
Remember:
Your goal when using missiles, are to obtain the optimum launching parameters for your missile to successfully hit the target. Positioning and teamwork are instrumental to be able to obtain these launch conditions for your missiles. Using missiles to force your target into an optimum position may be necessary to launch a second missile at the target.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Large seeker FOV (making it easier to obtain a lock without pointing the nose directly towards the target).
- Light missile (in comparison to other similar missiles, better performance at lower speeds and higher altitudes).
- Longer burn time (useful for longer range engagements).
- One of the best missiles for extremely short ranges
- Radar slaving (easier to lead targets)
Cons:
- Large seeker FOV (more prone to countermeasures such as flares, due to the increased likelihood of the countermeasures coming into view of the seeker).
- Lacking TNT load can fail to sufficiently damage targets even on close proximity
History
Development at the GMKB Vympel bureau (formerly OKB-4 prior to 1967) on what would be known as the R-60 (also known by the bureau designation K-60 or izdeliye 62) began in the early 1970s. The missile specifications were designed under the requirements for a short-launch range missile capable of high-G turns, high angle speed tracking, in a package of low weight and size for mounting on an aircraft.[1] In the United States and NATO, the R-60 was designated the AA-8 and Aphid respectively.[2]
The missile design's basis was from the R-13. One major design distinction on the R-60 was the addition of small fixed canard surfaces (termed "destabilisers") in front of the rudder to improve their efficiency at high angles of attack.[1] The missile is guided via the Komar (Mosquito) IR seeker with an uncooled optical element. The rudder actuators are powered by gases bled from the rocket motor, assisted with a pressure accumulator. Two turbine-driven generators are also present, powered by bleeding the rocket motor gases in order to provide the electrical power for the missile's systems.[1] The missile's solid-fuel rocket motor has a burn time of 3-5 seconds, and a self-destruct timer of 25 seconds should the missile miss.[2]
Measures to improve the R-60's resistance against electric counter-measures included the development of two different proximity fuses. The Strizh (Swift) optical fuse is the active fuse that detonates the missile within 1-5 metres of the target. The second is the Kolibri (Colibri) radar proximity fuse with antennas receiving pulsed radio signals. Missiles with the Kolibri installed are designated R-60K.[2] A variant of the R-60 was also produced, designated R-60U and lacks fins or rudders, with a data recorder installed in the warhead space and a ballast in the rocket motor space. This was intended for training with the missile retained on the pylon while the data recorder captured the pilot's actions to ensure proper preparations and requirements are met before a mock launch was attempted.[3][4]
The R-60 missiles production would start in 1973, with deployment in 1975. The missiles are installed onto aircraft via the APU-60-1 single missile rail or the APU-60-2 double missile rail, with the APU-60-1 usually mounted onto the BD3-60-23F1 or BD3-60-23F1 pylons.[5][3]
The R-60 would be refined further into the R-60M variant.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;
- references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.
External links
- References
- Bibliography
- GlobalSecurity.org "AA-8 APHID" Global Security, Website. Accessed 03 Jul. 2021 (Web Archive).
- Gordon, Yefim. Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War II. Midland Publishing, 2004.