Difference between revisions of "MIM146"
Inceptor57 (talk | contribs) (→History: Added image) |
esroofing901 (talk | contribs) (→General info) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| − | + | Length: 2.05m | |
| + | |||
| + | Weight: 51kg | ||
| + | |||
| + | warhead; 12.5kg HE frag/shaped charge with impact and proximity fuze | ||
| + | |||
| + | Speed: mach 3+ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Range: 10km | ||
| + | |||
| + | ceiling: 7km | ||
| + | |||
| + | Propulsion: Hercules low-smoke solid-fuel rocket | ||
| + | |||
| + | Guidance: Digitally coded laser beam-riding | ||
| + | |||
| + | Penetration: 900mm RHA | ||
=== Effective damage === | === Effective damage === | ||
| Line 26: | Line 42: | ||
'''Pros:''' | '''Pros:''' | ||
| + | |||
* | * | ||
'''Cons:''' | '''Cons:''' | ||
| + | |||
* | * | ||
| Line 36: | Line 54: | ||
[[File:ADATS launch.jpg|thumb|x250px|left|none|The ADATS firing a MIM-146 missile during US testings.]] | [[File:ADATS launch.jpg|thumb|x250px|left|none|The ADATS firing a MIM-146 missile during US testings.]] | ||
| − | In 1986, the Canadian Forces accepted the missile as part of their {{annotation|LLAD|Low-Level Air Defence}} program.<ref name="ParschMIM146"/><ref name="RheinmetallADATS">Rheinmetall Canada Inc. "History"</ref> The first deliveries begun in 1988 with a total of 36 ADATS weapons procured by 1994.<ref name="ParschMIM146"/><ref name="FAS_ADATS">Pike and Sherman 1999</ref><ref name="ArmyTechnology_ADATS">Army Technology. "ADATS Short Range Air Defence System"</ref> The ADATS would serve in the Canadian military until 31 March 2011.<ref name="RheinmetallADATS"/> | + | In 1986, the Canadian Forces accepted the missile as part of their {{annotation|LLAD|Low-Level Air Defence}} program.<ref name="ParschMIM146" /><ref name="RheinmetallADATS">Rheinmetall Canada Inc. "History"</ref> The first deliveries begun in 1988 with a total of 36 ADATS weapons procured by 1994.<ref name="ParschMIM146" /><ref name="FAS_ADATS">Pike and Sherman 1999</ref><ref name="ArmyTechnology_ADATS">Army Technology. "ADATS Short Range Air Defence System"</ref> The ADATS would serve in the Canadian military until 31 March 2011.<ref name="RheinmetallADATS" /> |
| − | In the United States, as the [[M247]] {{annotation|DIVAD|Division Air Defense}} vehicle was cancelled in 1985, the search was still on for a FAAD (Forward-Area Air Defense) weapon to replace aging equipment such as the MIM-72 ''Chaparral''. In 1989, the ADATS was evaluated as a {{annotation|LOS-F-H|Line-Of-Sight, Forward, Heavy}} air defense system, with the missiles designated the '''MIM146'''. However, the MIM146 was found to have low reliability during testing of the equipment in combat conditions, and so the ADATS procurement was cancelled in 1992.<ref name="ParschMIM146"/> To fill in their role, the Bradley Stinger Fighting Vehicle was obtained, mounting [[AIM-92 Stinger|FIM-92 Stinger]] missiles as their primary anti-aircraft weapon.<ref name="ParschMIM146"/><ref name="FAS_ADATS"/> | + | In the United States, as the [[M247]] {{annotation|DIVAD|Division Air Defense}} vehicle was cancelled in 1985, the search was still on for a FAAD (Forward-Area Air Defense) weapon to replace aging equipment such as the MIM-72 ''Chaparral''. In 1989, the ADATS was evaluated as a {{annotation|LOS-F-H|Line-Of-Sight, Forward, Heavy}} air defense system, with the missiles designated the '''MIM146'''. However, the MIM146 was found to have low reliability during testing of the equipment in combat conditions, and so the ADATS procurement was cancelled in 1992.<ref name="ParschMIM146" /> To fill in their role, the Bradley Stinger Fighting Vehicle was obtained, mounting [[AIM-92 Stinger|FIM-92 Stinger]] missiles as their primary anti-aircraft weapon.<ref name="ParschMIM146" /><ref name="FAS_ADATS" /> |
| − | Another user of the ADATS missile is the Royal Thai Air Force, who have linked them to their Skyguard fire control radar system<ref name="ArmyTechnology_ADATS"/> | + | Another user of the ADATS missile is the Royal Thai Air Force, who have linked them to their Skyguard fire control radar system<ref name="ArmyTechnology_ADATS" /> |
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| Line 50: | Line 68: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ||
| + | |||
* ''reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;'' | * ''reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;'' | ||
* ''references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.'' | * ''references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.'' | ||
| Line 57: | Line 76: | ||
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
* ''other literature.''--> | * ''other literature.''--> | ||
| + | |||
;References: | ;References: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
;Bibliography: | ;Bibliography: | ||
| + | |||
* Army Technology. "ADATS Short Range Air Defence System." ''Army Technology'', Verdict Media Limited, [https://www.army-technology.com/projects/adats/ Website]. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021. | * Army Technology. "ADATS Short Range Air Defence System." ''Army Technology'', Verdict Media Limited, [https://www.army-technology.com/projects/adats/ Website]. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021. | ||
* Parsch, Andreas. "MIM-146." ''Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles'', Designation-Systems.Net, 05 Nov. 2002, [http://www.designation-systems.net/dusrm/m-146.html Website]. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021. | * Parsch, Andreas. "MIM-146." ''Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles'', Designation-Systems.Net, 05 Nov. 2002, [http://www.designation-systems.net/dusrm/m-146.html Website]. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021. | ||
Revision as of 07:08, 1 April 2021
Contents
Description
Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
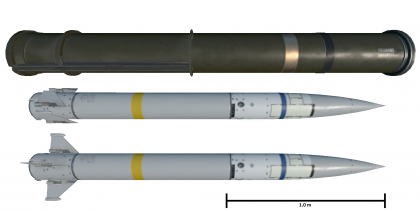
General info
Length: 2.05m
Weight: 51kg
warhead; 12.5kg HE frag/shaped charge with impact and proximity fuze
Speed: mach 3+
Range: 10km
ceiling: 7km
Propulsion: Hercules low-smoke solid-fuel rocket
Guidance: Digitally coded laser beam-riding
Penetration: 900mm RHA
Effective damage
Describe the type of damage produced by this type of missile (high explosive, splash damage, etc)
Comparison with analogues
Give a comparative description of missiles that have firepower equal to this weapon.
Usage in battles
Describe situations when you would utilise this missile in-game (vehicle, pillbox, base, etc)
Pros and cons
Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.
Pros:
Cons:
History
In the 1970s, the Swiss company Oerlikon-Bührle company researched into the viability of a low-cost anti-aircraft missile that can also act in an anti-tank role. Designated under ADATS, Oerlikon partnered with the American company Martin Marietta in 1979 for the missile program. The first missile firing was conducted in June 1981.[1]
In 1986, the Canadian Forces accepted the missile as part of their LLAD program.[1][2] The first deliveries begun in 1988 with a total of 36 ADATS weapons procured by 1994.[1][3][4] The ADATS would serve in the Canadian military until 31 March 2011.[2]
In the United States, as the M247 DIVAD vehicle was cancelled in 1985, the search was still on for a FAAD (Forward-Area Air Defense) weapon to replace aging equipment such as the MIM-72 Chaparral. In 1989, the ADATS was evaluated as a LOS-F-H air defense system, with the missiles designated the MIM146. However, the MIM146 was found to have low reliability during testing of the equipment in combat conditions, and so the ADATS procurement was cancelled in 1992.[1] To fill in their role, the Bradley Stinger Fighting Vehicle was obtained, mounting FIM-92 Stinger missiles as their primary anti-aircraft weapon.[1][3]
Another user of the ADATS missile is the Royal Thai Air Force, who have linked them to their Skyguard fire control radar system[4]
Media
- Videos
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;
- references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.
External links
- References
- Bibliography
- Army Technology. "ADATS Short Range Air Defence System." Army Technology, Verdict Media Limited, Website. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021.
- Parsch, Andreas. "MIM-146." Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Designation-Systems.Net, 05 Nov. 2002, Website. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021.
- Pike, John; Sherman, Robert. "Air Defense Anti-Tank System [ADATS]." Federation of American Scientists - Military Analysis Network, 02 Jul. 1999, Website. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021.
- Rheinmetall Canada Inc. "History." Rheinmetall Canada Inc., Website. Accessed 21 Mar. 2021.