Difference between revisions of "Tu-1"
Colok76286 (talk | contribs) (Added StoreImages) |
m (→Flight performance) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
{{Specs-Avia-Flight}} | {{Specs-Avia-Flight}} | ||
<!-- ''Describe how the aircraft behaves in the air. Speed, manoeuvrability, acceleration and allowable loads - these are the most important characteristics of the vehicle.'' --> | <!-- ''Describe how the aircraft behaves in the air. Speed, manoeuvrability, acceleration and allowable loads - these are the most important characteristics of the vehicle.'' --> | ||
| − | The Tupolev Tu-1 has a high top speed. However, its acceleration is noticeably slow as it is heavy aircraft and it is degraded even further by the drag of bombs carried externally | + | The Tupolev Tu-1 has a high top speed. However, its acceleration is noticeably slow as it is a heavy aircraft and it is degraded even further by the drag of bombs carried externally |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" width="70%" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" width="70%" | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
{{Specs-Avia-Armour}} | {{Specs-Avia-Armour}} | ||
<!-- ''Examine the survivability of the aircraft. Note how vulnerable the structure is and how secure the pilot is, whether the fuel tanks are armoured, etc. Describe the armour, if there is any, and also mention the vulnerability of other critical aircraft systems.'' --> | <!-- ''Examine the survivability of the aircraft. Note how vulnerable the structure is and how secure the pilot is, whether the fuel tanks are armoured, etc. Describe the armour, if there is any, and also mention the vulnerability of other critical aircraft systems.'' --> | ||
| + | |||
;Armour plates | ;Armour plates | ||
| + | |||
* 65 mm armoured glass in front of and behind the pilot | * 65 mm armoured glass in front of and behind the pilot | ||
* 12 mm steel on the pilot's seat | * 12 mm steel on the pilot's seat | ||
Revision as of 01:11, 23 November 2021
Contents
Description
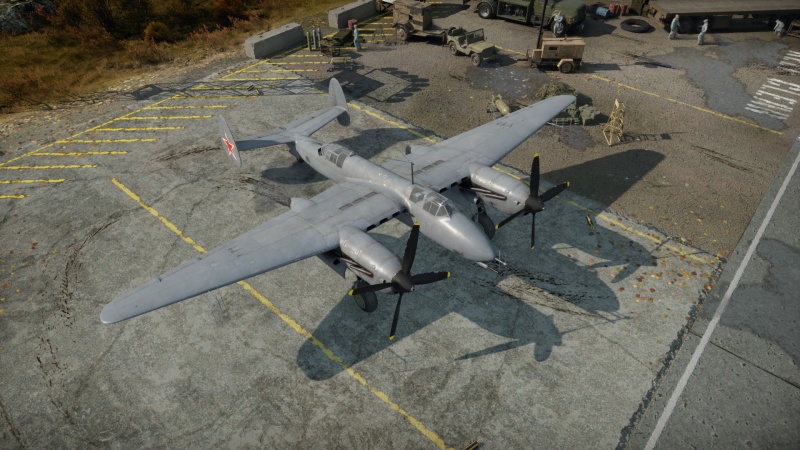
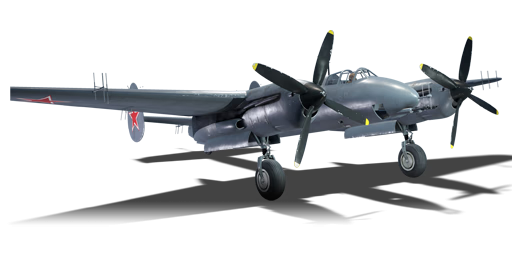
The Tu-1 is a premium gift rank IV Soviet strike aircraft with a battle rating of 5.7 (AB/SB) and 5.3 (RB). It was introduced in Update "Direct Hit". A perfect addition for ground and naval battles at mid tiers.
General info
Flight performance
The Tupolev Tu-1 has a high top speed. However, its acceleration is noticeably slow as it is a heavy aircraft and it is degraded even further by the drag of bombs carried externally
| Characteristics | Max Speed (km/h at 7,150 m) |
Max altitude (metres) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (metres/second) |
Take-off run (metres) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | |||
| Stock | ___ | ___ | 11500 | __._ | __._ | __._ | __._ | 480 |
| Upgraded | 726 | 687 | 27.6 | 29.0 | 15.8 | 11.5 | ||
Details
| Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flaps | Take-off flaps | Landing flaps | Air brakes | Arrestor gear |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | X |
| Limits | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wings (km/h) | Gear (km/h) | Flaps (km/h) | Max Static G | |||
| Combat | Take-off | Landing | + | - | ||
| 0 | 390 | 437 | 380 | 310 | ~__ | ~__ |
| Optimal velocities (km/h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons | Rudder | Elevators | Radiator |
| < ___ | < ___ | < ___ | > ___ |
Survivability and armour
- Armour plates
- 65 mm armoured glass in front of and behind the pilot
- 12 mm steel on the pilot's seat
- 10 mm of steel behind the radar
- 65 mm armoured glass behind the radar
- 5 mm steel beneath the rear gunner
- 12 mm of steel in front of the dorsal gunner
- 12 mm of steel in front of the ventral gunner
All this armour and a good defensive armament makes for a pretty survivable aircraft. This plane also gets self-sealing fuel tanks, which helps liniting fire damage.
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Offensive armament
The Tu-1 is armed with:
- 2 x 45 mm NS-45 cannons, chin-mounted (50 rpg = 100 total)
- 2 x 23 mm NS-23 cannons, wing-mounted (130 rpg = 260 total)
Suspended armament
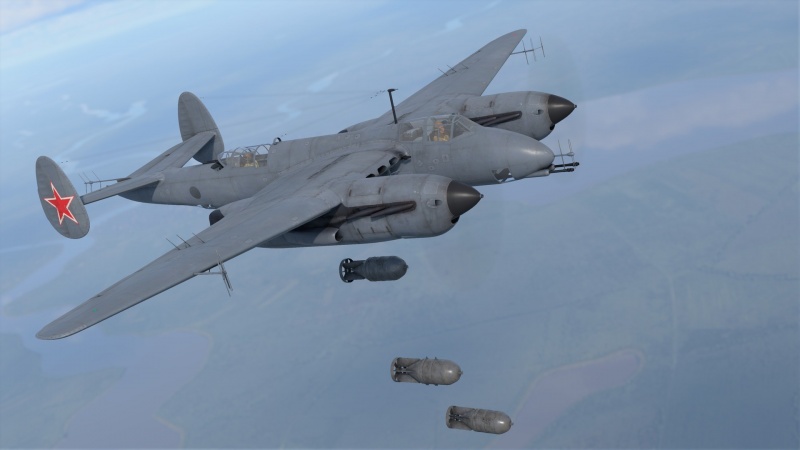
The Tu-1 can be outfitted with the following ordnance:
- Without load
- 6 x 250 kg FAB-250M-44 bombs (1,500 kg total)
- 3 x 500 kg FAB-500M-44 bombs (1,500 kg total)
- 3 x 1,000 kg FAB-1000M-44 bombs (3,000 kg total)
- 2 x 450 mm 45-36NU torpedoes
Defensive armament
The Tu-1 is defended by:
- 1 x 12.7 mm Berezin UB machine gun, dorsal turret (250 rpg)
- 1 x 12.7 mm Berezin UB machine gun, ventral turret (350 rpg)
The defensive guns have limited coverage, so if an enemy aircraft comes from above, you will have a hard time defending yourself.
Usage in battles
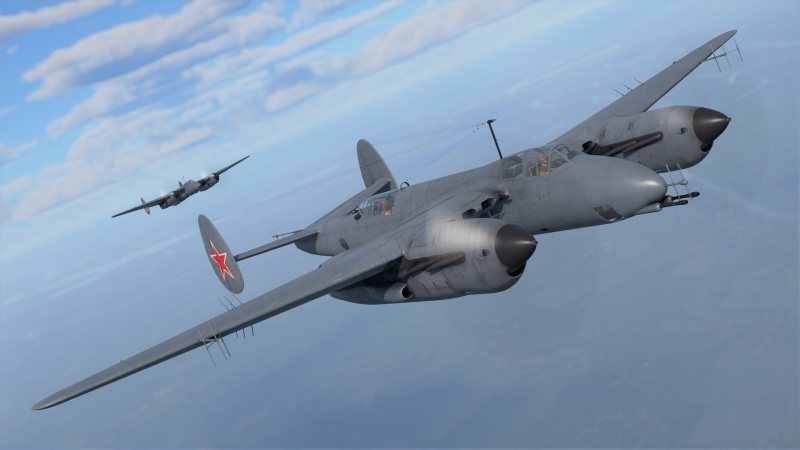
In RB, the aircraft is given a strike fighter spawn, meaning it does not have as much room to dive and gain speed as a bomber. The Tu-1 is capable of destroying enemy fighters in head-on engagements or unsuspecting attackers, thanks to its 23 mm and 45 mm cannons. For usage in combined forces, the Tu-1 makes for a very potent attacker, carrying three 1,000 kg ofbombs as well as the pair of 45 mm cannons having the option to fire API-T rounds, which can knock out all but the heaviest tanks at its BR from the tops and sides.
Manual Engine Control
| MEC elements | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixer | Pitch | Radiator | Supercharger | Turbocharger | ||
| Oil | Water | Type | ||||
| Controllable | Controllable Not auto controlled |
Controllable Not auto controlled |
Controllable Auto control available |
Separate | Not controllable 1 gear |
Not controllable |
Pros and cons
Pros:
- 2 powerful 45 mm cannons
- Great payload options with up to 3 tons of bombs
- 2 torpedoes in naval battles can sink battleships
- Has access to a target detection radar
Cons:
- Targeting radar is next to useless outside of simulator battles
- Weak against enemies from above
- Heavy weight
History
Devblog
Back in the pre-war period, while working on the Tu-2 front-line bomber, the Tupolev design team had the idea of creating a multipurpose aircraft on its basis that could perform a wider range of tasks, including escorting bombers at high altitudes and intercepting enemy aircraft. The first tests of the Tu-2 convinced the military authorities to initiate development for the role of a heavy fighter. However, the outbreak of the war forced the designers to focus on the modifications of the Tu-2 bomber series. Nonetheless, work on the version of the heavy fighter did not stop, moreover, one of the key components of the new aircraft was to become a radar, which would allow the location of targets at distances of up to 8 km and at any time of the day. Andrey Tupolev personally attended lectures on aviation radars, after which he enthusiastically started adapting the latest developments on his aircraft. In the meantime, work continued on enhancing the combat and flight characteristics of the aircraft. The armament was significantly improved compared to the original concepts - two 45-mm NS-45 guns were installed in the front of the bomb bay, supported by 2x 23-mm guns in the wings. The defensive armament of the aircraft was represented by two 12.7mm UBT machine guns. After experiments with the power-plant, the choice fell on the M-43V engines with a four-blade propeller. The finished prototype made her maiden flight only in the spring of 1947. Despite the good test results, the project of the Tupolev heavy fighter was not continued. The era of jet aircraft was approaching.
Media
- Videos
See also
External links
| Tupolev Design Bureau (Ту́полев Опытное конструкторское бюро) | |
|---|---|
| Bombers | TB-3M-17-32 · SB 2M-100 · SB 2M-103 MV-3 · SB 2M-103 · SB 2M-103U · SB 2M-103U MV-3 · SB 2M-105 |
| Tu-2 · Tu-2S · Tu-2S-44 · Tu-2S-59 · Tu-4 | |
| Arkhangelsky Bomber | Ar-2* |
| Strike Aircraft | Tu-1 |
| Jet Bomber | Tu-14T |
| Export | ␗SB 2M-103U · ␗Tu-2S-44 · ␗Tu-4 |
| ◔Tu-2S-59 | |
| * While Andrei Tupolev was imprisoned, Alexander Arkhangelsky, second in command at Tupolev OKB was able to append his name to the final production series of the SB bomber. | |
| USSR strike aircraft | |
|---|---|
| IL-2 | IL-2 (1941) · IL-2 (1942) · IL-2M (1943) · IL-2M type 3 · IL-2M "Avenger" · IL-2-37 · IL-2 M-82 |
| IL-8 | IL-8 (1944) |
| IL-10 | IL-10 · IL-10 (1946) |
| Pe-3 | Pe-3 (e) · Pe-3 · Pe-3bis |
| Su-2 | BB-1 · Su-2 MV-5 · Su-2 TSS-1 · Su-2 (M-82) |
| Su-6 | Su-6 · Su-6 (AM-42) · Su-6 (M-71F) |
| Su-8 | Su-8 |
| Tandem MAI | Tandem MAI |
| TIS MA | TIS MA |
| Tu-1 | Tu-1 |
| Yak-2 | Yak-2 KABB |
| USSR premium aircraft | |
|---|---|
| Fighters | Krasnolutsky's I-15bis · I-16 type 28 · Zhukovsky's I-153-M62 · I-153P · I-180S · I-301 · ITP (M-1) |
| LaGG-3-4 · LaGG-3-23 · LaGG-3-34 · Dolgushin's La-7 · La-11 | |
| Eremin's Yak-3(e) · Yak-3 (VK-107) · Yak-3T · Golovachev's Yak-9M | |
| ▂P-39K-1 · ▂Pokryshkin's P-39N-0 · ▂P-39Q-15 · ▂P-40E-1 · ▂P-47D-27 · ▂P-63A-5 · ▂P-63A-10 · ▂P-63C-5 | |
| ▂Hurricane Mk IIB · ▂Spitfire Mk IXc · ▂Fw 190 D-9 | |
| Twin-engine fighters | I-29 |
| Jet fighters | Su-11 · MiG-15bis ISh · MiG-17AS · MiG-21S (R-13-300) · MiG-23ML |
| Strike aircraft | IL-2M "Avenger" · IL-2 M-82 · IL-8 (1944) · Su-6 · Tandem MAI · TIS MA · Su-8 · Tu-1 |
| Yak-38 · Su-7BMK · Su-25K · Su-39 | |
| Bombers | Po-2M · Be-6 · MBR-2-M-34 · Pe-2-205 · TB-3M-17-32 |
| ▂PBY-5A Catalina · ▂Hampden TB Mk I · ▂A-20G-30 · ▂B-25J-30 | |