Difference between revisions of "Me 163 B"
(Updated format) |
m (→External links) |
||
| Line 212: | Line 212: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | + | <!-- ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' |
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
* ''encyclopedia page on the aircraft;'' | * ''encyclopedia page on the aircraft;'' | ||
| − | * ''other literature.'' | + | * ''other literature.''--> |
| + | |||
| + | * [https://forum.warthunder.com/index.php?/topic/320874-messerschmitt-me-163-b-1/ Official data sheet - more details about the performance] | ||
{{AirManufacturer BFW}} | {{AirManufacturer BFW}} | ||
{{Germany jet aircraft}} | {{Germany jet aircraft}} | ||
Revision as of 19:34, 25 January 2021
| This page is about the German jet fighter Me 163 B. For version equipped with 20 mm MG 151 cannons, see Me 163 B-0. |
Contents
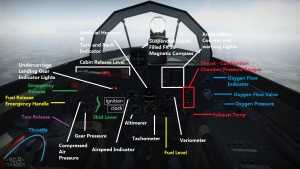
Description
The Me 163 B is a rank V German jet fighter with a battle rating of 8.0 (AB/RB/SB). It has been in the game since the start of the Open Beta Test prior to Update 1.27.
Even at BR 8.0, few jets can out run, out climb, or out turn the Komet, and even fewer can do all three at the same time. Even the highest BR jets cannot threaten this tiny terror lightly, lest it feasts on their blood! Although hard to catch, it is not hard to kill. The very short 6-minute fuel supply is its Achilles heel: if possible, just avoid the Komet until its fuel is spent for an easier kill. Still, any disciplined Komet jockey can overcome its shortcomings, rocketing high above the map, cut throttle, and easily glide at a mind-blowing 400 km/h to action. Stay above 5,000 m for its best performance, unless all targets are lower, and perform vertical manoeuvres to preserve precious energy. The craft is very sturdy and only the most extreme manoeuvres can break the wings so push it. Conversely don't chase top jets, get altitude, let them come to you (they will). High closing speeds require maxed out crews Keen Vision and G-Tolerance and majority of Awareness, and of course Expert qualification.
There are two characteristics that make the Me 163 what it is in War Thunder. The first is its powerful rocket engine, the second is its low fuel supply. The latter means that the Komet must rush into the battlefield quickly before its fuel supply falls low and it needs to land at an airbase. Its huge thrust-to-weight ratio guarantees however that the Komet will be able to engage the enemy very early on in a match. Whenever the enemy team is climbing or gaining speed at sea level, the experienced Me 163 pilot will always find some unsuspecting prey. Remember, when engaging an enemy, turning off the rocket engine is the wisest choice, as to operate on safe speeds and to conserve fuel.
The Me 163 B-1 is a fun to play aircraft that provides a very different play style. For that reason, it always succeeds in seducing players. It may be frustrating at times, but its particularity will always make it a plane worth flying.
General info
Flight performance
| Characteristics | Max Speed (km/h at 4,500 m) |
Max altitude (metres) |
Turn time (seconds) |
Rate of climb (metres/second) |
Take-off run (metres) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | RB | AB | RB | AB | RB | |||
| Stock | 943 | 933 | 15000 | 21.2 | 21.3 | 27.7 | 25.0 | 850 |
| Upgraded | 966 | 955 | 20.8 | 21.0 | 46.4 | 37.0 | ||
Details
| Features | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combat flaps | Take-off flaps | Landing flaps | Air brakes | Arrestor gear | Drogue chute |
| ✓ | X | ✓ | X | X | X |
| Limits | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wings (km/h) | Gear (km/h) | Flaps (km/h) | Max Static G | |||
| Combat | Take-off | Landing | + | - | ||
| 1040 | 550 | 620 | N/A | 420 | ~9 | ~4 |
| Optimal velocities (km/h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailerons | Rudder | Elevators | Radiator |
| < 790 | < 600 | < 690 | N/A |
Engine performance
| Engine | Aircraft mass | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine name | Number | Empty mass | Wing loading (full fuel) | ||
| Walter HWK 109-509A-2 | 1 | 1,900 kg | 199 kg/m2 | ||
| Engine characteristics | Mass with fuel (no weapons load) | Max Takeoff Weight | |||
| Weight (each) | Type | 1m fuel | 6m fuel | ||
| 166 kg | Liquid-fuel rocket | 2,235 kg | 3,910 kg | 4,297 kg | |
| Maximum engine thrust @ 0 m (RB / SB) | Thrust to weight ratio @ 0 m (100%) | ||||
| Condition | 100% | WEP | 1m fuel | 6m fuel | MTOW |
| Stationary | 1,700 kgf | N/A | 0.76 | 0.43 | 0.40 |
| Optimal | 1,700 kgf (any speed) |
N/A | 0.76 | 0.43 | 0.40 |
Survivability and armour
- 90 mm Bulletproof glass in front of the pilot.
- 15 mm Steel plate cone in the nose.
- 13 mm Steel plates behind the pilot.
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Offensive armament
The Me 163 B is armed with:
- 2 x 30 mm MK 108 cannons, wing-mounted (60 rpg = 120 total)
The two cannons are mounted with one in each wing. Each is armed with the same amount of ammunition, which means that all guns will fire together until empty.
Usage in battles
Tactics
For RB and SB: The Me 163 brings energy fighting to a whole new level thanks to its immense rate of climb and acceleration, creating its own subgenre of fighting style only shared with the Ki-200 and partially with the Heimatschützer variants of the Me-262. Instead of just the usual speed/altitude dynamic, the German rocket fighter brings in a new element, fuel supply. Fuel management is a constant worry when flying in the 163. The most energy-efficient way of using the Komet's engine is to use it to its fullest when climbing, to then shut it off whilst engaging enemies, so, if possible, avoid using the Komet's engine in a straight line. If you are chasing an enemy and you're at a lower energy state than the bandit, it is, of course, reasonable to turn on the engine to catch the enemy, but then, if you are at a lower energy state than an enemy, you've probably done something wrong.
It is important for the Komet pilot to pick targets with care and to only commit to a target when there's a good chance of success as to not waste any advantages. Fortunately, the Me 163 B's weaponry allows for neutralizing foes in just a short burst. When engaging or evading a target, the Komet can make use of its splendid turning ability, yet every pilot should keep in mind that when its fuel tank is full, this aircraft's wings are very prone to rip at high G's due to the extra weight.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Very high climb rate and acceleration
- Good speed
- Can go over Mach 1 in level flight at very high altitudes (~15,500 m)
- Excellent manoeuvrability
- One of the best turn rates of the rank
- Powerful 30 mm MK 108 cannons that are extremely deadly
- Small target
- Reasonable repair cost
Cons:
- Extremely limited fuel capacity
- Prone to wing overload crashes when the fuel tanks are full
- Vulnerable airframe
- Aircraft easily compresses during high speed
- Unfavourable armament ballistics for fighting jets
- No take-off flaps
- No airbrakes
History
The aptly named "Komet" (Comet) was not an emergency fighter but a result of years of development, all the brainchild of one of the great aircraft pioneers, Dr. Alexander Lippisch. Following the first world war, he was employed with the Zeppelin Company, a prestigious company with leading aeronautical research. There he became interested in tailless aircraft and despite the Versailles Treaty restricted times experimented and developed many tail first (canards, French for "duck") and tailless gliders. In 1928 Fritz von Opel, son of the famous automotive manufacture and infamous for rocket-powered vehicles wanted to make a rocket-powered aircraft, and the Lippisch "Ente" (duck) was perfect. Although the Ente was destroyed on its second flight and Opel moved on to make his own design, the seed for rocket-powered aircraft was planted in Lippisch.
By the late 1930's the basic design of what would eventually become the Me 163 was taking shape. The engine that was eventually chosen was made by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft, maker of reliable RATO units. On 2 January 1939 Lippisch joined the Messerschmitt group with its much better manufacturing ability, completing the experimental aircraft. With the successful experimental design test flights in the 1940 work progressed on the next version, the Me 163A - reusing an RLM airframe number from the cancelled Bf 163 as a disguise - and first flew on 1 September 1941. The aircraft had phenomenal performance, but the cutting edge technology was highly unreliable and dangerous. It was not a priority project and it was another 2 years before the larger combat capable Me 163 B was ready for action and a few months after that before it has its baptism of fire and history.
The Me-163 began life at the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug as a modification of the Lippisch Delta IV glider, known as the DFS 39.
A larger version, called the DFS 194, powered by a propeller, was abandoned before completion, and Lippisch's team (now at Messerschmitt) focused entirely on the design of the rocket-powered version. The airframe was finally completed in 1940, and the first production model flew in 1941.
Attempts to optimize the Me-163 for mass production, as well as the fitting of the HWK 109-509, as opposed to the old Walter R-1-203 engine, resulted in the Me-163B, that began production in late 1941.
In July 1944 a tiny aircraft tore through the formation of B-17 bombers spitting fire. The turrets could not turn fast enough, barely able to follow the streak with their eyes too. Although none of the B-17s were hit, the incident shook the bomber crews to the core, an enemy fighter that came out of nowhere, too fast to track and too small to aim at. In later encounters, P-51 fighter escorts also found themselves impotent against this little plane. So advanced was this revolutionary fighter.
Intended for point intercept when everything worked just right it fulfilled its duty admirably, but those chances were rare and in the end, with about a dozen kill credits it did not achieve its ambitious goals.
Although a failure as a fighter, the Komet was the most revolutionary aircraft ever and achieved many world records, including the first to exceed 1,000 km/h and to reach its critical Mach in level flight. It inspired many experimental rocket aircraft in its wake, Ki-200, X-1, X-15, even the Space Shuttle are descendants of that little plane. Dr. Lippisch also greatly contributed to flight, working for Convair post-war developing his delta wing designs, this technology eventually resulting in the supersonic F-102, F-106, B-58, and inspiration for Concorde and shape of the Space Shuttle among dozens of others. This tiny plane and its inventor literally changed the shape of aviation.
In-game description
The Messerschmitt Ме 163 Komet was a German rocket-powered interceptor. Its first flight took place on 1st September 1941. A very small number was produced; only 91 before the end of 1944. First combat for the Komet took place on 14th May 1944.
The Me 163 was a unique aircraft standing virtually alone in aviation history. The Komet was the only operational tailless aircraft and the only operational rocket fighter of WWII. In addition, it had other unique features, including its very narrow role, a daylight short-range interceptor used for pin-point defense of strategic targets, with a record-breaking top speed and climb rate.
First production Me 163 B-0 variants, produced in early 1943, were armed with twin 20mm Mauser MG 151/20 cannon with 100 rounds per gun. By the 47th production variant, the Komet was upgunned to twin 30mm Mk 108 cannon. The designation was then changed to Me 163 B-1. The B-1 had 60 rounds per gun. This armament met with some criticism from contemporary engineers. The Mk 108 had a low rate of fire and poor reliability. Statistically, the weapon failed once per every 100 rounds fired. In the constantly changing conditions of aerial combat, the 163 could simply run out of shells before having a chance to successfully destroy a heavy bomber.
Media
- Skins
- Videos
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the aircraft;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
| Germany jet aircraft | |
|---|---|
| |
Luftwaffe |
| He 162 | He 162 A-1 · He 162 A-2 |
| Me 163 | Me 163 B · Me 163 B-0 |
| Ho 229 | Ho 229 V3 |
| Ar 234 | Ar 234 B-2 · Ar 234 C-3 |
| Me 262 | Me 262 A-1a · Me 262 A-1a/Jabo · Me 262 A-1a/U1 · Me 262 A-1/U4 · Me 262 A-2a |
| Me 262 C-1a · Me 262 C-2b | |
| |
LSK |
| Fighters | ◊MiG-15bis · ◊Lim-5P · ◊MiG-19S |
| ◊MiG-21MF · ◊MiG-21bis-SAU · ◊MiG-21 "Lazur-M" | |
| ◊MiG-29 | |
| Attackers | ◊MiG-23BN · ◊MiG-23MF · ◊MiG-23MLA |
| ◊Su-22UM3K · ◊Su-22M4 | |
| ◊IL-28 | |
| |
Luftwaffe |
| F-84 | ◄F-84F |
| F-86 | ◄CL-13A Mk 5 · ◄CL-13B Mk.6 · ◄F-86K |
| F-104 | ◄F-104G |
| F-4 | ◄F-4F Early · ◄F-4F · ◄F-4F KWS LV |
| G.91 | ◄G.91 R/3 · ◄G.91 R/4 |
| Tornado | ◄Tornado IDS WTD61 · ◄Tornado IDS MFG · ◄Tornado IDS ASSTA1 |
| Other | Alpha Jet A · ◄Sea Hawk Mk.100 |
| Ex-LSK | ◄MiG-21 SPS-K · ◄MiG-29G · ◄Su-22M4 WTD61 |
| |
Swiss Air Force |
| ◌Hunter F.58 · FFA P-16 | |