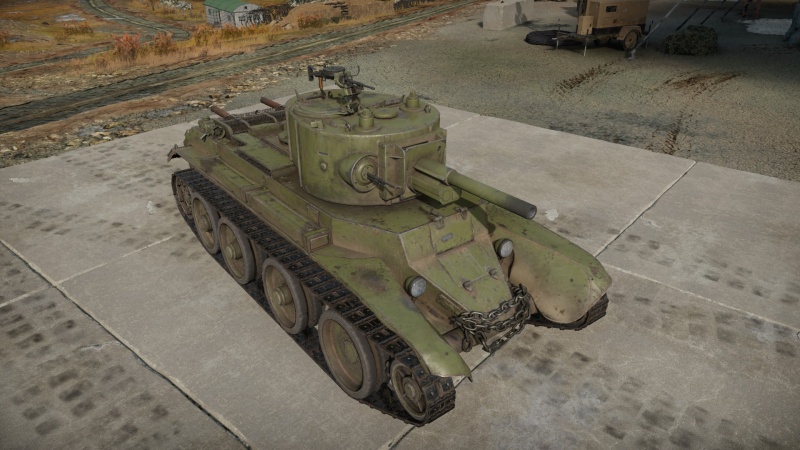
BT-7A (F-32)
| This page is about the gift Soviet light tank BT-7A (F-32). For other versions, see BT-7 (Family). |
Contents
Description
The BT-7A (F-32) is a premium gift rank II Soviet light tank with a battle rating of 3.7 (AB) and 4.0 (RB/SB). It was introduced during Update 1.89 "Imperial Navy" as one of the rewards for Operation H.E.A.T. It uses the same chassis as the BT-7 and as such, possesses the same armour, engine and crew layout but adds a new turret fitted with the 76 mm F-32 gun.
Like the BT-7 before it, it is very fast while having light armour, which at its BR can be penetrated by virtually all vehicles, meaning it must rely on stealth and speed even more than its predecessor. It comes armed with the much more powerful 76 mm F-32 cannon, which has higher penetration and explosive mass, allowing it to easily knock out larger tanks from the side with a single shot. It also comes with a pintle-mounted light machine gun, a rarity among early Soviet tanks, allowing it slightly more AA firepower.
General info
Survivability and armour
The crew compartment is very small and inhabited by the driver, a loader and a gunner. The turret crew operate in a very small environment, so it is very rare that only one of them would die from a shot. "Not getting shot at" is the best advice for the crew to survive.
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour (hull, turret)
- Cast homogeneous armour (MG port)
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 15 mm (61°) Front glacis 20 mm (18°) Driver's hatch 20 mm (cylindrical) Lower hull |
20 mm Front 15 + 4 mm Rear |
10 mm (55°) Top 13 mm (16°) Bottom 13 mm (58°) Lower glacis |
10 mm 4 mm Engine vents |
| Turret | 15 mm (6-12°) Gun mantlet 15 mm (cylindrical) Turret front 15 mm MG port |
15 mm Front 13 mm Rear |
13 mm Rear 15 mm MG port |
10 mm |
Notes
- Suspension wheels, tracks and torsion bars are 15 mm thick.
- Belly armour is 6 mm thick and mudguards are 4 mm thick.
- There is an inner wall (4 mm thick) acting as spaced armour along the flanks of the tanks and separating the engine compartment from the crew compartment.
Being lightly armoured, the BT-7A (F-32) is very vulnerable to nearby ammo rack detonations and bomb blasts.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 55 | 11 | 13.7 | 620 | 763 | 45.26 | 55.69 |
| Realistic | 50 | 10 | 354 | 400 | 25.84 | 29.2 | |
As a light tank, the BT-7A (F-32) is very agile and has a very high top speed. Due to its high HP ratio, the acceleration is outstanding: 59 km/h in about 6 seconds off-road. The brakes are powerful and will make it skid rather than slow down when travelling at maximum speed. The reverse speed is good (-11 km/h): it will get you out of a dangerous situation quickly. While the BT-7A (F-32) lacks neutral steering, the turning speed on the spot is still good (8 km/h). It reaches 20 km/h when fording, 27 km/h when driving uphill with some speed built-up but only 13 km/h uphill from a stop. The narrow tracks will grant you a decent mobility on hard terrain (solid ground, roads) but poor mobility on soft terrain (mud, snow, sand), especially when changing direction as the tracks are long and close to one another. Light obstacles (fences and bushes) are not a problem but medium to large obstacles (posts, trees, concrete blocks and parked vehicles) will reduce your mobility: avoid them.
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
| 76 mm F-32 | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 50 | -6°/+25° | ±180° | N/A | 15.23 | 21.08 | 25.6 | 28.31 | 30.12 | 8.19 | 7.25 | 6.68 | 6.30 |
| Realistic | 9.52 | 11.20 | 13.60 | 15.04 | 16.00 | ||||||||
The F-32 gun offers a good penetration power at its battle rating. Its below-average muzzle velocity still allows for pretty flat firing trajectories. The accuracy drop is noticeable from a 1,000 m distance and becomes a handicap over 1,300 m. The rotation speed of the turret is rather slow but average compared to other tanks at the same rank or battle rating. The elevation angle of the gun is important, allowing you to fire at an elevated position but the depression angle is poor, making it impossible to fire from behind a ridge. Lacking a stabilizer, the tank can't reliably fire on the move. The reload time of the gun is rather long but in line with other tanks equipped with a 76 mm cannon at the same BR. The gun recoil is average for a Soviet vehicle and not important enough to throw your gun off target after firing.
Ammunition
The available ammunition allows for engaging all types of targets:
- BR-350A (MD-5 fuze): APHEBC; an armour-piercing shell with high explosive mass that will destroy any tank it penetrates but has an average penetration power.
- BR-350B (MD-8 fuze): APHEBC; the same shell but with an increased penetration power at the cost of slightly less explosive filler.
- OF-350M: HE; useful for destroying open and lightly armoured vehicles.
- Sh-354T: Shrapnel; useful against vehicles that are resistant to the HE shells but too thinly armoured to trigger the fuzes of AP shells.
- D-350A: Smoke; useful to blind enemy vehicles that are too remote for you to disable so that you can progress towards objectives.
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| BR-350A (MD-5 fuse) | APHEBC | 78 | 76 | 70 | 62 | 56 | 50 |
| BR-350B (MD-8 fuse) | APHEBC | 88 | 86 | 77 | 67 | 59 | 51 |
| OF-350M | HE | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Sh-354T | Shrapnel | 35 | 34 | 30 | 26 | 22 | 19 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | |||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| BR-350A (MD-5 fuse) | APHEBC | 615 | 6.3 | 1.2 | 14 | 150 | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
| BR-350B (MD-8 fuse) | APHEBC | 615 | 6.5 | 0.9 | 14 | 100.1 | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
| OF-350M | HE | 615 | 6.2 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 621 | 79° | 80° | 81° | |||
| Sh-354T | Shrapnel | 615 | 6.44 | 1.2 | 14 | 85 | 62° | 69° | 73° | |||
| Smoke shell characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Screen radius (m) |
Screen deploy time (s) |
Screen hold time (s) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
| D-350A | 615 | 6.45 | 13 | 5 | 20 | 50 |
Ammo racks
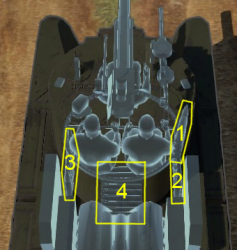
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 47 (+3) | 39 (+11) | 31 (+19) | 1 (+49) | No |
Notes:
- Racks are modeled by sets of 2 shells. They disappear from the rack once all shells in the set have been loaded/fired.
- Turret and sides empty: 39 (+11) shells.
Machine guns
The small calibre of the DT machine gun makes it largely ineffective against all armoured vehicles but the ones with an open compartment. It still can be used to ping targets as a rangefinding help. The clip capacity of the machine gun is quite poor, as it relies on a magazine of 63 bullets instead of a belt like similar machine guns from other nations.
| 7.62 mm DT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Coaxial | 1,890 (63) | 600 | N/A | N/A |
| Pintle | 1,890 (63) | 600 | -10°/+15° | ±180° |
Usage in battles
- Combat tactics
The BT-7A (F-32) is a light tank and should be played as such: flank the opposing forces, surprise the enemy, take a shot before they can react and get to cover before other enemy tanks come to help and engage your light tank.
- Avoid rushing into the enemy head-on, staying in the open and exposing yourself.
- Prioritise flanking, taking the least travelled path and "sneak-peek" attacks.
- Always be on the move: change positions after having destroyed an enemy and retreat if needed. Mobility is key to your survival.
- Use your light tank's abilities to spot hiding enemies and help with repairs.
- Notable enemies
Any tank is capable of easily penetrating your thin armour. Here is the ammunition type by order of lethality:
- shells with explosive damage (HEAT, HE);
- shells with post-penetration damage (APHE, APCBC);
- autocannon rounds (API-T, HVAP, etc.);
- heavy calibre MG rounds.
- Defeating a BT-7A (F-32)
- With a limited crew of 3, any penetrating shot with good post-penetration damage in the crew compartment means the destruction of your vehicle.
- In a frontal encounter, aim for the driver's hatch/pike nose under the turret.
- When flanking, aim for the flanks right under the turret. Follow up with a shot at the driver's position if it survives.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Very fast and nimble
- Excellent offroad capability
- Powerful engine and wide tracks make the BT-7 a good climber
- Excellent cannon with a good rate of fire and 150 g explosive shell
- Performs well even when up-tiered
- Slightly better gun depression than other 76 mm counterparts (-6° over -5°)
- Features active scouting, repair assistance unlike other BT tanks
- Additional DT machine gun on pintle mount useful for spotting, attacking open-topped vehicles
Cons:
- Exposed tracks and suspensions are prone to be damaged
- Very thin armour and packed crew
- Pretty large and difficult to hide
- Difficult to drive with precision - can slew on turns and bounces a lot after braking.
- More flat un-angled areas than BT-5
- Vulnerable to heavy machine gun fire
- Sometimes stalls on turns on soft terrain
History
Development
The success of the BT light tanks in Soviet service prompted additional upgrades and other developmental projects done on the design to increase its service life. The development led to the final model of the BT light tank series, the BT-7. The tank differed from the older BT-5 tank with a welded hull, redesigned hull front, and a new engine in the Model 1935 version. The Model 1937 version of the BT-7 added a redesigned turret that featured sloping armour.
The BT-7 (F32) is a modification of the BT-7 Artillery model sometimes called BT-7A. The artillery model took the design of the T-26-4 turret fitted with a KT-28 short-barrelled howitzer and mounted a 76 mm (3 in) ST short-barrelled howitzer. Due to the extra weight of the turret, the BT lost its ability to drive on the road wheels. 155 BT-7A models were created, 11 converted into command versions and a few were tested with a bigger 76 mm gun, the F-32 gun designed by famous Soviet weapon designer, Vasily Grabin.
Devblog
The pre-war Soviet BT-7s stood out as reliable, manoeuvrable vehicles that worked especially well when attacking in conjunction with infantry. However, the 45 mm cannon had insufficient destructive potential for combat with serious enemy fortifications. In 1939 two experimental BT-7 models were tested with a more powerful 76 mm cannon: the L-11, which was then installed on early KV-1s, and the F-32, the precursor to the gun mounted on the first T-34s. The L-11 turned out to be too large to be installed on the BT-7's small turret, but the F-32 not only fit well on the tank's turret, but also beat the competing gun in a number of tactical and technical characteristics. The committee unequivocally recommended the BT-7 (F-32) modification for serial production, but, due to a series of factors, the tank never saw mass production, and only the experimental model was ever produced.
Media
- Skins
- Videos
See also
- Other vehicles of similar configuration and role
External links
| Kharkov Design Bureau for Mechanical Engineering named after A. A. Morozov | |
|---|---|
| Light Tanks | |
| BT-5 | BT-5 · RBT-5 |
| BT-7 | BT-7 · BT-7M · BT-7A (F-32) |
| Medium Tanks | |
| T-34-76 | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1940) · T-34 (1941) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34 (1942) · T-34E STZ · T-34E |
| T-34-57 | T-34-57 · T-34-57 (1943) |
| T-34-85 | T-34-85 (D-5T) · T-34-85 · T-34-85E |
| T-34-100 | T-34-100 |
| T-44 | T-44 · T-44-100 · T-44-122 |
| Main Battle Tanks | |
| T-54 | T-54 (1947) · T-54 (1949) · T-54 (1951) |
| T-64 | T-64A (1971) · T-64B |
| Export/Captured | |
| T-34 | ▀T 34 747 (r) · ▄T-34 · ▄T-34-85 · ␗T-34 (1943) · ␗Т-34-85 (S-53) |
| T-54 | ▄T-54 |
| See Also | Uralmashzavod · Uralvagonzavod |
| USSR light tanks | |
|---|---|
| T-26 | T-26 · T-26 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-26-4 · T-26E |
| BT | BT-5 · RBT-5 · BT-7 · BT-7 TD · BT-7M · BT-7A (F-32) |
| T-50 | T-126 · T-50 |
| T-70 | T-70 · T-80 |
| PT-76 | PT-76B · PT-76-57 · Object 906 |
| BMP | BMP-1 · BMP-2 · BMP-2M · BMP-3 |
| BMD | BMD-4 |
| 2S25 | 2S25 · 2S25M |
| Wheeled | BA-11 · BTR-80A |
| Other | T-60 · Object 685 · 2S38 |
| China | ▂Type 62 |
| USSR premium ground vehicles | |
|---|---|
| Light tanks | BA-11 · RBT-5 · BT-7A (F-32) · T-26 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-26E · T-126 · PT-76-57 · 2S38 |
| Medium tanks | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34E · T-34-57 (1943) · T-34-85E · T-34-100 · T-44-122 · TO-55 · T-55AM-1 · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-80UD · Т-80U-Е1 |
| ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 · ▂T-III · ▂T-V · ▂МК-IX "Valentine" | |
| Heavy tanks | SMK · T-35 · ▂MK-II "Matilda" · KV-1E · KV-2 (1940) · KV-2 (ZiS-6) · KV-122 · KV-220 · IS-2 "Revenge" · Object 248 · IS-6 · T-10A |
| Tank destroyers | BM-8-24 · BM-13N · BM-31-12 |
| SU-57 · SU-76D · SU-76M (5th Gv.Kav.Corps) · SU-85A · SU-100Y · SU-122P · Object 120 | |
| SPAA | ▂Phòng không T-34 · ZUT-37 |






