Difference between revisions of "MK-IX "Valentine" (USSR)"
Inceptor57 (talk | contribs) (→History: Added images) |
Colok76286 (talk | contribs) (→Description: Added link to event) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
<!-- ''In the description, the first part should be about the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle, as well as its key features. In the second part, tell the reader about the ground vehicle in the game. Insert a screenshot of the vehicle, so that if the novice player does not remember the vehicle by name, he will immediately understand what kind of vehicle the article is talking about.'' --> | <!-- ''In the description, the first part should be about the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle, as well as its key features. In the second part, tell the reader about the ground vehicle in the game. Insert a screenshot of the vehicle, so that if the novice player does not remember the vehicle by name, he will immediately understand what kind of vehicle the article is talking about.'' --> | ||
| − | The '''{{Specs|name}}''' is a premium gift rank {{Specs|rank}} Soviet medium tank {{Battle-rating}}. It was introduced during [[Update 1.95 "Northern Wind"]] as a special Valentine's Day vehicle. This is a Lend-Lease Valentine, shipped to the USSR by the British. The tank was made available to purchase in-game with Golden Eagles ({{GE}}) for specific mini-events like the [[wt:en/news/6583-special-valentine-s-day-en|2020]], [[wt:en/news/7042-special-lunar-new-year-and-valentine-s-day-en|2021]], and [[wt:en/news/ | + | The '''{{Specs|name}}''' is a premium gift rank {{Specs|rank}} Soviet medium tank {{Battle-rating}}. It was introduced during [[Update 1.95 "Northern Wind"]] as a special Valentine's Day vehicle. This is a Lend-Lease Valentine, shipped to the USSR by the British. The tank was made available to purchase in-game with Golden Eagles ({{GE}}) for specific mini-events like the [[wt:en/news/6583-special-valentine-s-day-en|2020]], [[wt:en/news/7042-special-lunar-new-year-and-valentine-s-day-en|2021]] [[wt:en/news/7555-special-happy-valentine-s-day-en|2022]], and [[wt:en/news/8093-special-happy-valentine-s-day-en|2023]] Valentine's Day events. |
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
==== Ammunition ==== | ==== Ammunition ==== | ||
| − | { | + | {{:6pdr OQF Mk.III (57 mm)/Ammunition|Shot Mk.5, Shot Mk.5 HV, Shot Mk.8, Shot Mk.9, Shell Mk.10}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | Shot Mk.5 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== [[Ammo racks]] ==== | ==== [[Ammo racks]] ==== | ||
| Line 203: | Line 159: | ||
===Canadian Production=== | ===Canadian Production=== | ||
| − | [[File:Valentine tanks en route by rail to the Soviet Union.jpg| | + | [[File:Valentine tanks en route by rail to the Soviet Union.jpg|x275px|right|thumb|none|Canadian-produced Valentines from CPR company being loaded onto flat cars to be shipped to the Soviet Union.]] |
Due to the positive reception of the Valentine tanks, the British decided that future Valentine tank deliveries to the Soviet Union would be fulfilled by Canada. With the Canadian Pacific Railway Company originally ordered to produce 300 Valentine tanks for the British and 488 for the Canadian army in June 1940, the British order was increased to 1,420 tanks in October 1941, with 30 of those tanks being Valentine VI slated for the Canadian army.<ref name="CliveLaw1">Law 2001, 11, 20</ref> Canadian tank industry, producing their first tank in 22 May 1941,<ref name="CliveLaw2">Law 2001, 12</ref> began their deliveries of Valentine VII tanks to the Soviet Union in November 1941, but their first shipments would not arrive until 1942. Deliveries continued until May 1943 upon completion of the Canadian orders, with 1,388 (2 were retained for British trial purposes) sent to the Soviet Union, and 1,208 arriving in the Soviet Union ports.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(3)">Zaloga 2017, 17-18</ref> | Due to the positive reception of the Valentine tanks, the British decided that future Valentine tank deliveries to the Soviet Union would be fulfilled by Canada. With the Canadian Pacific Railway Company originally ordered to produce 300 Valentine tanks for the British and 488 for the Canadian army in June 1940, the British order was increased to 1,420 tanks in October 1941, with 30 of those tanks being Valentine VI slated for the Canadian army.<ref name="CliveLaw1">Law 2001, 11, 20</ref> Canadian tank industry, producing their first tank in 22 May 1941,<ref name="CliveLaw2">Law 2001, 12</ref> began their deliveries of Valentine VII tanks to the Soviet Union in November 1941, but their first shipments would not arrive until 1942. Deliveries continued until May 1943 upon completion of the Canadian orders, with 1,388 (2 were retained for British trial purposes) sent to the Soviet Union, and 1,208 arriving in the Soviet Union ports.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(3)">Zaloga 2017, 17-18</ref> | ||
| Line 209: | Line 165: | ||
===Valentine with 6-pdr for the Soviet Union=== | ===Valentine with 6-pdr for the Soviet Union=== | ||
By late 1942, the Valentine has been upgraded to the Mark IX variant by Vickers with a [[6pdr OQF Mk.III (57 mm)|6-pdr]] gun, with the Soviets discovering the tank type in late December 1942. The Soviet would receive the first 6-pdr equipped Valentine in February 1943.<ref name="Pasholok_TankArchives_ValentineLong">Pasholok 2019</ref> | By late 1942, the Valentine has been upgraded to the Mark IX variant by Vickers with a [[6pdr OQF Mk.III (57 mm)|6-pdr]] gun, with the Soviets discovering the tank type in late December 1942. The Soviet would receive the first 6-pdr equipped Valentine in February 1943.<ref name="Pasholok_TankArchives_ValentineLong">Pasholok 2019</ref> | ||
| − | |||
Evaluations were carried out to determine if the Soviets should order more. Soviets praised the improved penetration power of the 6-pdr, but there was still lack of high-explosive shell production for the 6-pounder gun. The new turret used to equip the 6-pdr removed the coaxial machine gun and replaced the turret bomb thrower with external launchers, both changes that the Soviets were not enthusiastic about. These characteristics led to the Soviet to consider the Valentine IX moreso as a tank destroyer than a tank, and as such issued the Valentine IX out in heterogenous formations alongside older 2-pdr equipped Valentines that had better characteristics to fight infantry. The Valentine Mk IX issues would be addressed by American supplies and British development. The Americans, producing their own version of the 6-pounder as the [[M1 (57 mm)|57 mm M1 gun]], were also concerned about the lack of available HE shells and began to produce their own, supplying it to the Soviets for their Valentines alongside the 57 mm M1 equipped T48 GMC (which the Soviets would use as the [[SU-57]]). While the lack of coaxial machine gun was initially resolved with the installment of a BREN machine gun on an anti-aircraft pintle-mount, the coaxial machine gun mount would be reintroduced in the Valentine X variant with a new turret design, which would begin arriving in 1944. These resolutions, even just equipping the Valentines with high-explosive shells, allowed the Soviets to issue the 6-pdr equipped Valentines in homogenous formations without 2-pdr Valentines.<ref name="Pasholok_TankArchives_ValentineLong">Pasholok 2019</ref> | Evaluations were carried out to determine if the Soviets should order more. Soviets praised the improved penetration power of the 6-pdr, but there was still lack of high-explosive shell production for the 6-pounder gun. The new turret used to equip the 6-pdr removed the coaxial machine gun and replaced the turret bomb thrower with external launchers, both changes that the Soviets were not enthusiastic about. These characteristics led to the Soviet to consider the Valentine IX moreso as a tank destroyer than a tank, and as such issued the Valentine IX out in heterogenous formations alongside older 2-pdr equipped Valentines that had better characteristics to fight infantry. The Valentine Mk IX issues would be addressed by American supplies and British development. The Americans, producing their own version of the 6-pounder as the [[M1 (57 mm)|57 mm M1 gun]], were also concerned about the lack of available HE shells and began to produce their own, supplying it to the Soviets for their Valentines alongside the 57 mm M1 equipped T48 GMC (which the Soviets would use as the [[SU-57]]). While the lack of coaxial machine gun was initially resolved with the installment of a BREN machine gun on an anti-aircraft pintle-mount, the coaxial machine gun mount would be reintroduced in the Valentine X variant with a new turret design, which would begin arriving in 1944. These resolutions, even just equipping the Valentines with high-explosive shells, allowed the Soviets to issue the 6-pdr equipped Valentines in homogenous formations without 2-pdr Valentines.<ref name="Pasholok_TankArchives_ValentineLong">Pasholok 2019</ref> | ||
| + | [[File:Valentine Mk IX in Ukraine.jpg|x300px|left|thumb|none|Valentine IX in Red Army service during the Battle of the Dnieper.]] | ||
Despite the initial flaws, the Soviets accepted the 6-pdr equipped Valentines and continued to request it in their Lend-Lease shipments. With Canada's production order finished, the British continued to produce Valentines in 1943 for Soviet Union deliveries, though the British were perplexed that the Soviet Union has continued interest in a tank that they have already considered obsolete.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(3)"/> 910 Valentine IX and X would be sent between 1943 and 1944, with 884 received by the Soviet Union.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(Tables)">Zaloga 2017, 78</ref> The number of Valentine tanks in Soviet inventory, as well as their overall positive combat performance, led to the Soviet Union deciding to end their light tank production and have the Valentines continue to fulfill their light tank role, with the light tank factories committing to [[SU-76M|SU-76]] production.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(3)"/> | Despite the initial flaws, the Soviets accepted the 6-pdr equipped Valentines and continued to request it in their Lend-Lease shipments. With Canada's production order finished, the British continued to produce Valentines in 1943 for Soviet Union deliveries, though the British were perplexed that the Soviet Union has continued interest in a tank that they have already considered obsolete.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(3)"/> 910 Valentine IX and X would be sent between 1943 and 1944, with 884 received by the Soviet Union.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(Tables)">Zaloga 2017, 78</ref> The number of Valentine tanks in Soviet inventory, as well as their overall positive combat performance, led to the Soviet Union deciding to end their light tank production and have the Valentines continue to fulfill their light tank role, with the light tank factories committing to [[SU-76M|SU-76]] production.<ref name="Zaloga_LL(3)"/> | ||
| Line 253: | Line 209: | ||
;Bibliography: | ;Bibliography: | ||
* Axe, David. 2020. "To Russia With Love: The British Valentine tank in the Red Army." Medium. Last modified March 20, 2020. [https://medium.com/angry-planet/to-russia-with-love-76a2e4ca6c46 Website] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20220904171001/https://medium.com/angry-planet/to-russia-with-love-76a2e4ca6c46 Archive]) | * Axe, David. 2020. "To Russia With Love: The British Valentine tank in the Red Army." Medium. Last modified March 20, 2020. [https://medium.com/angry-planet/to-russia-with-love-76a2e4ca6c46 Website] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20220904171001/https://medium.com/angry-planet/to-russia-with-love-76a2e4ca6c46 Archive]) | ||
| − | * Law, Clive M. | + | * Law, Clive M. 2001. ''Making Tracks: Tank Production in Canada''. Ottawa, Ontario: Service Publications. |
* Newsome, Bruce Oliver. 2016. ''Valentine Infantry Tank 1938-45''. Great Britain: Osprey Publishing. Kindle. | * Newsome, Bruce Oliver. 2016. ''Valentine Infantry Tank 1938-45''. Great Britain: Osprey Publishing. Kindle. | ||
* Pasholok, Yuri. 2016. "Valentine Mods in the USSR." Tank Archives. Translated by Peter Samsonov. Last modified March 13, 2016. [http://www.tankarchives.ca/2016/03/valentine-mods-in-ussr.html Website] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20220904171015/http://www.tankarchives.ca/2016/03/valentine-mods-in-ussr.html Archive]) | * Pasholok, Yuri. 2016. "Valentine Mods in the USSR." Tank Archives. Translated by Peter Samsonov. Last modified March 13, 2016. [http://www.tankarchives.ca/2016/03/valentine-mods-in-ussr.html Website] ([https://web.archive.org/web/20220904171015/http://www.tankarchives.ca/2016/03/valentine-mods-in-ussr.html Archive]) | ||
Latest revision as of 14:02, 14 February 2023
| This page is about the Soviet medium tank MK-IX "Valentine" (USSR). For other versions, see Valentine (Family). |
Contents
Description
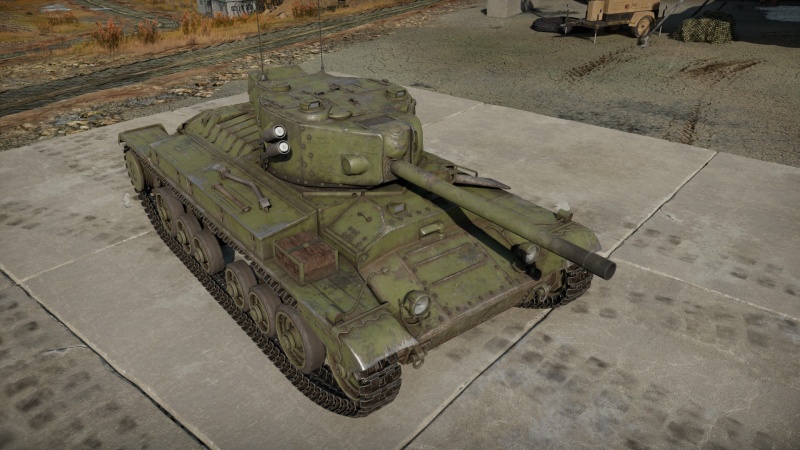
The ▂МК-IX "Valentine" is a premium gift rank II Soviet medium tank
with a battle rating of 3.0 (AB/RB/SB). It was introduced during Update 1.95 "Northern Wind" as a special Valentine's Day vehicle. This is a Lend-Lease Valentine, shipped to the USSR by the British. The tank was made available to purchase in-game with Golden Eagles (![]() ) for specific mini-events like the 2020, 2021 2022, and 2023 Valentine's Day events.
) for specific mini-events like the 2020, 2021 2022, and 2023 Valentine's Day events.
General info
Survivability and armour
The armour on the MK-IX "Valentine" is quite mediocre head on, but slightly above par when angled. The maximum base armour thickness of the hull is 60 mm and is laid out flat on the designs, while the sloping portions are of thinner 30 mm armour plates. This gives an average thickness of ~60 mm of armour when facing the MK-IX "Valentine" flat from the front. However if angled, the armour has an effective thickness of 80mm, as such this is heavily advised. The turret is more well protected than the hull, with its front armoured with 65 mm armour plates and sloped with its circular shape, but the cast construction of the gun mantlet can lead to some enemies attacking the gun breech to disable the Valentine's firepower, if they do not aim for the hull directly.
The mediocre armour construction means that there will be multiple types of enemies the MK-IX "Valentine" can encounter that can easily penetrate through the armour, especially if the opponent is firing at a close range and have a good knowledge on the MK-IX "Valentine"'s weak spots. These armour vulnerabilities adds up with the Valentine's fault of not being a particularly fast vehicle. This means any exposure from cover can be a long one that enemies can take the time to line up their next shot towards an armour weak point.
The Valentines biggest advantage when it comes to survival is its small size. Because of this, the majority of enemies will have difficulties hitting the weak spots and penetrating the armour at medium and long ranges. At close range, this advantage is largely nullified and the enemy can easily shoot the exposed 30 mm thick driver's hatches even if the Valentine is angled.
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour (Hull, Turret)
- Cast homogeneous armour (Gun mantlet)
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 60 mm (1°) Front plate 30 mm (65-67°) Front glacis 60 mm (24°) Lower glacis |
50 mm | 17 mm (51-54°) Top 60 mm (1°) Bottom |
20 mm (40-89°) |
| Turret | 65 mm (0-73°) Turret front 65 mm (1-61°) Gun mantlet |
60 mm (0-1°) | 65 mm (2-58°) | 20 mm (76-89°) |
Notes:
- Belly armour is 20 mm thick.
- Suspension wheels, bogies, and tracks are all 20 mm thick.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 27 | 4 | 17.3 | 256 | 315 | 14.8 | 18.21 |
| Realistic | 25 | 3 | 146 | 165 | 8.44 | 9.54 | |
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
The 57 mm 6pdr OQF Mk.III is a potent gun at its rank. Although it lacks explosive filler, due to the high penetration of its rounds and the quick reload (especially compared to other Russian tanks), the Valentine will be able to penetrate most enemy tanks from the front. It is advised to bring more ammo than expected as it will take a few shots to completely destroy an enemy. Since the ammo is largely stored in the same place, the exact number of shells brought into battle doesn't matter.
| 57 mm 6pdr OQF Mk.III | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 53 | -8°/+17° | ±180° | N/A | 15.2 | 21.1 | 25.6 | 28.3 | 30.1 | 5.20 | 4.60 | 4.24 | 4.00 |
| Realistic | 9.5 | 11.2 | 13.6 | 15.0 | 16.0 | ||||||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| Shot Mk.5 | AP | 101 | 97 | 82 | 66 | 53 | 43 |
| Shot Mk.5 HV | AP | 108 | 104 | 87 | 70 | 57 | 46 |
| Shot Mk.8 | APC | 110 | 106 | 89 | 72 | 59 | 48 |
| Shot Mk.9 | APCBC | 122 | 118 | 101 | 84 | 70 | 58 |
| Shell Mk.10 | HE | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay | Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | |||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| Shot Mk.5 | AP | 815 | 2.8 | - | - | - | 47° | 60° | 65° | |||
| Shot Mk.5 HV | AP | 853 | 2.8 | - | - | - | 47° | 60° | 65° | |||
| Shot Mk.8 | APC | 853 | 2.87 | - | - | - | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
| Shot Mk.9 | APCBC | 801 | 3.23 | - | - | - | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
| Shell Mk.10 | HE | 655 | 2.72 | 0 | 0.1 | 590 | 79° | 80° | 81° | |||
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
5th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 53 | 43 (+10) | 32 (+21) | 21 (+32) | 11 (+42) | 1 (+52) | No |
Optics
| MK-IX "Valentine" (USSR) Optics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Which ones | Default magnification | Maximum magnification |
| Main Gun optics | x1.85 | x3.5 |
| Comparable optics | M4A1 | |
Usage in battles
The MK-IX Valentine fits in a niche battle rating in the Soviet line-up with its own unique traits. Its armour is a considerable improvement from preceding medium tanks like the T-28. The firepower with the 57 mm gun gives penetration values similar to the tank destroyers like the ZiS-30, along with a faster reloading rate, superior gun depression and an enclosed turret with good armour. However, its mobility is a downgrade compared to anything available to the Soviets, even the ~30 ton heavier KV-1 can move faster than the Valentine on the battlefield. As such, finding a place for the Valentine in the Soviet line-up can be tricky.
The Valentine's excelling role is in a methodical march towards its objective, as its mobility precludes any attempt to make a speedy flanking manoeuvre. Teammates are more than likely to reach and capture the point before the Valentine will, but this does not mean the Valentine should not participate in the effort.
One must use the Valentine wisely to not expose it too long in the open when travelling to the objective; make the most of any cover available, which will be easy due to its small size. It is in these periods that the Valentine is most vulnerable to a concealed enemy a distance away taking a shot at the Valentine's armour straight at the front or from the sides. As such, always angle the armour when moving through contested areas since the flat surfaces are presentable weak points for any frontal enemy to attack at, and the guns at this rank are more than likely to penetrate even at slightly angled armour plates. Whether uptiered or downtiered, the main concerning enemy unit are tank destroyers, as their guns have a high chance of penetrating the Valentine's armour no matter how the vehicle is angled.
Once a position is taken however, the Valentine can plant itself securely at the location at suitable firing positions and make use of the fast-firing and potent 57 mm gun to take out any enemy assault units. The green paint on the Valentine can assist in concealment on foliage-rich environment for a good ambush position. Whether from behind cover or a hull-down position, the Valentine can end up victorious in an engagement if it hits with the first shot. However, due to the poor mobility, the Valentine's movement is restricted. This means it is important to make sure the enemy's ability to fire back and/or move is knocked out in the first shot so it is not required to retreat back into cover during the brief reloading period, then out again to fire, especially since that whole manoeuvre can take more time than simply reloading in place while exposing the tank to return fire. The poor mobility also means the Valentine needs to be aware of any flanking vehicles coming up, as the Valentine would not be able to react fast enough to the new threat.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- The 57 mm gun has good stock shells to do significant damages upon penetrating
- Heavily sloped upper glacis can bounce a few shots
- Around 80 mm of effective armour on hull when angled at ~35 degrees
- Low profile allows it to hide behind more obstacles in the battlefield
- Turret is angled and has a complex construction, allowing it to bounce some shots
- Fast reload speed
Cons:
- No machine gun
- Side armour is very weak
- Slow top speed (22 km/h)
- No explosive filler in shells
- Only three tightly sitting crew members (crew can be knocked out very easily)
- Thin top armour makes it vulnerable to air attacks
History
Lend-Lease to the Soviet Union
As part of the Lend-Lease program, the Soviet Union requested tanks and other military supplies from American and Great Britain to replenish their losses during their defense against Nazi Germany. Evaluating the available tank models that can be sent to the Soviet Union, the Soviet liaison mission in Britain decided on two tanks, the Matilda and the Valentine tank.[1] The shipments of Valentine tanks would be fulfilled by the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company, which began on September 28, 1941.[2]
The first British tanks Lend-Lease shipment, carrying 20 Valentine tanks, arrived to the Soviet Union on October 11, 1941 at the port of Arkhangelsky as part of the Arctic convoys. A training program for the Valentines were created at the Kazan Courses of Armoured Force Improvement (KUKS) by October 15th, while the tanks themselves arrive to the location on October 28th. Alongside the second tank shipment of 120 Valentine tanks were 22 British men to help the Soviets organize repair workshops and other knowledge transfers about the tanks, which was concluded in November 11th. Training was expedited to a 15-day course, but 120 crew members were trained by the middle of November.[1][2] By the end of 1941, 259 Valentine tanks have been sent to the Soviet Union, with 216 of them issued to combat formations.[3]
The Valentines first saw use in late November 1941 among the 136th, 137th, 138th, and 139th Independent Tank Battalions with a total of 97 Valentines, mostly in the defense of Moscow around what was considered second-rate enemies.[3] In Soviet designations, the Valentines were referred to as "English tank MK-III*". Problems with the Valentine design became apparent, especially in cold weather where the ventilation system design made the interiors too cold, a cooling system that overcooled the engine, and tracks that lost traction in deep snow.[2] Another complaint was the Valentine II's armament, the 2-pdr gun, for its lack of high-explosive shell availability. The Soviets attempted to remedy the issue by replacing the 2-pdr gun with a 45 mm 20-K gun at the Grabin design bureau at Factory #92. While the redesign proved feasible, the shortage of 45 mm guns and lack of significant improvements in anti-tank performance led to the project's cancellation in January 1942.[4] Overall, while the Soviets have criticism on the Valentine's design, they judged the performance to be more useful than the Matilda, even in the winter, and equivalent or better to their domestic light tanks, with Soviets classifying the Valentines as light tanks during the Battle of Moscow. Due to this, on December 03, 1941, Stalin requested to the British Minister of Supply, Lord Beaverbrook, to prioritize the shipment of Valentine tanks over the Matilda tanks.[5]
Canadian Production
Due to the positive reception of the Valentine tanks, the British decided that future Valentine tank deliveries to the Soviet Union would be fulfilled by Canada. With the Canadian Pacific Railway Company originally ordered to produce 300 Valentine tanks for the British and 488 for the Canadian army in June 1940, the British order was increased to 1,420 tanks in October 1941, with 30 of those tanks being Valentine VI slated for the Canadian army.[6] Canadian tank industry, producing their first tank in 22 May 1941,[7] began their deliveries of Valentine VII tanks to the Soviet Union in November 1941, but their first shipments would not arrive until 1942. Deliveries continued until May 1943 upon completion of the Canadian orders, with 1,388 (2 were retained for British trial purposes) sent to the Soviet Union, and 1,208 arriving in the Soviet Union ports.[8]
Valentine with 6-pdr for the Soviet Union
By late 1942, the Valentine has been upgraded to the Mark IX variant by Vickers with a 6-pdr gun, with the Soviets discovering the tank type in late December 1942. The Soviet would receive the first 6-pdr equipped Valentine in February 1943.[9]
Evaluations were carried out to determine if the Soviets should order more. Soviets praised the improved penetration power of the 6-pdr, but there was still lack of high-explosive shell production for the 6-pounder gun. The new turret used to equip the 6-pdr removed the coaxial machine gun and replaced the turret bomb thrower with external launchers, both changes that the Soviets were not enthusiastic about. These characteristics led to the Soviet to consider the Valentine IX moreso as a tank destroyer than a tank, and as such issued the Valentine IX out in heterogenous formations alongside older 2-pdr equipped Valentines that had better characteristics to fight infantry. The Valentine Mk IX issues would be addressed by American supplies and British development. The Americans, producing their own version of the 6-pounder as the 57 mm M1 gun, were also concerned about the lack of available HE shells and began to produce their own, supplying it to the Soviets for their Valentines alongside the 57 mm M1 equipped T48 GMC (which the Soviets would use as the SU-57). While the lack of coaxial machine gun was initially resolved with the installment of a BREN machine gun on an anti-aircraft pintle-mount, the coaxial machine gun mount would be reintroduced in the Valentine X variant with a new turret design, which would begin arriving in 1944. These resolutions, even just equipping the Valentines with high-explosive shells, allowed the Soviets to issue the 6-pdr equipped Valentines in homogenous formations without 2-pdr Valentines.[9]
Despite the initial flaws, the Soviets accepted the 6-pdr equipped Valentines and continued to request it in their Lend-Lease shipments. With Canada's production order finished, the British continued to produce Valentines in 1943 for Soviet Union deliveries, though the British were perplexed that the Soviet Union has continued interest in a tank that they have already considered obsolete.[8] 910 Valentine IX and X would be sent between 1943 and 1944, with 884 received by the Soviet Union.[10] The number of Valentine tanks in Soviet inventory, as well as their overall positive combat performance, led to the Soviet Union deciding to end their light tank production and have the Valentines continue to fulfill their light tank role, with the light tank factories committing to SU-76 production.[8]
The Valentine tanks of all variants would continue to see use in the Red Army, seeing use in locations such as Ukraine, Czechoslovakia, and Germany, all the way until the end of the war in Europe. The Valentines would continue to see use in the Soviet's operation in Manchuria against the Japanese, with up to 81 Valentine tanks present alongside Valentine bridgelayer companies.[11]
Total Lend-Lease Numbers
Of the 7,260 Valentine tank models that would be produced by Britain and Canada (5,840 British, 1,420 Canada), 3,665 of the Valentine tanks would be shipped to the Soviet Union, alongside 25 Valentine bridgelayer variants for a total of 3,690. The British and Canadian shipped a large variety of Valentine tank models towards the Soviet Union, With Britain encompassing Valentine II, III, IV, V, IX and X while Canada provided the Valentine VII.[12] Of the 3,665 turreted tanks sent to the Soviet Union (Mk II: 161, Mk III: 346, Mk IV: 520, Mk V: 340, Mk VII: 1,388, Mk IX: 836, Mk X: 74), 415 would be lost at sea during the transit, and so the Soviets received a total of 3,250 Valentine tanks at their ports (Mk II: 136, Mk III: 346, Mk IV: 449, Mk V: 227, Mk VII: 1,208, Mk IX: 818, Mk X: 66).[13]
Media
- Skins
- Videos
See also
- Other British lend-lease vehicles
External links
References
- Citations
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zaloga 2017, 9
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Pasholok 2017
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Newsome 2016, Soviet Use
- ↑ Pasholok 2016
- ↑ Zaloga 2017, 11-14
- ↑ Law 2001, 11, 20
- ↑ Law 2001, 12
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Zaloga 2017, 17-18
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Pasholok 2019
- ↑ Zaloga 2017, 78
- ↑ Axe 2020
- ↑ Newsome 2016, Production
- ↑ Newsome 2016, New Zealand Use
- Bibliography
- Axe, David. 2020. "To Russia With Love: The British Valentine tank in the Red Army." Medium. Last modified March 20, 2020. Website (Archive)
- Law, Clive M. 2001. Making Tracks: Tank Production in Canada. Ottawa, Ontario: Service Publications.
- Newsome, Bruce Oliver. 2016. Valentine Infantry Tank 1938-45. Great Britain: Osprey Publishing. Kindle.
- Pasholok, Yuri. 2016. "Valentine Mods in the USSR." Tank Archives. Translated by Peter Samsonov. Last modified March 13, 2016. Website (Archive)
- Pasholok, Yuri. 2017. "British Tank for Soviet Infantry." Tank Archives. Translated by Peter Samsonov. Last modified November 04, 2017. Website (Archive)
- Pasholok, Yuri. 2019. "Valentine With a Long Gun." Tank Archives. Translated by Peter Samsonov. Last modified January 26, 2019. Website (Archive)
- Zaloga, Steven J. 2017. Soviet Lend-Lease Tanks of World War II. Great Britain: Osprey Publishing. Kindle.
| Vickers-Armstrongs Limited | |
|---|---|
| Ships | |
| Tribal-class | HMS Eskimo · HMCS Haida |
| Invincible-class | HMS Invincible* |
| Kongō-class | IJN Kongo** |
| Tanks | |
| Light Tanks | VFM5*** · Vickers Mk.11*** |
| Light Tank Mk VI | Light AA Mk I |
| Light Tank Mk VII | Tetrarch I |
| Light Tank Mk VIII | Alecto I |
| Tank, Infantry, Valentine | Valentine I · Valentine IX · Valentine XI · Archer |
| Vickers MBT | Vickers Mk.1 · Vickers Mk.3 · Vickers Mk.7*** |
| Heavy Tanks | Independent**** |
| Export | ▂МК-IX "Valentine" · Vickers Mk.E**** |
| See also | Vickers-Armstrongs Aircraft Limited |
| *Previously Armstrong Whitworth | |
| **Built for Japan | |
| ***Vickers Defence Systems | |
| ****Previously Vickers Limited | |
| USSR medium tanks | |
|---|---|
| T-28 | T-28 (1938) · T-28 · T-28E |
| T-34-76 | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1940) · T-34 (1941) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34 (1942) · T-34E STZ · T-34E |
| T-34-57 | T-34-57 · T-34-57 (1943) |
| T-34-85 | T-34-85 (D-5T) · T-34-85 · T-34-85E |
| T-34-100 | T-34-100 |
| T-44 | T-44 · T-44-100 · T-44-122 |
| T-54 | T-54 (1947) · T-54 (1949) · T-54 (1951) |
| T-55 | TO-55 · T-55A · T-55AM-1 · T-55AMD-1 |
| T-62 | T-62 · T-62M-1 |
| T-64 | Object 435 · T-64A (1971) · T-64B |
| T-72 | T-72A · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-72B · T-72B (1989) · T-72B3 · T-72M2 Moderna |
| T-80 | T-80B · T-80U · T-80UD · T-80UK · T-80UM2 · Т-80U-Е1 · T-80BVM · Object 292 |
| T-90 | Т-90А · T-90M |
| Trophies/Lend-Lease | |
| Germany | ▂T-III · ▂T-V |
| Great Britain | ▂МК-IX "Valentine" |
| USA | ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 |
| USSR premium ground vehicles | |
|---|---|
| Light tanks | BA-11 · RBT-5 · BT-7A (F-32) · T-26 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-26E · T-126 · PT-76-57 · 2S38 |
| Medium tanks | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34E · T-34-57 (1943) · T-34-85E · T-34-100 · T-44-122 · TO-55 · T-55AM-1 · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-80UD · Т-80U-Е1 |
| ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 · ▂T-III · ▂T-V · ▂МК-IX "Valentine" | |
| Heavy tanks | SMK · T-35 · ▂MK-II "Matilda" · KV-1E · KV-2 (1940) · KV-2 (ZiS-6) · KV-122 · KV-220 · IS-2 "Revenge" · Object 248 · IS-6 · T-10A |
| Tank destroyers | BM-8-24 · BM-13N · BM-31-12 |
| SU-57 · SU-76D · SU-76M (5th Gv.Kav.Corps) · SU-85A · SU-100Y · SU-122P · Object 120 | |
| SPAA | ▂Phòng không T-34 · ZUT-37 |









