Difference between revisions of "ShKAS (7.62 mm)"
Inceptor57 (talk | contribs) m |
Indo_Pilot (talk | contribs) (→Vehicles equipped with this weapon: Added IL-8 (1944)) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | [[File:ShKAS_Su-2_M-82_turret.jpg|520px|thumb|right|Side view of an '''{{PAGENAME}}''' machine gun in the defensive turret of an [[Su-2 (M-82)]].]] |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | <!--''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.''--> | + | <!-- ''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.'' --> |
| − | + | [[File:ShKAS_sideview.jpg|thumbnail|left|x75px|]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Break}} | {{Break}} | ||
| − | The ''' | + | The '''7.62 mm ShKAS''' (Shpitalny-Komaritski Aviatsionny Skorostrelny or ''Shipitalny-Komaritski rapid-fire for aircraft'' – Russian: '''ШКАС''' - Шпитального-Комарицкого Авиационный Скорострельный) is a 7.62 mm calibre machine gun which was first produced in 1933 for usage in Soviet aircraft which saw action all the way through World War II in many of the fighters, attackers and bombers of the day. The ShKAS is a single chamber, gas-operated revolver-type machine gun in which a firing pin strikes the primer of the bullet in the chamber to fire the round. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | === Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | ||
<!-- ''List out vehicles that are equipped with the weapon.'' --> | <!-- ''List out vehicles that are equipped with the weapon.'' --> | ||
| + | |||
{{Navigation-Start|Vehicles equipped with this weapon}} | {{Navigation-Start|Vehicles equipped with this weapon}} | ||
| + | |||
{{Navigation-First-Line|'''Fighters'''}} | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Fighters'''}} | ||
| − | {{Navigation-Line|I- | + | {{Navigation-Line|I-16}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type5}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type5_1935_china}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type10}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type10_china}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type17_china}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{Navigation-Line| }}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type18}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type24}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type27}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-16_type28}} |
| − | {{Navigation-Line| | + | {{Navigation-Line|I-153}}{{Specs-Link|i-153_m62}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-153_m62_zhukovskiy}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|i-153_m62_china}} |
| + | {{Navigation-Line|I-180}}{{Specs-Link|i_180}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|I-301}}{{Specs-Link|lagg-i-301}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|LaGG-3}}{{Specs-Link|lagg-3-4}} | ||
{{Navigation-Line|MiG-3}}{{Specs-Link|mig_3_series_1_15}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig_3_series_1_15_bk_pod}} | {{Navigation-Line|MiG-3}}{{Specs-Link|mig_3_series_1_15}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|mig_3_series_1_15_bk_pod}} | ||
| − | {{Navigation-Line|Yak}}{{Specs-Link|yak-1_early}} | + | {{Navigation-Line|Yak-1}}{{Specs-Link|yak-1_early}} |
| − | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Twin-engine fighters'''}}{{Specs-Link|i_29}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe- | + | |
| + | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Twin-engine fighters'''}}{{Specs-Link|i_29}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-3_early}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-3}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-3_bis}} (Defensive) | ||
| + | |||
{{Navigation-First-Line|'''Attackers'''}} | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Attackers'''}} | ||
| − | {{Navigation-Line|IL-2}}{{Specs-Link|il_2_1941}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il-2i}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il_2_1942_luftwaffe}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il_2_37_1943}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il- | + | {{Navigation-Line|BB-1}}{{Specs-Link|bb-1}} |
| + | {{Navigation-Line|IL-2}}{{Specs-Link|il_2_1941}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il-2i}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il_2_1942_luftwaffe}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il_2_m82}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il_2_37_1943}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|IL-2M}}{{Specs-Link|il-2m_mstitel}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il_2m_1943}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|il-2m}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|IL-8}}{{Specs-Link|il_8_1944}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|IL-10}}{{Specs-Link|il-10}} | ||
{{Navigation-Line|Su-2}}{{Specs-Link|su-2_m82}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|su-2_mv5}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|su-2_tss1}} | {{Navigation-Line|Su-2}}{{Specs-Link|su-2_m82}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|su-2_mv5}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|su-2_tss1}} | ||
| − | {{Navigation-Line|Su-6}}{{Specs-Link| | + | {{Navigation-Line|Su-6}}{{Specs-Link|su_6_single}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|su-6_am42}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|su-6_m71}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{Navigation-Line|Su-8}}{{Specs-Link|su-8}} |
| + | {{Navigation-Line|Tandem MAI}}{{Specs-Link|tandem_mai}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|Yak-2}}{{Specs-Link|yak_2_kabb}} | ||
| + | |||
{{Navigation-First-Line|'''Bombers'''}} | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Bombers'''}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|Ar-2}}{{Specs-Link|ar_2}} (Defensive) | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|DB-3}}{{Specs-Link|db_3a_china}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|db_3b}} (Defensive) | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|IL-4}}{{Specs-Link|il-4}} (Defensive) | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|KOR-1}}{{Specs-Link|kor_1}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|MBR-2}}{{Specs-Link|mbr-2}} (Defensive) | ||
{{Navigation-Line|Pe-2}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-1}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-31}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-83}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-110}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-205}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-359}} | {{Navigation-Line|Pe-2}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-1}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-31}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-83}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-110}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-205}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|pe-2-359}} | ||
| − | {{Navigation-Line| | + | {{Navigation-Line|Pe-8}}{{Specs-Link|pe-8_m82}} (Defensive) |
| − | {{Navigation-Line| | + | {{Navigation-Line|Po-2}}{{Specs-Link|po-2}} (Defensive) |
| − | {{Navigation-Line| | + | {{Navigation-Line|SB-2M}}{{Specs-Link|sb_2m_100}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|sb_2m_103c}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|sb_2m_103_mv3}} (Defensive) |
| + | {{Navigation-Line| }}{{Specs-Link|sb_2m_103u}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|sb_2m_103u_china}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|sb_2m_103u_mv3}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|sb_2m_105}} (Defensive) | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|Yak-4}}{{Specs-Link|yak-4}} | ||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|Yer-2}}{{Specs-Link|er-2_m105_mv3}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|er-2_m105_tat}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|er-2_m105r_lu2b}} (Defensive){{-}}{{Specs-Link|er-2_m105r_tat}} (Defensive) | ||
| + | |||
{{Navigation-End}} | {{Navigation-End}} | ||
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| − | <!--''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the cannon or machine gun.''--> | + | <!-- ''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the cannon or machine gun.'' --> |
| − | + | With 1,800 RPM, the ShKAS has the highest rate of fire of any machine guns in World War II. Aside from the default ball and plain tracer rounds, the ShKAS's common round composition involves the API-T, API, and AI rounds. Due to the ineffectiveness of the AI rounds due to tiny explosive filler, uses of belt with only the API-T and API are recommended as both rounds has a high chance of lit up the enemy plane on fire if enough shots were hit. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | === Available ammunition === | |
| − | + | <!-- ''Describe the shells that are available for the weapon and their features and purpose. If it concerns autocannons or machine guns, write about different ammo belts and what is inside (which types of shells).'' --> | |
| − | + | * '''Default:''' {{Annotation|T|Tracer}}{{-}}{{Annotation|Ball|Omni-purpose}}{{-}}{{Annotation|Ball|Omni-purpose}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AI|Adjustment incendiary}} | |
| − | + | * '''Universal:''' {{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AI|Adjustment incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|API-T|Armour-piercing incendiary tracer}} | |
| − | + | * '''Tracers:''' {{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|API-T|Armour-piercing incendiary tracer}} | |
| − | + | * '''Stealth:''' {{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AI|Adjustment incendiary}} | |
| − | + | * '''Armored targets (turret):''' {{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AP-I|Armour-piercing incendiary}}{{-}}{{Annotation|API-T|Armour-piercing incendiary tracer}} | |
| − | + | * '''Universal (turret):''' {{Annotation|API-T|Armour-piercing incendiary tracer}}{{-}}{{Annotation|API-T|Armour-piercing incendiary tracer}}{{-}}{{Annotation|API-T|Armour-piercing incendiary tracer}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AI|Adjustment incendiary}} | |
| − | |||
| − | === Available | ||
| − | <!-- ''Describe the shells that are available for the | ||
| − | |||
| − | * '''Default''' | ||
| − | * '''Universal''' | ||
| − | * '''Tracers''' | ||
| − | * '''Stealth''' (AP-I | ||
=== Comparison with analogues === | === Comparison with analogues === | ||
| − | <!--''Give a comparative description of cannons/machine guns | + | <!-- ''Give a comparative description of cannons/machine guns that have firepower equal to this weapon.'' --> |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | !colspan = " | + | !colspan = "7"| Comparable machine guns to {{PAGENAME}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! |
| − | ! | + | ! Name |
| − | ! | + | ! Year of Creation |
| − | ! | + | ! Mass |
| − | ! | + | ! Rounds Per Minute |
| − | ! | + | ! Ammunition |
| − | ! | + | ! {{Annotation|Feed Type|Denotes whether belt, drum or magazine fed ammunition}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:USA_flag.png|20px|link=]] |
| [[Browning (7.62 mm)]] | | [[Browning (7.62 mm)]] | ||
| − | | style="text-align:center;"|1919 | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1919 |
| + | | 14 kg | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,000 RPM | ||
| + | | 7.62 × 63 mm | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Belt | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Germany_flag.png|20px|link=]] | ||
| + | | [[MG 17 (7.92 mm)]] | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1934 | ||
| + | | 10.2 kg | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,150 RPM | ||
| + | | 7.92 × 57 mm | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Belt | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Germany_flag.png|20px|link=]] | ||
| + | | [[MG 15 (7.92 mm)]] | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1932 | ||
| + | | 12.4 kg | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,150 RPM | ||
| + | | 7.92 × 57 mm | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Drum | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Britain_flag.png|20px|link=]] | ||
| + | | [[Browning (7.7 mm)]] | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1919 | ||
| 14 kg | | 14 kg | ||
| − | | style="text-align:center;"| | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,000 RPM |
| − | | 7. | + | | 7.7 × 56 mm R |
| − | | style="text-align:center;"| Belt | + | | style="text-align:center;" | Belt |
| − | | | + | |- |
| − | | | + | | [[File:Britain_flag.png|20px|link=]] |
| − | | | + | | [[Vickers K (7.7 mm)]] |
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1935 | ||
| + | | 13.4 kg | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 950 RPM | ||
| + | | 7.7 × 56 mm R | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Pan | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Japan_flag.png|20px|link=]] | ||
| + | | [[Type 1 (7.92 mm)]] | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1932 | ||
| + | | 12.8 kg | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,150 RPM | ||
| + | | 7.92 × 57 mm | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Drum | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Japan_flag.png|20px|link=]] |
| [[Type 92 navy (7.7 mm)]] | | [[Type 92 navy (7.7 mm)]] | ||
| − | | style="text-align:center;"|1932 | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1932 |
| 8 kg | | 8 kg | ||
| − | | style="text-align:center;"|600 RPM | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 600 RPM |
| − | | 7.7 | + | | 7.7 × 56 mm R |
| − | | style="text-align:center;"| | + | | style="text-align:center;" | Pan |
| − | | | + | |- |
| − | | | + | | [[File:Japan_flag.png|20px|link=]] |
| − | | | + | | [[Type 98 (7.92 mm)]] |
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1932 | ||
| + | | 12.8 kg | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,150 RPM | ||
| + | | 7.92 × 57 mm | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Drum | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Japan_flag.png|20px|link=]] |
| − | | [[ | + | | [[Lewis (7.7 mm)]] |
| − | | style="text-align:center;"| | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1911 |
| − | | | + | | 13 kg |
| − | | style="text-align:center;"| | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 900 RPM |
| − | | 7. | + | | 7.7 × 56 mm R |
| − | + | | style="text-align:center;" | Pan | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Italy_flag.png|20px|link=]] |
| − | | [[ | + | | [[Breda-SAFAT (7.7 mm)]] |
| − | | style="text-align:center;"|1935 | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1935 |
| 12.5 kg | | 12.5 kg | ||
| − | | style="text-align:center;"| | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 900 RPM |
| − | | 7.7 | + | | 7.7 × 56 mm R |
| − | | style="text-align:center;"| Belt | + | | style="text-align:center;" | Belt |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | [[File:France_flag.png|20px|link=]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| [[MAC 1934 (7.5 mm)]] | | [[MAC 1934 (7.5 mm)]] | ||
| − | | style="text-align:center;"|1934 | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1934 |
| 10.7 kg | | 10.7 kg | ||
| − | | style="text-align:center;"|1, | + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,350 RPM |
| − | | 7.5 | + | | 7.5 × 54 mm MAS |
| − | | style="text-align:center;"|Belt/Magazine | + | | style="text-align:center;" | Belt/Magazine |
| − | | | + | |- |
| − | | | + | | [[File:Sweden_flag.png|20px|link=]] |
| − | | | + | | [[Ksp m/22-37 R (8 mm)]] |
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1919 | ||
| + | | 11.7 kg | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | 1,200 RPM | ||
| + | | 8 × 63 mm | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center;" | Belt | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Usage in battles == | == Usage in battles == | ||
| − | ''Describe the cannon/machine gun in the game - its distinctive features, tactics of usage against | + | <!-- ''Describe the cannon/machine gun in the game - its distinctive features, tactics of usage against notable opponents. Please don't write a "guide" - do not impose a single point of view, but give the reader food for thought.'' --> |
| + | The ShKAS are one of the more powerful .30 cal machine guns in the game, only the rotary [[M134 Minigun (7.62 mm)|M134 Minigun]] and [[GShG-7.62 (7.62 mm)|GShG-7.62]] surpass it in terms of raw firepower for its calibre. However, it is still held back by the common impotence of small-calibre guns, along with its tendency to jam, thus making trigger discipline vital to its success. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Due to its superior ballistic properties and ammunition compared to other similar guns, the ShKAS is an easy-to-use weapon for beginners. As plenty of early Soviet planes were equipped with this machine gun, this allows the newcomer to learn how to utilize these weapons for various purposes. Though be sure to fire it only in short burst as the gun can be jammed easily, and only fire them for ranging or when you're sure that the shot will land on target. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In some higher tier planes equipped with the ShKAS, the ShKAS's small calibre rounds will started to show its age, as the round has very low damage compared to the more abundant .50 cal machine guns or 20 mm autocannons, though it remains deadly against pilot and internal modules if enough shots land. The gun also has a use against ground targets and slow-flying AI aircraft, in which the ShKAS can take them down with a few shots, allowing the player to conserve more valuable autocannon rounds for enemy planes while earning extra points from destroying AI targets. | ||
=== Pros and cons === | === Pros and cons === | ||
| − | <!-- '' | + | <!-- ''Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.'' --> |
| + | |||
| + | '''Pros:''' | ||
| − | |||
* The fastest firing rifle-calibre machine gun in WWII | * The fastest firing rifle-calibre machine gun in WWII | ||
| + | * High shell velocity, only small leads are needed while aiming | ||
| + | * Very accurate at short-to-medium range (~800 m), ideal for attacking ground targets and AI aircraft | ||
* Every belt is extremely effective at causing fires on enemy aircraft (tracers and stealth are the most effective) | * Every belt is extremely effective at causing fires on enemy aircraft (tracers and stealth are the most effective) | ||
* Incredibly easy to knock out gunners and pilots on enemy aircraft (or exposed crew members on ground and naval forces) | * Incredibly easy to knock out gunners and pilots on enemy aircraft (or exposed crew members on ground and naval forces) | ||
* If fired in short bursts, most aircraft can make a belt last an entire game in realistic battle | * If fired in short bursts, most aircraft can make a belt last an entire game in realistic battle | ||
| − | '''Cons:''' | + | '''Cons:''' |
| + | |||
| + | * Accuracy and penetration drops off at longer ranges (beyond 1 km), restricting it to close range weapon | ||
* Can easily jam. It is recommended to fire in bursts lasting no longer than one second | * Can easily jam. It is recommended to fire in bursts lasting no longer than one second | ||
| + | * Limited damage output due to small shell size, thus requiring multiple hits to knock out the target. This is especially apparent on the defensive version where enemy has more chance to dodge it | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of | + | <!-- ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' --> |
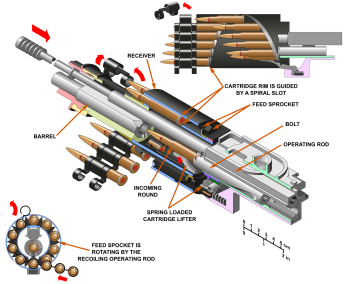
| + | [[File:ShKAS_feed_system_operation.png|350px|thumb|right|A diagram of the operation of the '''{{PAGENAME}}''' machine gun with identification of parts.]] | ||
| + | The 7.62 mm ShKAS machine gun is a Soviet .30 calibre machine gun designed by Boris Shpitalniy and Irinarkh Komaritsky for use on Soviet aircraft. It was designed in 1932 and entered service a year later. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The designers departed from traditional methods of feeding belt linked ammunition into the ShKAS and utilised a feed design nicknamed "bird-cage" or "squirrel-cage".<ref name="Hogg"></ref> Even declassified documents regarding the United States' evaluation of the feed system stated, ''"…an interesting departure was made from the heretofore orthodox practice of feeding ammunition to a gun of this caliber [sic]."'' <ref name="Chinn"></ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The ammunition belt enters the feed cage forward of the firing chamber. When the gun is fired, a gas piston actuates an arm connected to the cylindrical feed cage, rotating it one position to introduce the new bullet. As the feed cage (holding ten rounds) rotates a helical groove and guides the bullets rearward. Through this process of working the bullets rearwards, they are automatically delinked from the metal disintegrating link belt. The rounds make it to the final position at the bottom of the drum where they are then chambered into the receiver, ready to be fired. | ||
| + | |||
| + | One of the benefits of this feed system is during the camming of the rounds; there is relatively no drag on the ammunition allowing the gun to be fired at high rates of speed; however, prolonged actuation can provoke these guns to jam. Rates of fire could be regulated through changing of the holes in the gas regulator, three different hole sizes going from largest to smallest would slow down the rate of fire to a more moderate rate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Quote | ||
| + | |The ShKAS machine gun had a high rate of fire but it also had 48 ways of jamming. Some of them could be fixed immediately, some could not. And 1,800 rounds a minute was an insanely high rate of fire. If you pulled the trigger too long, the ShKAS would fire all its ammo in one go and that would be it!!<ref name="Drabkin"></ref> | ||
| + | |Viktor M. Sinaisky - Soviet machine gun technician | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | By the end of World War II, over 150,000 ShKAS had been produced. The gun can be found on a wide range of Soviet aircraft, across fighters, attackers, and bombers. The gun also saw service in the Spanish Civil War with the Republican Spanish forces, as well as the Second Sino-Japanese War and the subsequent resumption of the Chinese Civil War on both the Nationalist and Communist Chinese sides. | ||
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| − | <!--'' | + | <!-- ''Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.'' --> |
* [https://www.nicovideo.jp/watch/sm16506079 ShKAS Machine Gun - Video Documentary (Russian with Japanese subtitles; length = 6:18)] | * [https://www.nicovideo.jp/watch/sm16506079 ShKAS Machine Gun - Video Documentary (Russian with Japanese subtitles; length = 6:18)] | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| − | ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | + | <!-- ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' |
| + | * ''reference to the article about the variant of the cannon/machine gun;'' | ||
| + | * ''references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.'' --> | ||
| − | * | + | * [[ShVAK (20 mm)]] - aircraft autocannon also designed by Boris Shpitalniy |
| − | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | + | <!-- ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' |
| − | |||
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
* ''encyclopedia page on the weapon;'' | * ''encyclopedia page on the weapon;'' | ||
| − | * ''other literature.'' | + | * ''other literature.'' --> |
| + | |||
| + | === References === | ||
| + | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name="Hogg">Hogg, I. V. (1991). The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Firearms. Secausus, NJ: Chartwell Books. ISBN:978-0-906286-41-8 p. 279.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Chinn">Chinn, G. M. (1952). The Machine Gun (7th ed., Vol. 2). Washington D.C: U.S. Department of the Navy. p. 78-79.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Drabkin>Drabkin, A. (2007). Red air force at war Barbarossa and the retreat to Moscow - recollections o. Barnsley, South Yorkshire, U.K.: Pen & Sword Books. ISBN:1-84415-563-3.</ref> | ||
| + | </references> | ||
{{Aircraft machine guns}} | {{Aircraft machine guns}} | ||
[[Category:Aircraft machine guns]] | [[Category:Aircraft machine guns]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:05, 11 February 2024

Contents
Description
The 7.62 mm ShKAS (Shpitalny-Komaritski Aviatsionny Skorostrelny or Shipitalny-Komaritski rapid-fire for aircraft – Russian: ШКАС - Шпитального-Комарицкого Авиационный Скорострельный) is a 7.62 mm calibre machine gun which was first produced in 1933 for usage in Soviet aircraft which saw action all the way through World War II in many of the fighters, attackers and bombers of the day. The ShKAS is a single chamber, gas-operated revolver-type machine gun in which a firing pin strikes the primer of the bullet in the chamber to fire the round.
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
General info
With 1,800 RPM, the ShKAS has the highest rate of fire of any machine guns in World War II. Aside from the default ball and plain tracer rounds, the ShKAS's common round composition involves the API-T, API, and AI rounds. Due to the ineffectiveness of the AI rounds due to tiny explosive filler, uses of belt with only the API-T and API are recommended as both rounds has a high chance of lit up the enemy plane on fire if enough shots were hit.
Available ammunition
- Default: T · Ball · Ball · AP-I · AI
- Universal: AP-I · AI · API-T
- Tracers: AP-I · API-T
- Stealth: AP-I · AP-I · AP-I · AI
- Armored targets (turret): AP-I · AP-I · AP-I · API-T
- Universal (turret): API-T · API-T · API-T · AI
Comparison with analogues
| Comparable machine guns to ShKAS (7.62 mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Year of Creation | Mass | Rounds Per Minute | Ammunition | Feed Type | |
| |
Browning (7.62 mm) | 1919 | 14 kg | 1,000 RPM | 7.62 × 63 mm | Belt |
| |
MG 17 (7.92 mm) | 1934 | 10.2 kg | 1,150 RPM | 7.92 × 57 mm | Belt |
| |
MG 15 (7.92 mm) | 1932 | 12.4 kg | 1,150 RPM | 7.92 × 57 mm | Drum |
| |
Browning (7.7 mm) | 1919 | 14 kg | 1,000 RPM | 7.7 × 56 mm R | Belt |
| |
Vickers K (7.7 mm) | 1935 | 13.4 kg | 950 RPM | 7.7 × 56 mm R | Pan |
| |
Type 1 (7.92 mm) | 1932 | 12.8 kg | 1,150 RPM | 7.92 × 57 mm | Drum |
| |
Type 92 navy (7.7 mm) | 1932 | 8 kg | 600 RPM | 7.7 × 56 mm R | Pan |
| |
Type 98 (7.92 mm) | 1932 | 12.8 kg | 1,150 RPM | 7.92 × 57 mm | Drum |
| |
Lewis (7.7 mm) | 1911 | 13 kg | 900 RPM | 7.7 × 56 mm R | Pan |
| |
Breda-SAFAT (7.7 mm) | 1935 | 12.5 kg | 900 RPM | 7.7 × 56 mm R | Belt |
| |
MAC 1934 (7.5 mm) | 1934 | 10.7 kg | 1,350 RPM | 7.5 × 54 mm MAS | Belt/Magazine |
| |
Ksp m/22-37 R (8 mm) | 1919 | 11.7 kg | 1,200 RPM | 8 × 63 mm | Belt |
Usage in battles
The ShKAS are one of the more powerful .30 cal machine guns in the game, only the rotary M134 Minigun and GShG-7.62 surpass it in terms of raw firepower for its calibre. However, it is still held back by the common impotence of small-calibre guns, along with its tendency to jam, thus making trigger discipline vital to its success.
Due to its superior ballistic properties and ammunition compared to other similar guns, the ShKAS is an easy-to-use weapon for beginners. As plenty of early Soviet planes were equipped with this machine gun, this allows the newcomer to learn how to utilize these weapons for various purposes. Though be sure to fire it only in short burst as the gun can be jammed easily, and only fire them for ranging or when you're sure that the shot will land on target.
In some higher tier planes equipped with the ShKAS, the ShKAS's small calibre rounds will started to show its age, as the round has very low damage compared to the more abundant .50 cal machine guns or 20 mm autocannons, though it remains deadly against pilot and internal modules if enough shots land. The gun also has a use against ground targets and slow-flying AI aircraft, in which the ShKAS can take them down with a few shots, allowing the player to conserve more valuable autocannon rounds for enemy planes while earning extra points from destroying AI targets.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- The fastest firing rifle-calibre machine gun in WWII
- High shell velocity, only small leads are needed while aiming
- Very accurate at short-to-medium range (~800 m), ideal for attacking ground targets and AI aircraft
- Every belt is extremely effective at causing fires on enemy aircraft (tracers and stealth are the most effective)
- Incredibly easy to knock out gunners and pilots on enemy aircraft (or exposed crew members on ground and naval forces)
- If fired in short bursts, most aircraft can make a belt last an entire game in realistic battle
Cons:
- Accuracy and penetration drops off at longer ranges (beyond 1 km), restricting it to close range weapon
- Can easily jam. It is recommended to fire in bursts lasting no longer than one second
- Limited damage output due to small shell size, thus requiring multiple hits to knock out the target. This is especially apparent on the defensive version where enemy has more chance to dodge it
History
The 7.62 mm ShKAS machine gun is a Soviet .30 calibre machine gun designed by Boris Shpitalniy and Irinarkh Komaritsky for use on Soviet aircraft. It was designed in 1932 and entered service a year later.
The designers departed from traditional methods of feeding belt linked ammunition into the ShKAS and utilised a feed design nicknamed "bird-cage" or "squirrel-cage".[1] Even declassified documents regarding the United States' evaluation of the feed system stated, "…an interesting departure was made from the heretofore orthodox practice of feeding ammunition to a gun of this caliber [sic]." [2]
The ammunition belt enters the feed cage forward of the firing chamber. When the gun is fired, a gas piston actuates an arm connected to the cylindrical feed cage, rotating it one position to introduce the new bullet. As the feed cage (holding ten rounds) rotates a helical groove and guides the bullets rearward. Through this process of working the bullets rearwards, they are automatically delinked from the metal disintegrating link belt. The rounds make it to the final position at the bottom of the drum where they are then chambered into the receiver, ready to be fired.
One of the benefits of this feed system is during the camming of the rounds; there is relatively no drag on the ammunition allowing the gun to be fired at high rates of speed; however, prolonged actuation can provoke these guns to jam. Rates of fire could be regulated through changing of the holes in the gas regulator, three different hole sizes going from largest to smallest would slow down the rate of fire to a more moderate rate.
|
The ShKAS machine gun had a high rate of fire but it also had 48 ways of jamming. Some of them could be fixed immediately, some could not. And 1,800 rounds a minute was an insanely high rate of fire. If you pulled the trigger too long, the ShKAS would fire all its ammo in one go and that would be it!![3]
|
By the end of World War II, over 150,000 ShKAS had been produced. The gun can be found on a wide range of Soviet aircraft, across fighters, attackers, and bombers. The gun also saw service in the Spanish Civil War with the Republican Spanish forces, as well as the Second Sino-Japanese War and the subsequent resumption of the Chinese Civil War on both the Nationalist and Communist Chinese sides.
Media
See also
- ShVAK (20 mm) - aircraft autocannon also designed by Boris Shpitalniy
External links
References
- ↑ Hogg, I. V. (1991). The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Firearms. Secausus, NJ: Chartwell Books. ISBN:978-0-906286-41-8 p. 279.
- ↑ Chinn, G. M. (1952). The Machine Gun (7th ed., Vol. 2). Washington D.C: U.S. Department of the Navy. p. 78-79.
- ↑ Drabkin, A. (2007). Red air force at war Barbarossa and the retreat to Moscow - recollections o. Barnsley, South Yorkshire, U.K.: Pen & Sword Books. ISBN:1-84415-563-3.
| Aircraft machine guns | |
|---|---|
| USA | |
| 7.62 mm | Browning · M134 Minigun |
| 12.7 mm | GAU-19 · M2 Browning · M3 Browning |
| Germany | |
| 7.62 mm | MG3 |
| 7.92 mm | MG 15 · MG 17 · MG 81 |
| 12.7 mm | FN M3P |
| 13 mm | MG 131 |
| USSR | |
| 7.62 mm | DA · GShG-7.62 · PKT · PV-1 · ShKAS |
| 12.7 mm | A-12.7 · Berezin UB · TKB-481 · YaK-B |
| Britain | |
| 7.62 mm | FN 60.30 · L8A1 |
| 7.7 mm | Browning · Lewis · Vickers E · Vickers K |
| Japan | |
| 7.7 mm | Te-1 · Type 89 · Type 89 'special' · Type 92 · Type 97 navy |
| 7.92 mm | Type 1 · Type 98 |
| 12.7 mm | Ho-103 · Ho-104 |
| 13 mm | Type 2 |
| 13.2 mm | Type 3 |
| China | |
| 12.7 mm | QJK99-12.7-1 |
| Italy | |
| 7.7 mm | Breda-SAFAT · Lewis |
| 7.92 mm | FN Browning |
| 12.7 mm | Breda-SAFAT · FN M3M · Scotti |
| France | |
| 7.5 mm | Darne 1933 · Fabrique Nationale Mle 38 · FN Browning · MAC 1934 · MAC 1934T · Mle 33 · Mle 1923 |
| 7.62 mm | PKA |
| 7.92 mm | FN-Browning M.36 No.3 · FN-Browning M.36 No.4 |
| Sweden | |
| 7.7 mm | FN-Browning M.36 No.3 |
| 8 mm | Ksp m/22 · Ksp m/22 Fh · Ksp m/22 Fv · Ksp m/22-37 R |
| 12.7 mm | Akan m/39A · Akan m/40 · Akan m/45 · LKk/42 |
| 13.2 mm | Akan m/39 · Akan m/39A |