Difference between revisions of "KV-1E"
Colok76286 (talk | contribs) |
(→Ammo racks) |
||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
==== [[Ammo racks]] ==== | ==== [[Ammo racks]] ==== | ||
[[File:Ammoracks_KV-1 (L-11).png|right|thumbnail|x250px|Ammo racks of the KV-1 (L-11) (identical to {{PAGENAME}}).]] | [[File:Ammoracks_KV-1 (L-11).png|right|thumbnail|x250px|Ammo racks of the KV-1 (L-11) (identical to {{PAGENAME}}).]] | ||
| − | '''Last updated: 1.101.0.61''' | + | <!-- '''Last updated: 1.101.0.61''' --> |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 21:16, 5 November 2020
Contents
| This page is about the Soviet heavy tank KV-1E. For other uses, see KV-1 (Family). |
Description
The KV-1E is a gift rank III Soviet heavy tank
with a battle rating of 4.3 (AB/SB) and 4.0 (RB). It was introduced in Update 1.41.27. Its basis is that of the original KV-1 model, but up-armoured with bolted appliqué armour on the front and side of the hull and turret. The tank was initially purchasable as part of premiums packs in the Gaijin store but was removed in January 2018. The KV-1E has been since made available for purchase in-game (![]() ) for specific Soviet/Russian mini-events like the 2019 "Defender of the Fatherland" event or the 2020 "Tankers' Day" event.
) for specific Soviet/Russian mini-events like the 2019 "Defender of the Fatherland" event or the 2020 "Tankers' Day" event.
In the game this tank possesses great armour and a mostly adequate gun, however, it sometimes will not be able to destroy an enemy from the front and will require very close distance or a flank shot. The defining characteristic of this tank is its armour and it can be a tough tank to destroy, most of the weak spots from its predecessors have been armoured and the only frontal weak spot is the centre of the upper hull. When using this tank do not be afraid to advance towards the enemy, especially against tanks such as the 75 mm M4s and T-34s since they will find it very difficult to penetrate your armour. This tank can also be used for long-range support since when the armour is properly angled almost no tank that it faces can pierce its armour.
General info
Survivability and armour
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour
- Cast homogeneous armour (Barrel shroud,
| Armour | Front | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 75 + 25 mm (30-31°) Front plate 40 mm (72°) Front glacis 25 + 40-75 mm (7-71°) Joint plate 75 mm + 25 mm (26-51°) Lower glacis |
75 + 25 mm | 60 mm (13-89°) Top 70 mm (14-57°) Bottom |
30 mm |
| Turret | 75 + 30 mm (14°) Turret front 90 mm (0-62°) Gun mantlet shield 75 mm (4-36°) Gun mantlet |
75 + 30 mm (14-15°) | 75 mm (15-16°) | 40 mm |
Notes:
- Suspension wheels are 20 mm thick, tracks are 30 mm thick.
- Roof armour is quite excellent. 30 - 40 mm is nothing to ignore, even for heavy fighters. It will reliably protect from most autocannons. Although aircraft with good drive-ability and +30 mm arms may still pierce it. More importantly, it makes the vehicle quite resilient against rocket strikes from vehicles such as the Calliope.
- The lower glacis, unlike most other tanks, is not a weak spot! it is including your own turrets height significantly better angled than the upper frontal plate. Further, neither the MG port nor the drivers view slit are weak points. Discard them as targets if aiming for them.
- Gun mantlet is an extra 75 mm bolted on to the turret, with some parts with an extra 90 mm added instead. This results in a spaced overlapped part with ~150 mm. Only the cheeks left and right of the mantlet bulges should be shot! However, these areas are quite small and easily missed, if the turret is traversed.
- Extra armour indicated by the addition to the armour is not placed all over the tank, thus revealing some weaker areas on the front hull and sides.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 37 | 7 | 49 | 775 | 1,145 | 15.82 | 23.37 |
| Realistic | 35 | 7 | 531 | 600 | 10.84 | 12.24 | |
Armaments
Main armament
| F-32 (76 mm) | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 111 | -5°/+25° | ±180° | N/A | 9.7 | 13.4 | 16.3 | 18.0 | 19.2 | 8.1 | 7.2 | 6.6 | 6.3 |
| Realistic | 7.1 | 8.4 | 10.2 | 11.3 | 12.0 | ||||||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration in mm @ 90° | |||||
| 10m | 100m | 500m | 1000m | 1500m | 2000m | ||
| BR-350A | APHEBC | 78 | 76 | 69 | 61 | 53 | 47 |
| BR-350B | APHEBC | 86 | 84 | 76 | 67 | 59 | 52 |
| OF-350M | HE | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Sh-354T | Shrapnel | 37 | 35 | 29 | 25 | 20 | 17 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity in m/s |
Projectile Mass in kg |
Fuse delay
in m: |
Fuse sensitivity
in mm: |
Explosive Mass in g (TNT equivalent): |
Normalization At 30° from horizontal: |
Ricochet: | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||
| BR-350A | APHEBC | 615 | 6.3 | 0.15 | 10.0 | 150 | +4° | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| BR-350B | APHEBC | 615 | 6.8 | 0.9 | 15 | 108.8 | +4° | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| OF-350M | HE | 615 | 6.2 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 621 | +0° | 79° | 80° | 81° |
| Sh-354T | Shrapnel | 615 | 6.2 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 85 | +0° | 62° | 69° | 73° |
| Smoke characteristic | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Velocity in m/s |
Projectile Mass in kg |
Screen radius in m |
Screen time in s |
Screen hold time in s: |
Explosive Mass in g (TNT equivalent): |
| D-350A | 615 | 6.5 | 13 | 5 | 20 | 50 |
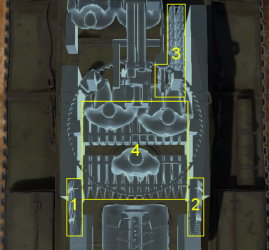
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 111 | 107 (+4) | 102 (+9) | 79 (+32) | 1 (+110) | No |
Notes:
- Racks are modeled by sets of 5 shells (+ 1 set of 3 & 2 sets of 4) and sets disappear from the rack once all shells in the set have been loaded/fired.
- Turret empty: 102 (+9) shells.
Machine guns
| 7.62 mm DT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Coaxial | 1,890 (63) | 600 | N/A | N/A |
The small caliber of the DT machine gun makes it largely ineffective against all armoured vehicles but the ones with an open compartment. It still can be used to ping targets as a rangefinding help. The clip capacity of the machine gun is quite poor, as it relies on a magazine of 63 bullets instead of a belt like similar machine guns from other nations.
Usage in battles
In game, this tank is possesses great armour and an adequate gun. However, it may not be able to destroy the enemy from the front at times. As such, the tank may require being at a very close distance or a flank shot to disable certain targets. The defining characteristic of this tank is its armour. It can be a tough tank to destroy, given that most of the weak spots from the predecessor have been armoured and, from the front, the only weak spot is the centre of the upper hull. When using this tank, do not be afraid to advance towards the enemy, especially against tanks such as the 75 mm M4s and T-34s since they will find it very difficult to penetrate your thick armour. This tank can also be used for long-range support, since when the armour is properly angled, almost no tank that it faces can pierce its armour.
Tactics
Urban environment
Urban areas tend to result in very close range engagements. At this range, the armour of this tank can no longer offer the degree of protection that it does at range. With this being said, urban can also present nice medium range opportunities, such as open-air squares and long streets in which this tank can utilise its armour. Urban fighting presents the largest challenge for this tank, as close range flank shots can easily pierce its mighty armour. As such, here are some tactics to use in a city setting:
- Hold down a street - set up in a way that minimizes the chance to be flanked while allowing for the largest angle fire. This will allow the KV-1B to fire at the enemy while minimizing the chance of getting knocked out by a close-range flank shot
- Move with a group of tanks - try to stay in the middle of a group as this will minimize the chances of a close-range flank shot. At this range, the cannon of the tank can penetrate most tanks and has a decent rate of fire, allowing it to quickly engage multiple targets.
- Never blindly drive through an intersection - always check both ways before crossing, as this presents the largest opportunity for danger for this tank.
Open country
The armour of this tank allows it to engage in the long-range fighting that defines an open country. However, the gun on this tank does not allow it to engage targets at range. This means that in while playing in open country, it is a good idea to get into a good overwatch position or to charge the enemy until the KV-1B is capable of engaging at the optimal range for the 76 mm weapon. While the armour on this tank is among the best for the enemies it faces, there are still certain tanks to worry about. The main tanks to work about are those with the American 76 mm, German 75 mm L/48, Russian 57 mm and 85 mm, and of course all the large calibre guns such as the KV-2. These weapons are capable of piercing through the KV-1B armour at range, though this requires a lucky hit on an un-angled plate. Here are some tips when fighting in open country:
- Always angle the tank - the unangled armour is good, but it is nearly impossible to pierce when properly angled.
- Don't be afraid to expose the tank - use the armour to give a degree of freedom in finding the targets.
- Advance - take the point or lead the charge, the KV-1B has the armour to break through enemy lines.
Hill country
This is the type of terrain that this tank excels in. The average range of engagements allows for both the armour and gun to shine. This type of terrain also makes flanking hard, since going over a hill exposes a tank to fire from multiple directions. Even with this, don't forget to check your surroundings. Here are some tips and tactics for fighting in this environment:
- Move through the area between hills - this will allow a degree of control on where the enemy will come from and angle the armour in accordance.
- Going over large hills can be dangerous as it exposes the KV-1B to fire from all directions and also exposes the bottom of the tank to fire.
- Check your surroundings - while it is dangerous to go over hills, many newer player will attempt to do this and will sometimes manage to flank the tank.
Long range
This tank does not excel here due to the low penetration of the gun. However, the armour of this tank makes it almost invulnerable to enemy fire at long ranges. Due to this, it is possible to safely attack enemies with little fear of penetrating return fire. Just remember to properly angle the tank in order to maximize its armour. While long range combat is not the best option for this tank, it can use its armour to sit in positions that no other tank could do safely. When using this tank from long range, the first piece of advice would be to close in on the enemy, though this is sometimes not possible. When one finds that long-range combat is necessary or is a preferred strategy, one can place this tank in a highly visible position to draw enemy fire. This will allow teammates to find the enemy and eliminate them. This will also allow for one to choose their target, since its gun necessitates shooting at weakly armoured targets or the sides and rear of tanks.
Medium range
This tank excels in medium range combat due to great armour. Many tanks it faces will find penetrating this tank almost impossible even from the side due to the additional armour.
Close range
This tank does not excel here due to bad mobility, and the greatest strength of this tank, its great armour, is no longer as potent.
Generally, it is a good idea to avoid engaging the enemy armoured vehicles mentioned below frontally if possible, as they can reliably harm you and vice versa.
- - Pz.IV F2 / G / H / J - Lethal at short ranges, shoot first.
- - M4A3E2 Jumbo / M4A3E2 (France) - Shoot at sides/rear or the armour weak spot above the gun-mantlet or Hull MG.
- - T14 - Shoot at the hull MG port + sides/rear.
- - Churchill III / Churchill VII - Hull at the MG port + sides/rear.
- - ARL-44 (ACL-1) - Difficult to engage frontally, shoot sides/rear.
Modules
| Tier | Mobility | Protection | Firepower | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Tracks | Parts | Horizontal Drive | ||
| II | Suspension | Brake System | FPE | Adjustment of Fire | BR-350B (MD-8 fuze) |
| III | Filters | Crew Replenishment | Elevation Mechanism | ||
| IV | Transmission | Engine | D-350A | ||
| This is a premium vehicle: all modifications are unlocked on purchase | |||||
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Great armour protection on all sides
- Weak spots like the flat sides are much better protected
- Acceleration is good on flat terrain
- Angling your hull makes the frontal armour immune to most guns it faces
- Gun does a lot of damage upon penetration
- Heavily armoured for a Rank II tank, even compared to original KV-1
- Crew of five allow for higher survivability
- Reload rate is decent for the cannon
Cons:
- Poor overall top speed
- Additional weight hampers the tanks already poor performance
- F-32 gun is same as L-11 in penetration, very bad for dealing with other vehicles it may face
- Slow turret traverse, if you need to change target quickly you must rotate both the turret and the hull
- Making turns will decrease your speed dramatically
- Climbing hills is very sluggish for the tank
- Can encounter other armoured fighting vehicles that are able to easily penetrate its armour, such as the Panzer IV F2
- Large fuel tanks lined up on the side
History
Development
The start of the KV-1 heavy tanks began after the heavy tank T-35 flaws came to light. Designers were ordered to draw up new designs to become the basis of a breakthrough heavy tank needed for the Soviet doctrine. This made for a tank that was heavily armoured, but not very mobile as it was to be for siege warfare. The designs offered all had heavy armour, wide tracks, and used the torsion-bar suspension. The designs were the SMK, T-100, and what would be the KV tank, which was named after the then Soviet Defense Commissar Kliment Voroshilov.
During the developmental progress, the prototypes of all these heavy tanks were made and the Winter War with Finland was on its way. The Soviets sent these tanks into Finland for combat testing, to which the KV design outperform in every way with its superior armour and firepower. The armour on the KV tank was impenetrable by a tank cannon in service and most anti-tank guns as well, the 76.2 cannon also gave it a huge firepower boost compared to the usual 37 mm in use by other countries. However, the design was found to be difficult to steer, the transmission was unreliable, ergonomics was poor and vision was limited, plus with its 45-ton weight, it was a very heavy tank for its time. In truth, while formidable in power and protection, courageous crew member willing to curse the name would speak out about the trouble the KV tank really was. The main variant of production before World War II broke out was the KV-1 model.
KV-1E
The initial production in 1939 had the KV-1 equipped with an L-11 cannon, this was upgraded to the F-32 in 1940. The Model 1940 production was the main KV-1 variant that was available during the German invasion in Operation Barbarossa. During the German invasion, it was found that the KV-1s, while invulnerable to even the German Panzer IIIs and Panzer IVs, was easily taken out by the German 88 mm FlaK cannon used in anti-tank roles. This caused the KV-1 production model to be up-armoured for increased survivability with applique armour bolted onto the tank. Though it varies on how much extra armour is bolted on, some KV-1s have overall armour width of 100 mm thick. These up-armoured Model 1940 KV-1s were called KV-1E, with "E" standing for "ekranami ", which means "with shields". This up-armouring of the tank caused the weight to be increased from its original 45 tons to 50 tons, further straining the drive system of the tank.
Combat usage
The main bulk of these up-armoured tanks was sent to the Northwestern and Leningrad fronts. Some of these tanks were captured intact and used by German forces against their former users. Nevertheless, the KV-1 continued to serve until the end of the war, though in dwindling numbers as they are lost due to mechanical failures or combat. Some 1941-built KV-1s still saw service in 1944 at the Leningrad front before being replaced by IS-2 tanks, then they saw service in Manchuria in 1945.
Survivors
Several KV-1s survive after the war, most as monuments, but also in museums. Only one genuine KV-1 was restored to running condition in Russia after it was found in the bottom of the Neva River. One KV-1B can also be found at the Bovington Tank Museum at England.
In-game description
After receiving the first reports from the front about the heavy tanks' deployment in battle, the LKZ factory began to work on strengthening the KV's armour. The only weapon capable of penetrating the Soviet tank's frontal armour was the 88 mm 8.8 Flak 18 anti-aircraft cannon. Its anti-aircraft rounds, even without an armour-piercing steel core, had an 810 m/s muzzle velocity and could penetrate an 80 mm thick armour plate set at a 30 degree angle from a range of 1,000 metres. As a rule, it disabled the KV-1 with 2-3 hits to its turret and hull.
Specialists at the Leningrad Kirovsk factory developed a simple but effective up-armouring design previously used on the T-28 tank. The tank's turret and hull sides were fitted with 25 mm add-on armour plates, increasing the overall armour width to 100 mm. Furthermore, a small gap was left between the turret and the add-on armour. This improved the tank's defences when under fire from shaped high explosive shells. These modifications increased the tank's combat-loaded weight to 50 tonnes. Tanks modified in such a way could be discerned by the huge heads of the bolts used to attach the add-on armour plates.
The main bulk of these up-armoured tanks was sent to the Northwestern and Leningrad fronts. Some of these tanks were captured intact and used by German forces. The stationary nature of combat encounters did not allow the KV to truly come into its own. Apart from that, tank units constantly complained about the vehicle's high weight, which didn't just lead to technical problems. All it took was a few KV tanks driving along a road to make it difficult to negotiate for other vehicles, even tracked ones. The heavy tank's mobility on loose ground or boggy terrain was unsatisfactory.
Media
- Skins
- Videos
See also
- Vehicles equipped with the same chassis
- Vehicles equipped with the same gun
- Other vehicles of similar configuration and role
External links
- [Historical] Zinovy Kolobanov’s feat of arms
- [Wikipedia] Kliment Voroshilov tank
- [Tanks Encyclopedia] KV-1
| USSR heavy tanks | |
|---|---|
| KV-1 | KV-1 (L-11) · KV-1 (ZiS-5) · KV-1E · KV-1S |
| KV-2 | KV-2 (1939) · KV-2 (1940) · KV-2 (ZiS-6) |
| Other KVs | KV-85 · KV-122 · KV-220 |
| IS-1/2 | IS-1 · IS-2 · IS-2 (1944) · IS-2 No.321 · IS-2 "Revenge" · Object 248 |
| Other IS tanks | IS-3 · IS-4M · IS-6 · IS-7 |
| T-10 | T-10A · T-10M |
| Multi-turreted | T-35 · SMK |
| Other | Object 279 |
| Lend-Lease | ▂MK-II "Matilda" |
| USSR premium ground vehicles | |
|---|---|
| Light tanks | BA-11 · RBT-5 · BT-7A (F-32) · T-26 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-26E · T-126 · PT-76-57 · 2S38 |
| Medium tanks | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34E · T-34-57 (1943) · T-34-85E · T-34-100 · T-44-122 · TO-55 · T-55AM-1 · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-80UD · Т-80U-Е1 |
| ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 · ▂T-III · ▂T-V · ▂МК-IX "Valentine" | |
| Heavy tanks | SMK · T-35 · ▂MK-II "Matilda" · KV-1E · KV-2 (1940) · KV-2 (ZiS-6) · KV-122 · KV-220 · IS-2 "Revenge" · Object 248 · IS-6 · T-10A |
| Tank destroyers | BM-8-24 · BM-13N · BM-31-12 |
| SU-57 · SU-76D · SU-76M (5th Gv.Kav.Corps) · SU-85A · SU-100Y · SU-122P · Object 120 | |
| SPAA | ▂Phòng không T-34 · ZUT-37 |