Difference between revisions of "Tiny Tim"
m (Edits.) |
(Updated for 1.91) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
<div class="ttx"> | <div class="ttx"> | ||
<div class="ttx-image">[[File:Tiny-tim-1.jpg]] | <div class="ttx-image">[[File:Tiny-tim-1.jpg]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="ttx-table-line"><span class="ttx-value">548 mph (245 m/s)</span><span class="ttx-name">Speed</span></div> | <div class="ttx-table-line"><span class="ttx-value">548 mph (245 m/s)</span><span class="ttx-name">Speed</span></div> | ||
| − | <div class="ttx-table-line"><span class="ttx-value">None</span><span class="ttx-name">Guidance System</span></div> | + | <div class="ttx-table-line"><span class="ttx-value">None</span><span class="ttx-name">Guidance System</span></div> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | <!--''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.''--> | + | <!-- ''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.'' --> |
| − | [[File:Tiny_Tim_sideview.png|520px|thumb|left|Side view of | + | [[File:Tiny_Tim_sideview.png|520px|thumb|left|Side view of a '''{{PAGENAME}}''' unguided rocket.]] |
{{break}} | {{break}} | ||
| − | During World War II, many attackers and dive-bomber aircraft were lost to anti-aircraft fire when attempting to bomb enemy ships. | + | During World War II, many attackers and dive-bomber aircraft were lost to anti-aircraft fire when attempting to bomb enemy ships. A hail of bullets and explosive shells attempted to knock these aircraft out of the sky before they could deliver their payload. In response to these challenges, the United States Navy sought to develop a weapon in which to be able to sink a ship while minimizing the threat of anti-aircraft fire to inbound aircraft. The outcome of this development resulted in the Tiny Tim anti-shipping rocket, the largest rocket produced at the time even dwarfing the German Nebelwerfer-based BR 21. |
| − | To help speed up the development process of the Tiny Tim rocket, engineers scrapped together existing parts and equipment where they could to help save time. | + | To help speed up the development process of the Tiny Tim rocket, engineers scrapped together existing parts and equipment where they could to help save time. The rocket body was manufactured from 11.75 in (298 mm) used oil field pipe and available in abundance and specifically because it was the perfect size to adapt existing 500-lb (226.7 kg) semi armour-piercing bombs in the military's arsenal. Fitted with a 24-nozzle engine firing on solid rocket propellant, the 10.25 ft (312 cm) Tiny Tim could travel at 548 mph (245 m/s). Utilising its TNT warhead, it was used to take out coastal defence guns, bridges, pillboxes, tanks and was credited with sinking one Japanese ship and damaging another. |
=== Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | === Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | ||
<!-- ''List out vehicles that are equipped with the weapon.'' --> | <!-- ''List out vehicles that are equipped with the weapon.'' --> | ||
{{Navigation-Start|Vehicles equipped with this weapon}} | {{Navigation-Start|Vehicles equipped with this weapon}} | ||
| − | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Fighters''' | + | |
| − | + | {{Navigation-First-Line|'''Fighters'''}}{{Specs-Link|f6f-3|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f6f-5_france|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f6f-5n|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f6f-5n_france|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|hellcat_fmk1|short}} | |
| − | {{Navigation-Line| | + | {{Navigation-Line| }}{{Specs-Link|f8f1|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f8f1b|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f8f1b_france|short}} |
| − | {{Navigation | + | |
| − | {{Navigation | + | {{Navigation-Line|'''Twin-engine fighters'''}}{{Specs-Link|f7f3|short}} |
| − | {{Navigation | + | |
| − | {{Navigation | + | {{Navigation-Line|'''Jet fighters'''}}{{Specs-Link|f3d_1|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f-84b|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f-84g|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f-84g_china|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f-84g_italy|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|f-84g_france|short}} |
| + | |||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|'''Attackers'''}}{{Specs-Link|douglas_ad_2|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|douglas_ad_4|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|douglas_ad_4_france|short}}{{-}}{{Specs-Link|am_1_mauler|short}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Navigation-Line|'''Bombers'''}}{{Specs-Link|pv_2d|short}} | ||
| + | |||
{{Navigation-End}} | {{Navigation-End}} | ||
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| − | <!--''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the | + | <!-- ''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the rocket.'' --> |
[[File:Tiny_Tim_3in_armour_test.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Testing the '''{{PAGENAME}}''' rocket against a 3-inch armoured target.]] | [[File:Tiny_Tim_3in_armour_test.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Testing the '''{{PAGENAME}}''' rocket against a 3-inch armoured target.]] | ||
| − | The Tiny Tim was a massive rocket weighing around 1,285.3 lbs (583 kg) and could only effectively be carried by more stout fighters, dive-bombers and attackers/medium bombers. | + | The Tiny Tim was a massive rocket weighing around 1,285.3 lbs (583 kg) and could only effectively be carried by more stout fighters, dive-bombers and attackers/medium bombers. The 3,000 lbf (13 kN) blast from the ignition of the solid rocket propellant could damage the delivery aircraft so the rocket was modified to be dropped like a bomb, attached to the rocket was a lanyard which would snap off after the rocket dropped several feet which would initiate the rocket motor safely away from the aircraft. |
| + | |||
| + | Due to the size and weight of the missile, the main function as a semi-armour piercing rocket was to not explode on the surface of an object, but rather to partially burrow into the object before exploding. This would allow the warhead to penetrate the hull of a ship, the concrete of a bunker or even weaken tank armour through blunt force before exploding sending shock waves from the inside-out rather than just from the outside-inward. | ||
| − | |||
=== Effective damage === | === Effective damage === | ||
| − | <!--''Describe the type of damage produced by this type of | + | <!-- ''Describe the type of damage produced by this type of rocket (high explosive, splash damage, etc)'' --> |
* Embeds into an object (brute force through the hull of a ship, reinforced concrete or tank armour) | * Embeds into an object (brute force through the hull of a ship, reinforced concrete or tank armour) | ||
* Delayed explosive damage | * Delayed explosive damage | ||
| Line 56: | Line 62: | ||
=== Comparison with analogues === | === Comparison with analogues === | ||
| − | <!--''Give a comparative description of | + | <!-- ''Give a comparative description of rockets that have firepower equal to this weapon.'' --> |
* No other rockets were produced by the United States or any other nation which come close to the size of the Tiny Tim rocket. | * No other rockets were produced by the United States or any other nation which come close to the size of the Tiny Tim rocket. | ||
| + | |||
== Usage in battles == | == Usage in battles == | ||
| − | <!--''Describe situations when you would | + | <!-- ''Describe situations when you would utilise this rocket in-game (vehicle, pillbox, base, etc)'' --> |
;Primary targets for Tiny Tim rockets: | ;Primary targets for Tiny Tim rockets: | ||
| Line 67: | Line 74: | ||
* Bridges | * Bridges | ||
[[File:Tiny_Tim_view_of_rocketmotor.png|450px|thumb|right|A '''{{PAGENAME}}''' unguided rocket mounted to a [[F6F-5N]]. Notice the detail of the rocket motor.]] | [[File:Tiny_Tim_view_of_rocketmotor.png|450px|thumb|right|A '''{{PAGENAME}}''' unguided rocket mounted to a [[F6F-5N]]. Notice the detail of the rocket motor.]] | ||
| + | |||
=== Pros and cons === | === Pros and cons === | ||
| − | <!--'' | + | <!-- ''Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.'' --> |
'''Pros:''' | '''Pros:''' | ||
| Line 79: | Line 87: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | <!--'' | + | <!-- ''Describe the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' --> |
| − | Towards the end of World War II saw the invention of equipment and weapons intending to help spare the lives of military personnel and their equipment while still inflicting damage on the enemy. | + | Towards the end of World War II saw the invention of equipment and weapons intending to help spare the lives of military personnel and their equipment while still inflicting damage on the enemy. One such invention was the United States Navy's Tiny Tim rocket which could hit a ship while the attacking aircraft remained safely outside of the range of the anti-aircraft fire. The massive 1,285.3 lbs (583 kg), 10.25 ft (312 cm) TNT tipped rocket fit the bill. To expedite the manufacturing of this rocket, available resources were used. 500-lb semi armour-piercing bombs already in the inventory were fitted to used oil-well casing pipe which could be found in abundance at abandoned oil wells. |
| − | Tiny Tim saw limited service in World War II and was used in the battle of Okinawa and later during the Korean War. | + | Tiny Tim saw limited service in World War II and was used in the battle of Okinawa and later during the Korean War. Targets selected included bridges, concrete reinforced pillboxes, tanks, ships and other hardened targets as the rocket specialized in embedding itself into an object before exploding causing both explosive and shock damage from within the target. |
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| − | <!--''An excellent addition to the article would be a video guide, as well as screenshots from the game and photos.''--> | + | <!-- ''An excellent addition to the article would be a video guide, as well as screenshots from the game and photos.'' --> |
| − | <div><ul> | + | <div><ul> |
<li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:F-84_Tiny_Tim.JPG|thumb|none|200px|Image of a '''{{PAGENAME}}''' rocket mounted on an under-wing pylon of an [[F-84 (Family)|F-84]] while stationed in Korea in 1952.]] </li> | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:F-84_Tiny_Tim.JPG|thumb|none|200px|Image of a '''{{PAGENAME}}''' rocket mounted on an under-wing pylon of an [[F-84 (Family)|F-84]] while stationed in Korea in 1952.]] </li> | ||
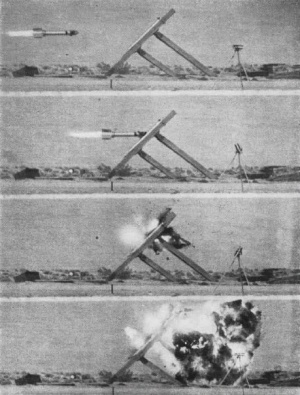
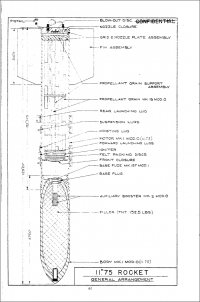
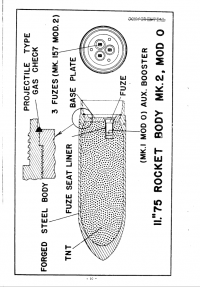
<li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:Tiny Tim Info pg48.png|thumb|none|200px|Diagram of the '''{{PAGENAME}}''' rocket.]]</li> | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:Tiny Tim Info pg48.png|thumb|none|200px|Diagram of the '''{{PAGENAME}}''' rocket.]]</li> | ||
| Line 103: | Line 111: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | <!--''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | + | <!-- ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' |
* ''topic on the official game forum;'' | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
* ''encyclopedia page on the weapon;'' | * ''encyclopedia page on the weapon;'' | ||
| − | * ''other literature.''--> | + | * ''other literature.'' --> |
* [http://bulletpicker.com/pdf/USNBD%20-%20US%20Rockets%20and%20Fuzes.pdf US Rockets and Fuzes - United States Navy Bomb Disposal Manual, 15 May 1945, pg. 48-51] | * [http://bulletpicker.com/pdf/USNBD%20-%20US%20Rockets%20and%20Fuzes.pdf US Rockets and Fuzes - United States Navy Bomb Disposal Manual, 15 May 1945, pg. 48-51] | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 2 October 2019

Contents
Description
During World War II, many attackers and dive-bomber aircraft were lost to anti-aircraft fire when attempting to bomb enemy ships. A hail of bullets and explosive shells attempted to knock these aircraft out of the sky before they could deliver their payload. In response to these challenges, the United States Navy sought to develop a weapon in which to be able to sink a ship while minimizing the threat of anti-aircraft fire to inbound aircraft. The outcome of this development resulted in the Tiny Tim anti-shipping rocket, the largest rocket produced at the time even dwarfing the German Nebelwerfer-based BR 21.
To help speed up the development process of the Tiny Tim rocket, engineers scrapped together existing parts and equipment where they could to help save time. The rocket body was manufactured from 11.75 in (298 mm) used oil field pipe and available in abundance and specifically because it was the perfect size to adapt existing 500-lb (226.7 kg) semi armour-piercing bombs in the military's arsenal. Fitted with a 24-nozzle engine firing on solid rocket propellant, the 10.25 ft (312 cm) Tiny Tim could travel at 548 mph (245 m/s). Utilising its TNT warhead, it was used to take out coastal defence guns, bridges, pillboxes, tanks and was credited with sinking one Japanese ship and damaging another.
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
| Vehicles equipped with this weapon | |
|---|---|
| Fighters | F6F-5 · ▄F6F-5 · F6F-5N · ▄F6F-5N · ▄Hellcat Mk II |
| F8F-1 · F8F-1B · ▄F8F-1B | |
| Twin-engine fighters | F7F-3 |
| Jet fighters | F3D-1 · F-84B-26 · F-84G-21-RE · ␗F-84G-21-RE · ▄F-84G-21-RE · ▄F-84G-26-RE |
| Attackers | AD-2 · AD-4 · ▄AD-4 · AM-1 |
| Bombers | PV-2D |
General info
The Tiny Tim was a massive rocket weighing around 1,285.3 lbs (583 kg) and could only effectively be carried by more stout fighters, dive-bombers and attackers/medium bombers. The 3,000 lbf (13 kN) blast from the ignition of the solid rocket propellant could damage the delivery aircraft so the rocket was modified to be dropped like a bomb, attached to the rocket was a lanyard which would snap off after the rocket dropped several feet which would initiate the rocket motor safely away from the aircraft.
Due to the size and weight of the missile, the main function as a semi-armour piercing rocket was to not explode on the surface of an object, but rather to partially burrow into the object before exploding. This would allow the warhead to penetrate the hull of a ship, the concrete of a bunker or even weaken tank armour through blunt force before exploding sending shock waves from the inside-out rather than just from the outside-inward.
Effective damage
- Embeds into an object (brute force through the hull of a ship, reinforced concrete or tank armour)
- Delayed explosive damage
- Delayed shockwave damage
Comparison with analogues
- No other rockets were produced by the United States or any other nation which come close to the size of the Tiny Tim rocket.
Usage in battles
- Primary targets for Tiny Tim rockets
- Tanks
- Pillboxes
- Ships
- Bridges

Pros and cons
Pros:
- Massive rocket, packs a huge punch
- Semi armour-piercing warhead
Cons:
- Massive rocket, limits aircraft which can carry it
- The 1,250 lb (569 kg) weight limits other payloads the aircraft can carry
History
Towards the end of World War II saw the invention of equipment and weapons intending to help spare the lives of military personnel and their equipment while still inflicting damage on the enemy. One such invention was the United States Navy's Tiny Tim rocket which could hit a ship while the attacking aircraft remained safely outside of the range of the anti-aircraft fire. The massive 1,285.3 lbs (583 kg), 10.25 ft (312 cm) TNT tipped rocket fit the bill. To expedite the manufacturing of this rocket, available resources were used. 500-lb semi armour-piercing bombs already in the inventory were fitted to used oil-well casing pipe which could be found in abundance at abandoned oil wells.
Tiny Tim saw limited service in World War II and was used in the battle of Okinawa and later during the Korean War. Targets selected included bridges, concrete reinforced pillboxes, tanks, ships and other hardened targets as the rocket specialized in embedding itself into an object before exploding causing both explosive and shock damage from within the target.
Media
- Image of a Tiny Tim rocket mounted on an under-wing pylon of an F-84 while stationed in Korea in 1952.
-
 An underaircraft view of a F6F-5N carrying two Tiny Tim rockets.
An underaircraft view of a F6F-5N carrying two Tiny Tim rockets. -
 A view of a F6F-5N firing off a Tiny Tim rocket at an enemy target.
A view of a F6F-5N firing off a Tiny Tim rocket at an enemy target. -
 A side view of the shackle connection of the Tiny Tim rocket to the external pylon of the F6F-5N.
A side view of the shackle connection of the Tiny Tim rocket to the external pylon of the F6F-5N.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the article about the variant of the weapon;
- references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.
External links