Difference between revisions of "Type 61"
Colok76286 (talk | contribs) (→Ammo racks: Updated section) |
Colok76286 (talk | contribs) (Edits) |
||
| Line 225: | Line 225: | ||
The initial specifications for the development of their domestic tank design followed as 1) Small enough to be train-transported, 2) Not be heavier than 25 tons, and 3) an armament of 90 mm calibre. The job of designing the tank was given to Mitsubishi, the same company responsible for making the majority of Japanese tanks in World War II. The first specification was important to not only improve cross-country travel but because if it could be followed, the tanks can be transported via truck transports as well. The second specification was a dodgy one in that 25 tons did not allow for much armour to be placed, but it was hoped a new engine could supplement a weight increase to 35 tons by improving mobility. When the new engine got delayed, the weight was reduced back to 25 tons to retain mobility. The last specification of a 90 mm gun was due to the Japanese experience with a [[M36 GMC|M36 tank destroyer]], believing the 90 mm to be sufficient in the mountainous region of Japan and be the limit where Japanese physique could adequately service the gun. These specifications would lead to the first prototype being developed in 1956. | The initial specifications for the development of their domestic tank design followed as 1) Small enough to be train-transported, 2) Not be heavier than 25 tons, and 3) an armament of 90 mm calibre. The job of designing the tank was given to Mitsubishi, the same company responsible for making the majority of Japanese tanks in World War II. The first specification was important to not only improve cross-country travel but because if it could be followed, the tanks can be transported via truck transports as well. The second specification was a dodgy one in that 25 tons did not allow for much armour to be placed, but it was hoped a new engine could supplement a weight increase to 35 tons by improving mobility. When the new engine got delayed, the weight was reduced back to 25 tons to retain mobility. The last specification of a 90 mm gun was due to the Japanese experience with a [[M36 GMC|M36 tank destroyer]], believing the 90 mm to be sufficient in the mountainous region of Japan and be the limit where Japanese physique could adequately service the gun. These specifications would lead to the first prototype being developed in 1956. | ||
| − | In December 1956, the first prototype labelled | + | In December 1956, the first prototype labelled [[ST-A1]] was produced. Testing and various changes led to the second prototype, [[ST-A2]], to be produced in February 1957. Two more prototypes labelled ST-A3 and ST-A4 were completed in 1959 and 1960 that led to the final production design to be produced in 1961. This would be accepted into service as the Type 61 main battle tank, with deployment to start within the same year. The Type 61 was formally adopted in 1961, but the starting numbers were low as production only put out 10 Type 61 tanks in the span of 1961 to 1962. This only marginally increases up to 1966, with 250 tanks. Production continued until 1975 with 560 tanks produced. |
===Service=== | ===Service=== | ||
| Line 236: | Line 236: | ||
;Skins | ;Skins | ||
| − | * [https://live.warthunder.com/feed/camouflages/? | + | * [https://live.warthunder.com/feed/camouflages/?vehicle=jp_type_61 Skins and camouflages for the {{PAGENAME}} from live.warthunder.com.] |
;Videos | ;Videos | ||
Revision as of 21:48, 5 August 2021
| This page is about the Japanese medium tank Type 61. For other variants, see Type 61 (Family). |
Contents
Description
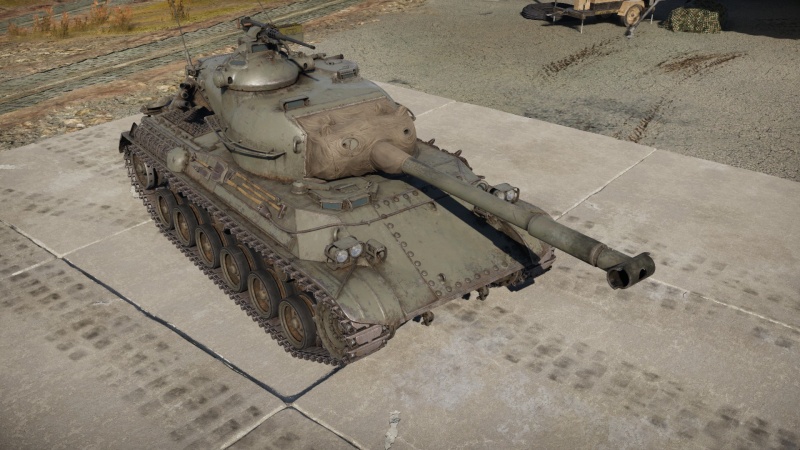
The Type 61 is a rank IV Japanese medium tank with a battle rating of 6.3 (AB) and 6.7 (RB/SB). It was introduced along with the initial Japanese Ground Forces tree in Update 1.65 "Way of the Samurai".
The Type 61 looks like a bizarre cross between the American M41 Walker Bulldog and M60 tanks. It is very similar in its overall length and size to the M41 and the turret looks like the M60's turret with the same prominent commander's cupola on top of the turret housing a rangefinder.
The Japanese Type 61 mimics the American M47 Patton in firepower and M41 Walker bulldog in armour, it has the large, tall profile and fairly mobile medium tank characteristics from of the M47 Patton, with the same decent 90 mm M36/Type61 cannon, but the armour protection qualities more akin to those of the M41 Walker Bulldog.
The Type 61 with its low armour protection and the presence of cannons like the 88 mm KwK43, 105 mm L7A1, 100 mm D-10T cannons at its BR of ~6.7 makes it extremely weak to incoming fire.
Good Type 61 users will typically use the decent mobility to position themselves on flanks of opposition pushes, allowing them to use the decent M318A1 AP round or the M82 shot APHE round to hit weaker side armour or weak spots, alternatively the M431 shell HEAT-FS is a viable choice for long range shooting, however it has meagre damage potential compares to the M318A1 AP round and M82 shot APHE round.
The quick turret traverse will benefit the Type 61 in a close range engagement however the large profile, low armour protection and non-stabilized gun combined with the sometimes lacking penetration of the M318A1 AP round, M82 shot APHE round and poor damage potential of the M431 shell HEAT-FS, means that it not a particularly effective at brawling combat.
General info
Survivability and armour
Armour Type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour
- Cast homogeneous armour (Turret)
| Armour | Front | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 45 mm (49-61°) Front glacis 50 mm (54°) Lower glaics |
30 mm (30°) Top 35 mm Bottom |
25 mm (13°) Top 20 mm (30°), 10 mm (59°) Bottom |
12 mm |
| Turret | 40 mm (4-78°) Turret front 80 mm (0-68°) Gun mantlet |
40-60 mm (0-38°) | 35 mm | 18 mm |
| Armour | Sides | Roof | ||
| Cupola | 31.7 mm | 31.7 mm |
Notes:
- Suspension wheels are 15 mm thick while tracks are 20 mm thick.
Due to its weak armour nearly every tank is a serious threat to the Type 61, as well as a number of SPAA vehicles, however fast medium tanks such as the T-44, M46/M47 Patton or Panther II which can match its mobile are a painful to avoid, while anything with heavy armour (T29, T32, T34 and King Tigers) forces the reliance on the M431 shell HEAT-FS to punch through frontally, taking multiple shots to overcome.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 51 | 9 | 34.3 | 883 | 1,240 | 25.74 | 36.15 |
| Realistic | 46 | 9 | 504 | 650 | 14.69 | 18.95 | |
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
| 90 mm Type 61 | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 51 | -10°/+13° | ±180° | N/A | 22.8 | 31.6 | 38.4 | 42.5 | 45.2 | 9.75 | 8.63 | 7.95 | 7.50 |
| Realistic | 14.3 | 16.8 | 20.4 | 22.6 | 24.0 | ||||||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| M318A1 shot | AP | 192 | 189 | 176 | 161 | 147 | 135 |
| M82 shot | APCBC | 185 | 182 | 170 | 155 | 142 | 130 |
| M431 shell | HEATFS | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 |
| M71 shell | HE | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Shell details | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile Mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive Mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
| M318A1 shot | AP | 912 | 10.91 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 47° | 60° | 65° |
| M82 shot | APCBC | 853 | 10.94 | 1.2 | 14 | 137.2 | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| M431 shell | HEATFS | 1,216 | 5.8 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 712.64 | 65° | 72° | 77° |
| M71 shell | HE | 823 | 10.55 | 0 | 0.1 | 925 | 79° | 80° | 81° |
| Smoke shell characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile Mass (kg) |
Screen radius (m) |
Screen deploy time (s) |
Screen hold time (s) |
Explosive Mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
| M313 | 821 | 10.7 | 13 | 5 | 20 | 50 |
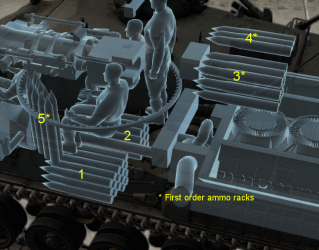
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
5th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 | 35 (+16) | 23 (+28) | 14 (+37) | 11 (+40) | 1 (+50) | No |
Notes:
- Shells are modeled individually and disappear after having been shot or loaded.
- Racks 3, 4 and 5 are first stage ammo racks. They total 22 shells and get filled first when loading up the tank.
- These racks are also emptied early: the rack depletion order at full capacity is: 3 - 4 - 5 - 1 - 2.
- Simply not firing when the gun is loaded will move ammo from racks 1 and 2 into racks 5 then 4 and 3. Firing will interrupt the restocking of the ready racks.
- Floor racks empty: 23 (+28) shells.
Machine guns
| 12.7 mm M2HB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Pintle | 500 (200) | 577 | -10°/+40° | ±180° |
| 7.62 mm M1919A4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Coaxial | 4,000 (250) | 500 | N/A | N/A |
Usage in battles
The Type 61 has excellent horizontal traverse and gun depression combined with a fairly mobile chassis, making it a good choice for progressing from turret down (be careful about the large cupola sticking up), to hull down and firing at the opposition before retreating back to turret down cover.
Its mobility is quite good at getting it to position, where it can ambush tanks early in the game or change position when required, particularly when disengaging when its position is discovered.
Its lack of armour and the decent but not overwhelmingly powerful gun means it is not a wonderful frontline tank to hold a defensive position when the opposition knows its position, as its armour is unlike to prevent any opposition rounds from penetrating and dealing damage, leaving the user to more often than not, rely on luck when engaging opposition frontally.
The biggest issue with the Type 61 is shot selection! Should one choose the M431 shell HEAT-FS which will punch through most opposition tanks, but do little damage? Or use the M318A1 AP round, M82 shot APHE rounds for more damage, but will struggle to penetrate opposition frontally at times?
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Fast turret rotation
- Excellent gun depression
- Good forward speed and mobility
- Good acceleration
- Great post-penetration damage on the M82 APCBC shell
Cons:
- 90 mm Type 61 can struggle to overcome certain opposing tanks frontally without relying on M431 HEAT-FS shell
- Very thin overall armour, any tank gun will make short work of the Type 61, and even certain SPAAs can give the tank trouble
- The reverse speed -8 kph can hinder the tank at times
- Very tall profile with the cupola on top of the turret, makes using certain cover impossible
History
Development
With the subsequent events of the Japanese surrender in September 1945, the end of World War II, and the ensuing Allied occupation of Japan, the Japanese were ordered to lay down their military activities, essentially abolishing the Imperial Japanese Army and Navy. For a short period past VE-Day, Japan was without a military with the exception of the Allied troops still occupying the country. This stance on a Japanese military was reversed with the advent of the Cold War and the much-closer Korean War in the early 1950s. With the departure of a majority of the Allied troops from Japan to Korea, there was a concern on the vulnerability of Japan without the aid of these nations. So in 1954, Japan formally organized the Defense Agency heading the Japan Self-Defense Force (JSDF). To jump-start the remilitarization of the JSDF, the United States gave Japan a handful of M4A3E8 Shermans and M24 Chaffees. However, in the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF) service, these tanks presented some problems. The problems the Sherman presented was that its interior was too large for an average Japanese stature, with drivers unable to even reach the foot pedals, and the M24 Chaffee was just plain outdated against Soviet armour. The Japanese were then given options to replace these tanks with the newer American M46 Patton and M47 Patton or develop their own tank. Given the price of buying the tanks and the tanks not suiting to their specifications, the Japanese opted to develop their own tank for the JGSDF.
The initial specifications for the development of their domestic tank design followed as 1) Small enough to be train-transported, 2) Not be heavier than 25 tons, and 3) an armament of 90 mm calibre. The job of designing the tank was given to Mitsubishi, the same company responsible for making the majority of Japanese tanks in World War II. The first specification was important to not only improve cross-country travel but because if it could be followed, the tanks can be transported via truck transports as well. The second specification was a dodgy one in that 25 tons did not allow for much armour to be placed, but it was hoped a new engine could supplement a weight increase to 35 tons by improving mobility. When the new engine got delayed, the weight was reduced back to 25 tons to retain mobility. The last specification of a 90 mm gun was due to the Japanese experience with a M36 tank destroyer, believing the 90 mm to be sufficient in the mountainous region of Japan and be the limit where Japanese physique could adequately service the gun. These specifications would lead to the first prototype being developed in 1956.
In December 1956, the first prototype labelled ST-A1 was produced. Testing and various changes led to the second prototype, ST-A2, to be produced in February 1957. Two more prototypes labelled ST-A3 and ST-A4 were completed in 1959 and 1960 that led to the final production design to be produced in 1961. This would be accepted into service as the Type 61 main battle tank, with deployment to start within the same year. The Type 61 was formally adopted in 1961, but the starting numbers were low as production only put out 10 Type 61 tanks in the span of 1961 to 1962. This only marginally increases up to 1966, with 250 tanks. Production continued until 1975 with 560 tanks produced.
Service
The first few Type 61 tanks were put into service of the JGSDF. Due to low production numbers, it was supplemented with the tanks America gave it. The time the Type 61 was deployed, it was already quite outdated in comparison to Soviet contenders such as the T-54/55 and T-62 tanks. In 1962, the successor of the Type 61 was already in the development process. Even when it was finished, which would be the Type 74, the Type 61 would stick around as supplement due to low production numbers as well, starting from 1980.
The Type 61 would start being retired in the 1990s, showing its obvious age in comparison with newer third-generation main battle tanks. The transition can be seen in that 400 Type 61 were still in service in 1990 to 190 tanks in 1995. In this time period, the Type 61 went through a modernization program to add infra-red searchlights and smoke dischargers. Regardless, all were decommissioned by 2000, paving the way to the newer Japanese tank designs.
Media
- Skins
- Videos
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
| Japan medium tanks | |
|---|---|
| Type 97 | Chi-Ha · Chi-Ha Kai · Chi-Ha Kai TD · Chi-Ha Short Gun |
| Type 1 | Chi-He · Chi-He (5th Regiment) · Ho-I |
| Type 3 | Chi-Nu · Chi-Nu II |
| Type 4 | Chi-To · Chi-To Late |
| Type 5 | Chi-Ri II |
| Type 61 MBT | ST-A1* · ST-A2* · ST-A3* · Type 61 |
| Type 74 MBT | ST-B2* · Type 74 (C) · Type 74 (E) · Type 74 (F) · Type 74 (G) |
| Type 90 MBT | Type 90 · Type 90 (B) · Type 90 (B) "Fuji" |
| Type 10 MBT | TKX (P)* · TKX* · Type 10 |
| Other | Ka-Chi |
| USA | ▅M4A3 (76) W · ▅M47 |
| *Prototype | |






