T-72B (1989)
| This page is about the Soviet medium tank T-72B (1989). For other versions, see T-72 (Family). |
Contents
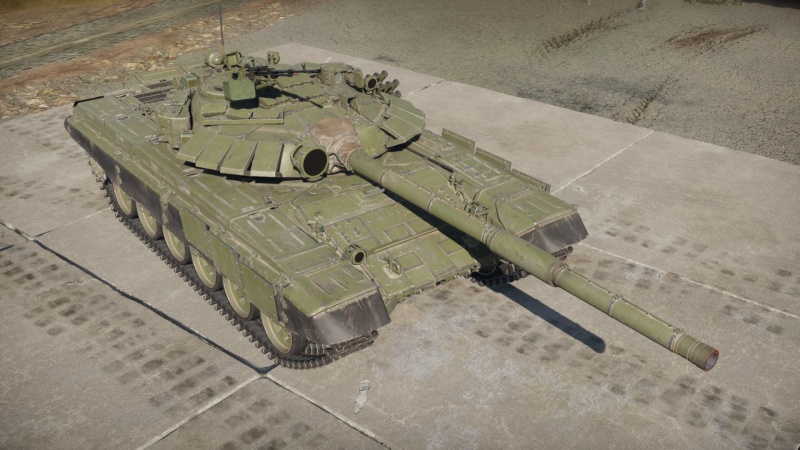
Description
The T-72B (1989) is a rank VII Soviet medium tank with a battle rating of 10.3 (AB/RB/SB). It was introduced in Update "Raining Fire".
General info
Survivability and armour
While being the same tank as the T-72B, the T-72B (1989) has CONTACT-5 ERA instead of CONTACT-1, making it able to withstand greater kinetic energy damage (APFSDS, APDS, etc) while keeping its capability against chemical energy (HEAT-FS, ATGM, etc). It should be noted that, depending on the calibre and round, the ERA plates may even survive a hit or two. However, this is not something that should be expected most of the time.
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 60 mm (60°) | 80 mm Top 20 mm Bottom |
40 mm | 20 - 30 mm |
| Turret | Variable thickness armour Turret front 220-600 mm Gun mantlet |
240 - 118 mm | 60 - 115 mm | 45 mm |
| Cupola | 100 mm (variable angles) | 100 mm | 100 mm | 40 mm |
Notes:
- ERA plates are 13 mm thick
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 67 | 5 | 44.5 | 1,302 | 1,603 | 29.26 | 36.02 |
| Realistic | 60 | 5 | 743 | 840 | 16.7 | 18.88 | |
The T-72B (1989) is a slow and sluggish tank which has poor acceleration and handling. It has really poor reverse speed as well as hull traverse. However, it has a powerful engine which makes it capable of pulling and pushing enemy tanks as well as moving through rough terrain with ease. It does not have enough horsepower to climb over steep elevations. Speed-wise, it has a decent top speed (~60-70 km/h) which under specific situations it is able to be reached.
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
The T-72B has the powerful 2A46M 125 mm smoothbore cannon. It has a powerful selection of rounds, each with different uses and similarities between same types.
| 125 mm 2A46M-1 | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 45 | -6°/+13° | ±180° | Two-plane | 22.8 | 31.6 | 38.4 | 42.5 | 45.2 | 7.10 | 7.10 | 7.10 | 7.10 |
| Realistic | 14.3 | 16.8 | 20.4 | 22.6 | 24.0 | ||||||||
Ammunition
- 3BK18M: this is the starting HEATFS round which can be seen as poor when in frontal engagements against modern MBTs. However, the decent explosive filler as well as not losing penetration over distance makes it a decent round for sniping. However, its muzzle velocity is not fast and will be hard to aim at long distances. It is able to hullbreak light armoured vehicles such as SPAA.
- 3BM22: this is a tier 1 tungsten core APFSDS which has the second highest muzzle velocity seen in Russian darts. However, the weight as well as penetration make it unreliable when facing top tier MBTs frontally.
- 9M119: this is a tier 3 SACLOS ATGM which is seen already in T-72B. It is also seen in later T-72 models. It has decent penetration and flight speed, making it reliable for taking out helicopters and targeting enemies when use of an APFSDS shell is more difficult.
- 3BM42: this is a tier 4 APFSDS which has different ballistic performance than 3BM22. While it has more penetration power and greater mass, it has reduced speed (1,760 m/s vs 1,700 m/s).
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| 3BK18M | HEATFS | 550 | 550 | 550 | 550 | 550 | 550 |
| 3OF26 | HE | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 |
| 3BM22 | APFSDS | 425 | 420 | 415 | 405 | 393 | 380 |
| 9M119 | ATGM | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 |
| 3BM42 | APFSDS | 479 | 477 | 470 | 462 | 453 | 445 |
| Shell details | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile Mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive Mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
| 3BK18M | HEATFS | 905 | 19 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 2,790 | 65° | 72° | 77° |
| 3OF26 | HE | 850 | 23 | 0 | 0.1 | 5,240 | 79° | 80° | 81° |
| 3BM22 | APFSDS | 1,760 | 4.83 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 76° | 77° | 80° |
| 9M119 | ATGM | 400 | 23.3 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 5,540 | 80° | 82° | 90° |
| 3BM42 | APFSDS | 1,700 | 4.85 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 78° | 80° | 81° |
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 41 (+4) | 34 (+11) | 22 (+23) | 0 (+45) | No |
Machine guns
| 12.7 mm NSVT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Pintle | 300 (150) | 700 | -4°/+75° | ±180° |
| 7.62 mm PKT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Coaxial | 2,000 (250) | 700 | N/A | N/A |
Usage in battles
The T-72B playstyle is near identical to the T-64B (and also subsequent Soviet MBTs). One of the key differences between the two vehicles is the T-72B's stronger armour. Thanks to the laser rangefinder, the T-72B is able to be a hulldown sniper as the high muzzle velocity of the dart and access to ATGM make it easier. However, it should be notted it has no access to thermals or a high magnifying zoom (8x only).
Enemies worth noting:
- XM-1 (Chrysler)/(GM): Avoid attempting combat with the 3BK18M HEATFS shells, despite their having thin composite armour
- AMX-30B2/AMX-30B2 BRENUS: DM23/33 have enough armour penetration to penetrate T-72 driver frontal plates, though all shells are effective against them in return.
- Leopard 2K: Turret mantlet is resistant to 3BK18M.
- AMX-40: Turret mantlet and lower frontal plate are highly resistant to 3BK18M.
- Strv 103: Depending on the hull angling, HEAT-FS rounds such as the 3BK18M might ricochet. APFSDS is recommended to be used when facing it frontally.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Powerful 125 mm 2A46M-1 gun with various shells, including APFSDS, HEAT-FS, HE, ATGM
- CONTACT-5 ERA blocks significantly increases CE protection, and slightly for KE protection
- Low profile, is a small target compared to Western main battle tanks
- Laser rangefinder and high velocity APFSDS make sniping long distances easier
- Has both smoke grenade launchers and ESS
- With correct angling, upper frontal armour can deflect most rounds from counterpart tanks of other countries
- Autoloader continues working even if fighting a fire or replacing a crew member, and is low on the hull, making it more difficult to hit and detonate
Cons:
- Painful reverse speed of only -5 km/h, can very much get the player destroyed if not careful
- -6 degrees gun depression limits its ability to adapt different battlefield environments
- 7.1 seconds of reload is slower than the 5-second reload of some Western MBTs
- No ammo rack protection, anything that hits it usually leads to ammo detonation, destroying the vehicle instantly
- 3 closely packed crew members are easily knocked out
- Has 3 major weakspots: gun mantlet, driver's armour cutout, and lower front plate
- No thermal optics, only has night vision device
History
Thanks to the increased combat seen in Middle East and threatening NATO powers, Uralzavodvagon decided to upgrade their previous T-72B tanks with CONTACT-1 (K1) ERA to CONTACT-5 (K5) ERA. It was also fitted with a new Fire Control System.
- Kontakt-1
The K1 ERA is a first generation ERA meant to stop early and mid Cold War super plastic slugs and small jets including a wide variety or propelled grenades, anti-tank rockets, HEAT ammunition and ATGM. The K1 are rather small boxes (314 x 148 mm base area) with 3 mm thick steel walls. The reactive sandwich with the designation 4S20 consists of a 2 mm thick steel plate, a 7 mm thick explosive and a 2 mm thick steel plate. Thanks to its double plating, the K1 was effective when repelling enemy jets from all angles thanks to the "V" shape unlike other ERA seen at the time like the Blazer ERA. The "V" shape plus the tank armour angling increased the effective protection of the ERA brick and the effective turret armour, this was the main reason why T-72AV, T-80B and T-64BV had clam shaped ERA displacement on the turret. It provided sufficient protection for all seen threats in combat at the time from NATO forces and related enemy forces. Germany and the United States drove tests on retrieved T-72B fitted with K1 ERA and estimated the protection range K1 has to offer against anti-tank munitions. It rounded between 300-480 mm of RHA agaisnt slug and small jets only with the following protection percentages:
- PG-7 and PG-9 launchers: less than 90%
- PG-7VL: less than 50%
- TOW-1: less than 60%
One of the first disatvantages of the K1 was its sensitibity against small-calibre firearms and heavy machinegun fire which prematurely detonated the ERA before it got hit by the anti-tank munition. For this reason, a non sensitive explosive was chosen in order to reduce this risk.
As the years passed, various threats started to show up against the K1 ERA, these were stronger and more canalized jets, tandem warheads and improved darts. For this reason, a more powerful explosive was required as well as an upgrade to the K1. Same as with K1, the plates (rather than bricks) are placed in a "V" shape on the turret (iconical T-90 turret) in order to increase the effectiveness.
- Kontakt-5
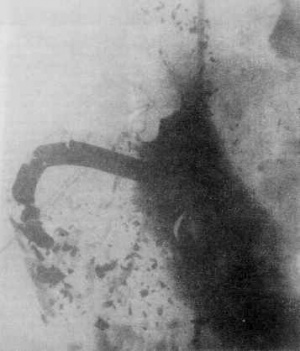
The K5 was a followed up design of ERA capable of surpassing the K1 capabilities agaisnt CE ammunition with added protection against KE ammunition, a capability that was never seen before, this made the K5 the world's first anti-KE ERA. The K5 was designated as an "integrated ERA" due to the way it was mounted on tanks. The K5 consists of the 4S22 explosive sandwiched between thick heavy steel plates. Thanks to this, the ERA is somewhat safe against tandem charges as the tandem charge precursor has to be heavier and stronger in order to detonate the ERA before the main charge detonates, this made it immune to heavy machine gun fire. Depending on the mount, a single layer or two is added. It is claimed that the K5 has a protection of 300 mm of RHA agaisnt KE with a CE protection ranging from 400-550mm. While these claims are not fully confirmed, it is known the K5 has at least a 20% penetration reduction agaisnt APFSDS, capable of dealing with DU darts such as the M829A1, increasing the CE effectiveness by 1.9-2.0 and KE effectiveness to 1.2. The United States and Germany drove tests on the K5 and captured an X-Ray image (see above). It can be clearly seen how the dart is completely fractured. This is due to the shockwave generated by the explosives which fly from the ballistic cap through the dart and end up on the tail. Non-segmented darts are more rigid and less flexible, meaning shockwaves will shatter them more than if it moved with the shockwave (similar effect hydraulic pistons and flexible concrete has on earthquake proof buildings). As seen in the second picture, segmented ERA is not safe from K5 either. It should be noted that, in segmented rods, the penetrator is segmented into various segments which make the overall penetration. Non segmented ones are full piece penetrator. While the K5 can fracture rods, it should be noted that the K5 cannot fully stop the dart. The remains are stopped by the actual tank armour but with reduced effort as dart penetration has already been reduced. Different from light ERA in which the container is fully destroyed by the explosion, K5 maintains the mounts as the explosion is made on the outer plates and not inside the container. This is the reason why T-80U and T-90 keep their "V" shaped turret even after being hit. The mounts provide appliqué armour but not sufficient protection to stop jets or darts.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
| USSR medium tanks | |
|---|---|
| T-28 | T-28 (1938) · T-28 · T-28E |
| T-34-76 | T-34 (Prototype) · T-34 (1940) · T-34 (1941) · T-34 (1st Gv.T.Br.) · T-34 (1942) · T-34E STZ · T-34E |
| T-34-57 | T-34-57 · T-34-57 (1943) |
| T-34-85 | T-34-85 (D-5T) · T-34-85 · T-34-85E |
| T-34-100 | T-34-100 |
| T-44 | T-44 · T-44-100 · T-44-122 |
| T-54 | T-54 (1947) · T-54 (1949) · T-54 (1951) |
| T-55 | TO-55 · T-55A · T-55AM-1 · T-55AMD-1 |
| T-62 | T-62 · T-62M-1 |
| T-64 | Object 435 · T-64A (1971) · T-64B |
| T-72 | T-72A · T-72AV (TURMS-T) · T-72B · T-72B (1989) · T-72B3 · T-72M2 Moderna |
| T-80 | T-80B · T-80U · T-80UD · T-80UK · T-80UM2 · Т-80U-Е1 · T-80BVM · Object 292 |
| T-90 | Т-90А · T-90M |
| Trophies/Lend-Lease | |
| Germany | ▂T-III · ▂T-V |
| Great Britain | ▂МК-IX "Valentine" |
| USA | ▂M3 Medium · ▂M4A2 |
- Ground vehicles
- USSR ground vehicles
- Seventh rank ground vehicles
- Medium tanks
- Ground vehicles with explosive reactive armour
- Ground vehicles with composite armour
- Ground vehicles with smoke grenades
- Ground vehicles with engine smoke generating system
- Ground vehicles with dozer blade
- Ground vehicles with autoloader
- Ground vehicles with gun stabilizer