#history
The development of Japanese armoured vehicles began like many other industrial nations, inspired by the pioneering tanks of World War I. Domestic production started in the late 1920s, with Japan's tanks battle-tested during the Sino-Japanese conflict and the early Pacific campaigns of the 1930s. However, stagnation set in due to budget cuts and turmoil in tactics, leaving Japan's tank forces outdated by World War II. Development in the 1940s was largely defensive, and the tanks on the frontlines were from the 1930s, giving a false impression of Japan’s capabilities. After the war, Japan relied on U.S. equipment until regaining sovereignty, when development resumed. Since the 1950s, Japanese tanks have embraced NATO principles while incorporating unique innovations, focusing on advanced, defence-oriented designs to maintain a robust self-defence force.
During the Second World War, there is no doubt that Germany led the world in military designs and innovations. However, in the years after the war, a near legendary status has surrounded Germany’s tanks, with names such as the Panther, Tiger I and King Tiger (and, of course, the redoubtable Maus) all coming to mind as nearly indestructable fighting machines. But was this actually the case? Were Panzers as amazing as we have been led to believe, and how have they gained such a formidable reputation?
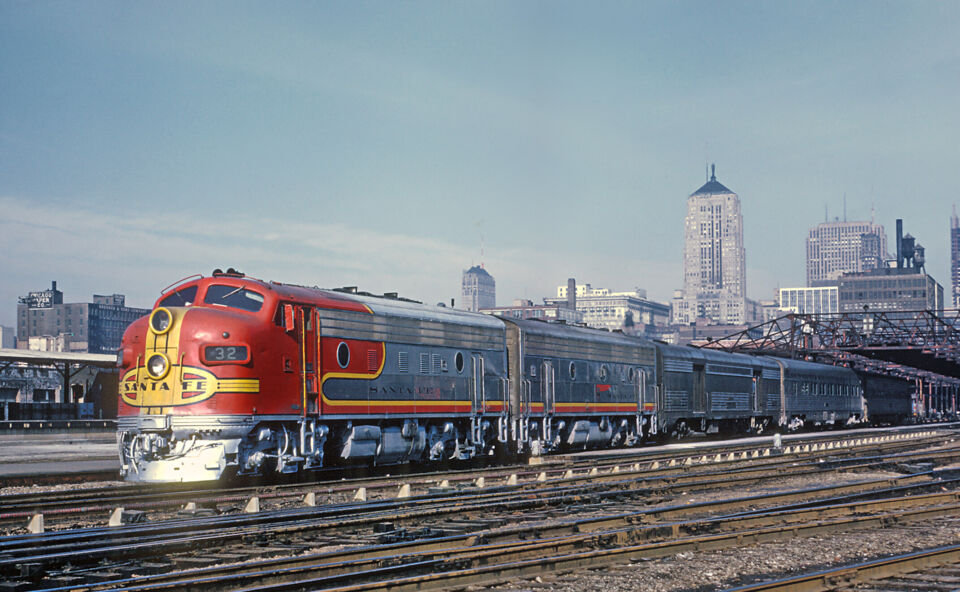
Today I’m going to tell you a little more about trains, but not the Br 52 this time. Today it’s about the EMD F series. The EMD F is an American diesel-electric locomotive from General Motors Electro-Motive Division. It was designed as a heavy freight locomotive, but it was also used for passenger trains. A total of 1,807 units were built between 1945 and 1949: 1,111 of type A and 696 of the cabless units of type B.
The Saab 39 Gripen, often called the JAS 39 Gripen, is a highly capable multirole fighter aircraft renowned for its exceptional maneuverability, advanced avionics, and cost-efficient operation. Since its first flight in 1988 and subsequent introduction into service in 1996, Gripen has become the cornerstone of the Swedish Air Force and has since been adopted by several other nations around the world.
Despite how common this element is, its purpose remains little known. This component is called the Leitkreuz, which translates from German as guide cross. It carries no symbolic weight and is purely a technical device, despite its resemblance to the Balkenkreuz. So, what does it actually do? Read on in the article.
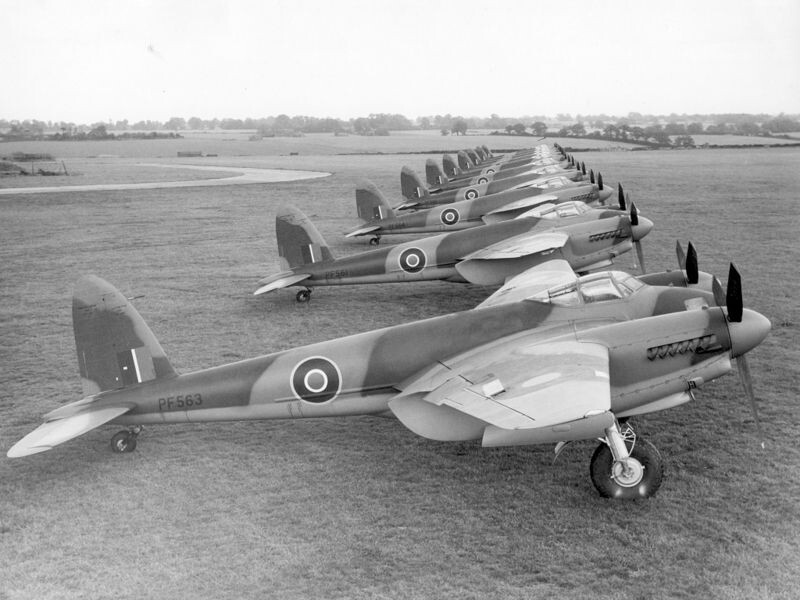
The story of the Mosquito begins with the founding of Geoffrey de Havilland’s aircraft company which bore his namesake, de Havilland. Around 1908, de Havilland designed his first aeronautical engine, which he then used to power his first aircraft — a small biplane. In 1920, when the aircraft company he worked for — Airco — shut down, he was able to create his own company, de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited, more commonly known as de Havilland.
Today I would like to talk about another vehicle, which is in the background of the game but still exists, namely the steam locomotive Br 52, a heavy German freight locomotive, of which more than 7,000 examples were built between 1942 and 1951 by Henschel & Sohn, Krauss Maffei, and Škoda, among others. They were widespread throughout Europe and in operation in more than 10 countries after the Second World War until today.