Difference between revisions of "SU-100 (China)"
(Updated format) |
CobraKingII (talk | contribs) (→History) |
||
| Line 181: | Line 181: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | ''Describe the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the vehicle and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Vehicle-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>. This section may also include the vehicle's dev blog entry (if applicable) and the in-game encyclopedia description (under <code><nowiki>=== In-game description ===</nowiki></code>, also if applicable).'' | + | <!-- ''Describe the history of the creation and combat usage of the vehicle in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the vehicle and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Vehicle-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>. This section may also include the vehicle's dev blog entry (if applicable) and the in-game encyclopedia description (under <code><nowiki>=== In-game description ===</nowiki></code>, also if applicable).'' --> |
| + | |||
| + | '''Development''' | ||
| − | |||
This tank destroyer takes its lineage from its predecessor [[SU-85]]. The SU-85's introduction with its 85 mm D-5 cannon made it a lethal weapon against German tanks, giving it much better firepower than the current T-34 with the 76.2 mm F-34 guns. However, the SU-85 became redundant when the T-34 began to upgrade into the [[T-34-85]], which contains the same 85 mm gun as the SU-85. No longer having the advantage in firepower, the SU-85 was discontinued, but the role of a self-propelled gun was still required to support the armoured forces. | This tank destroyer takes its lineage from its predecessor [[SU-85]]. The SU-85's introduction with its 85 mm D-5 cannon made it a lethal weapon against German tanks, giving it much better firepower than the current T-34 with the 76.2 mm F-34 guns. However, the SU-85 became redundant when the T-34 began to upgrade into the [[T-34-85]], which contains the same 85 mm gun as the SU-85. No longer having the advantage in firepower, the SU-85 was discontinued, but the role of a self-propelled gun was still required to support the armoured forces. | ||
| Line 190: | Line 191: | ||
While the vehicle is essentially a SU-85 reworked to mount the larger 100 mm cannon, the SU-100 body has some major improvements compared to its predecessor. Armour on the front is increased from the regular 45 mm to 75 mm, the commander's workplace was enlarged into a small sponson on the right side of the hull with a commander's cupola, which increased his combat effectiveness. Two new ventilator units were also installed for increased ventilation of the gun's propellant gases. Production started in September 1944 and continued until some time in 1947 with a total of 2,335 units produced. | While the vehicle is essentially a SU-85 reworked to mount the larger 100 mm cannon, the SU-100 body has some major improvements compared to its predecessor. Armour on the front is increased from the regular 45 mm to 75 mm, the commander's workplace was enlarged into a small sponson on the right side of the hull with a commander's cupola, which increased his combat effectiveness. Two new ventilator units were also installed for increased ventilation of the gun's propellant gases. Production started in September 1944 and continued until some time in 1947 with a total of 2,335 units produced. | ||
| − | + | '''Combat usage''' | |
| + | |||
In its introduction in the last few months of World War II, the SU-100 proved to be a very successful tank destroyer. The 100 mm D-10 gun could penetrate 125 mm of armour at 2,000 meters away, against the Panther, it could take it out from 1,500 meters away easily. Most of the SU-100 in service saw action in Hungary in March 1945, most notably in the German offensive Operation Frühlingserwachen (Spring Awakening). Although never intended for infantry support, the SU-100 even saw action in the Battle of Berlin in the close-quarters combat of urban warfare as its 100 mm gun was very good against heavy fortifications, but the lack of any machine guns has the vehicle work in cohesion with infantry or aircraft. | In its introduction in the last few months of World War II, the SU-100 proved to be a very successful tank destroyer. The 100 mm D-10 gun could penetrate 125 mm of armour at 2,000 meters away, against the Panther, it could take it out from 1,500 meters away easily. Most of the SU-100 in service saw action in Hungary in March 1945, most notably in the German offensive Operation Frühlingserwachen (Spring Awakening). Although never intended for infantry support, the SU-100 even saw action in the Battle of Berlin in the close-quarters combat of urban warfare as its 100 mm gun was very good against heavy fortifications, but the lack of any machine guns has the vehicle work in cohesion with infantry or aircraft. | ||
After World War II, the Red Army retained the SU-100 for a few more years until retiring them to reserves in 1947, still existing to this day. The SU-100 was given out to Warsaw Pact allies such as Egypt, Angola, Cuba, China, and Czechoslovakia. The SU-100 saw service in many Cold-War conflicts such as the Korean War in 1950, Vietnam War in 1955, Suez Crisis in 1956, the Six-Day War in 1967 and the Yom Kippur War in 1973. Some were modified to adapt to the sandy environment of the Middle East, these were designated the ''SU-100M''. These exported SU-100s continue to see service up to today in some countries, but most replaced it by 1970s. One of the most recent usages of the SU-100 is in Yemen during the Yemen Civil War of 2015. | After World War II, the Red Army retained the SU-100 for a few more years until retiring them to reserves in 1947, still existing to this day. The SU-100 was given out to Warsaw Pact allies such as Egypt, Angola, Cuba, China, and Czechoslovakia. The SU-100 saw service in many Cold-War conflicts such as the Korean War in 1950, Vietnam War in 1955, Suez Crisis in 1956, the Six-Day War in 1967 and the Yom Kippur War in 1973. Some were modified to adapt to the sandy environment of the Middle East, these were designated the ''SU-100M''. These exported SU-100s continue to see service up to today in some countries, but most replaced it by 1970s. One of the most recent usages of the SU-100 is in Yemen during the Yemen Civil War of 2015. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === PLA Service === | ||
| + | The People's Republic of China (PRC) acquired 99 SU-100 self-propelled guns and other armored vehicles from the Soviet Union in 1954, when the Soviet 39th Army withdrew from Lüda (now Dalian). Much of the armour, previously used by the Soviet 7th Mechanized Division, was used by the People's Liberation Army (PLA)'s 190th Division. The 190th Division was then renamed to the 1st Mechanized Division (第1机械化师), and among it's materiel were 24 of the SU-100 tank destroyers. | ||
== Media == | == Media == | ||
Revision as of 19:11, 1 February 2021
| This page is about the tank destroyer SU-100 (China). For the Soviet version, see SU-100. |
Contents
Description
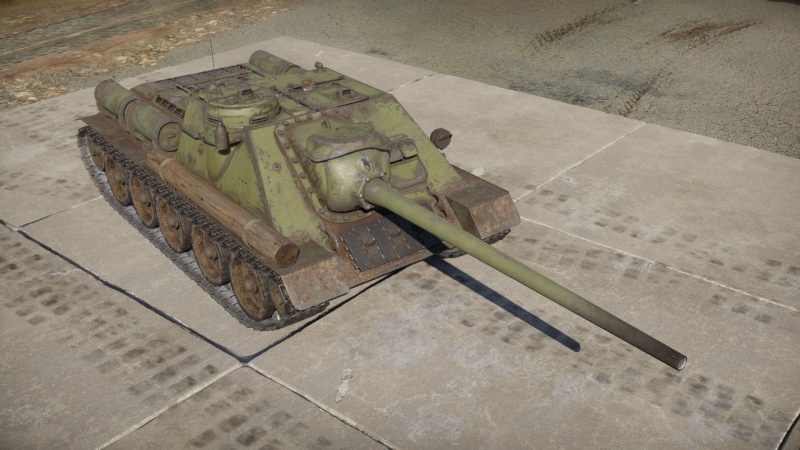
The ␗SU-100 is a rank IV Chinese tank destroyer with a battle rating of 6.0 (AB/RB/SB). It was introduced in Update 1.91 "Night Vision".
General info
Survivability and armour
- Rolled homogeneous armour (Casemate hull)
- Cast homogeneous armour (Gun mantlet, Driver's hatch)
| Armour | Front | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 75 mm (50°) Front glacis 45 mm (59°) Lower glacis 70 mm (50°) Driver's hatch 75 mm (3-55°) Gun mantlet |
45 mm (19°) Front 45 mm (41°) Rear 45 mm Bottom |
45 mm (48°) Top 45 mm (47-48°) Bottom |
20 mm |
| Armour | Sides | Roof | ||
| Cupola | 45 mm | 20 mm |
Notes:
- Suspension wheels and tracks are 20 mm thick.
- The commader's cupola extends out of the right side of the casemate, presenting a protrusion that could be penetrated from the front
- Driver's hatch maximum effective armour is 120 mm.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 55 | 9 | 31.6 | 710 | 992 | 22.47 | 31.39 |
| Realistic | 50 | 8 | 442 | 520 | 13.99 | 16.46 | |
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
| 100 mm D-10S | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 33 | -3°/+20° | ±8° | N/A | 6.2 | 8.5 | 10.4 | 11.5 | 12.2 | 13.7 | 12.1 | 11.2 | 10.5 |
| Realistic | 4.2 | 4.9 | 6.0 | 6.6 | 7.0 | ||||||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| BR-412 | APHE | 218 | 213 | 192 | 169 | 148 | 130 |
| BR-412B | APHEBC | 218 | 214 | 195 | 173 | 154 | 137 |
| BR-412D | APCBC | 239 | 236 | 223 | 207 | 192 | 178 |
| OF-412 | HE | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| Shell details | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile Mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive Mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
| BR-412 | APHE | 895 | 15.9 | 1.2 | 19 | 100.1 | 47° | 60° | 65° |
| BR-412B | APHEBC | 895 | 15.9 | 1.2 | 19 | 100.1 | 47° | 60° | 65° |
| BR-412D | APCBC | 887 | 15.9 | 1.2 | 19 | 93.94 | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| OF-412 | HE | 900 | 15.6 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1,460 | 79° | 80° | 81° |
| Smoke shell characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile Mass (kg) |
Screen radius (m) |
Screen deploy time (s) |
Screen hold time (s) |
Explosive Mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
| 3D3 | 880 | 15.6 | 20 | 5 | 25 | 272 |
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | 25 (+8) | 17 (+16) | 9 (+24) | 1 (+32) | No |
Usage in battles
The SU-100, as a Rank IV vehicle with a battle rating of 6.3, can be effortlessly defeated by a majority of the enemies faced at the BR bracket. As such, it is most important that the SU-100 makes the first, damaging shot before the enemy could get a shot first. The SU-100 is a classical casemate tank destroyer and as such has a fixed forward gun for its main armament, not too unlike the SU-85(M) tank destroyers. This gives the SU-100 a preference towards a defensive playstyle than an offensive one. As such, it is best to play the SU-100 in a supporting role, firing at distant enemies and ambushing them rather than facing them head-on. The SU-100 boasts high firepower and long effective range due to its 100 mm armament. The gun is able to penetrate armour similar to the 122 mm on the IS-2, but also a faster reload rate while retaining suitable post-penetration damage to devastating enemy tanks. As such, the SU-100 can lay in wait hidden in an open field and confidently attack enemies up to 1,000 meters away.
- Panther A,G,F: Though the Panther's 75 mm gun can penetrate the SU-100's front armour with little difficulty, the 100 mm gun can penetrate the Panther's front glacis plate at quite a distance (>500m). Thus, getting the first shot off will turn the battle situation towards the SU-100's advantage.
- Tiger (P) and (H): The front glacis of the Tiger II is impervious to the 100 mm, but the turret cheeks are still a major weak point that the gun can easily penetrate. At closer range, the lower glacis is also a weak point on the front area. If the Tiger II decides to traverse its turret slightly away from towards the SU-100, the 100 mm also has enough power to penetrate through the Tiger II turret side rather easily.
- IS-2 (1944): The IS-2 is easily disposable by a good firing on the front glacis, though the 1944 version requires careful aiming on the front glacis, thus it is better to aim at the lower glacis for an easier time at penetrating. The turret cheeks are also easy to penetrate like other heavy tanks.
- M4A3E2: when the Jumbo isn't angling, the SU-100 can penetrate its frontal hull and turret with ease. However when it's angling the hull, it is best to shoot the rather vertical turret for better chances of penetration. The explosives can knock out almost all its crew even when exploding inside the turret.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Powerful 100 mm gun to familiarize with before T-54 series of tanks
- Stock shells have high penetration and explosive filler
- Can easily penetrate and one-shot common heavily armored tanks like the Panther, Jagdpanther and M4A3E2. Can penetrate the Tiger IIs' turret frontally.
- Great top speed and manoeuvrability (56 km/h)
- Decent ammo count
Cons:
- Although the front armour is sloped, it's thin and easily penetrated by the long 88mm.
- Bad gun depression of 3 degrees
- Can be easily taken out in one shot due to the cramped internals
- Large profile and long cannon make the tank hard to conceal
History
Development
This tank destroyer takes its lineage from its predecessor SU-85. The SU-85's introduction with its 85 mm D-5 cannon made it a lethal weapon against German tanks, giving it much better firepower than the current T-34 with the 76.2 mm F-34 guns. However, the SU-85 became redundant when the T-34 began to upgrade into the T-34-85, which contains the same 85 mm gun as the SU-85. No longer having the advantage in firepower, the SU-85 was discontinued, but the role of a self-propelled gun was still required to support the armoured forces.
It was decided to up-gun the SU-85 model with a much bigger cannon. Lev I. Gorlitsky, the chief designer of Soviet medium self-propelled guns, began the development of improving the SU-85. It was decided that the new cannon will be of 100 mm in calibre, and work started on developing the prototype in February 1944. In March, the prototype named "Object 138" was made for testing, mainly by trying many different 100 mm guns to see which would prove most effective. It was decided that the 100 mm D-10 gun produced by Fyodor F. Petrov's design bureau, which was an adapted S-34 naval gun, was to be used as the main armament of the self-propelled gun, now named the SU-100.
While the vehicle is essentially a SU-85 reworked to mount the larger 100 mm cannon, the SU-100 body has some major improvements compared to its predecessor. Armour on the front is increased from the regular 45 mm to 75 mm, the commander's workplace was enlarged into a small sponson on the right side of the hull with a commander's cupola, which increased his combat effectiveness. Two new ventilator units were also installed for increased ventilation of the gun's propellant gases. Production started in September 1944 and continued until some time in 1947 with a total of 2,335 units produced.
Combat usage
In its introduction in the last few months of World War II, the SU-100 proved to be a very successful tank destroyer. The 100 mm D-10 gun could penetrate 125 mm of armour at 2,000 meters away, against the Panther, it could take it out from 1,500 meters away easily. Most of the SU-100 in service saw action in Hungary in March 1945, most notably in the German offensive Operation Frühlingserwachen (Spring Awakening). Although never intended for infantry support, the SU-100 even saw action in the Battle of Berlin in the close-quarters combat of urban warfare as its 100 mm gun was very good against heavy fortifications, but the lack of any machine guns has the vehicle work in cohesion with infantry or aircraft.
After World War II, the Red Army retained the SU-100 for a few more years until retiring them to reserves in 1947, still existing to this day. The SU-100 was given out to Warsaw Pact allies such as Egypt, Angola, Cuba, China, and Czechoslovakia. The SU-100 saw service in many Cold-War conflicts such as the Korean War in 1950, Vietnam War in 1955, Suez Crisis in 1956, the Six-Day War in 1967 and the Yom Kippur War in 1973. Some were modified to adapt to the sandy environment of the Middle East, these were designated the SU-100M. These exported SU-100s continue to see service up to today in some countries, but most replaced it by 1970s. One of the most recent usages of the SU-100 is in Yemen during the Yemen Civil War of 2015.
PLA Service
The People's Republic of China (PRC) acquired 99 SU-100 self-propelled guns and other armored vehicles from the Soviet Union in 1954, when the Soviet 39th Army withdrew from Lüda (now Dalian). Much of the armour, previously used by the Soviet 7th Mechanized Division, was used by the People's Liberation Army (PLA)'s 190th Division. The 190th Division was then renamed to the 1st Mechanized Division (第1机械化师), and among it's materiel were 24 of the SU-100 tank destroyers.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:
- topic on the official game forum;
- encyclopedia page on the tank;
- other literature.
| China tank destroyers | |
|---|---|
| PLA | |
| Gun vehicles | PLZ83 · PLZ83-130 · PTZ89 |
| Missile vehicles | AFT09 |
| ROC | |
| Missile vehicles | CM25 |
| USA | |
| Gun vehicles | ␗M8 HMC · LVT(A)(4) (ZiS-2) · ␗M10 GMC · ␗M36 GMC |
| Missile vehicles | ␗M113A1 (TOW) |
| USSR | |
| Gun vehicles | ␗SU-76M · ␗ISU-152 · ␗ISU-122 · ␗SU-100 |





