Difference between revisions of "Pvkv m/43 (1963)"
(→Usage in battles) (Tag: Visual edit) |
(→History: spelling/English translation issues) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 187: | Line 187: | ||
The Pvkv m/43 used the chassis of the Strv m/42, but with a casemate superstructure replacing the turret. The superstructure was located at the front of the vehicle, and the glacis was sloped. It had an open tarp to keep the weight down, and used a tarp to protect the crew from the elements. The Pvkv m/43 had a crew of 4, and was initially armed with a 75mm luftvärnskanonen m/36 antiaircraft gun, modified with a longer barrel for increased armour penetration. The gun could traverse 15 degrees to the left and right. It had a Ksp m/39 machine gun as the secondary armament. It was powered by a Volvo A8B engine producing 360 hp. The gearbox was different than the gearbox of the Strv m/42, and the drive wheels had to be reinforced to handle the increased weight of the vehicle. The Swedish military ordered 87 Pvkv m/43 in 1942, but deliveries were delayed and the last vehicle was delivered in 1948. | The Pvkv m/43 used the chassis of the Strv m/42, but with a casemate superstructure replacing the turret. The superstructure was located at the front of the vehicle, and the glacis was sloped. It had an open tarp to keep the weight down, and used a tarp to protect the crew from the elements. The Pvkv m/43 had a crew of 4, and was initially armed with a 75mm luftvärnskanonen m/36 antiaircraft gun, modified with a longer barrel for increased armour penetration. The gun could traverse 15 degrees to the left and right. It had a Ksp m/39 machine gun as the secondary armament. It was powered by a Volvo A8B engine producing 360 hp. The gearbox was different than the gearbox of the Strv m/42, and the drive wheels had to be reinforced to handle the increased weight of the vehicle. The Swedish military ordered 87 Pvkv m/43 in 1942, but deliveries were delayed and the last vehicle was delivered in 1948. | ||
| − | In 1954, the vehicle was given an armoured roof to better protect the crew. Other improvements included a muzzle | + | In 1954, the vehicle was given an armoured roof to better protect the crew. Other improvements included a muzzle brake, a gun travel lock, and a bore evacuator/fume extractor. The Strv m/41 was retired from service in 1957, which allowed the two Scania-Vabis L603 engines per vehicle to be used in the Pvkv m/43. The two L603 engines produced less horsepower (320 hp) than the Volvo A8B, but were much more reliable. In 1970, the Pvkv m/43 was retired from service, and the guns were used in static fortifications until 1995. |
== Media == | == Media == | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 12 April 2021
Contents
Description
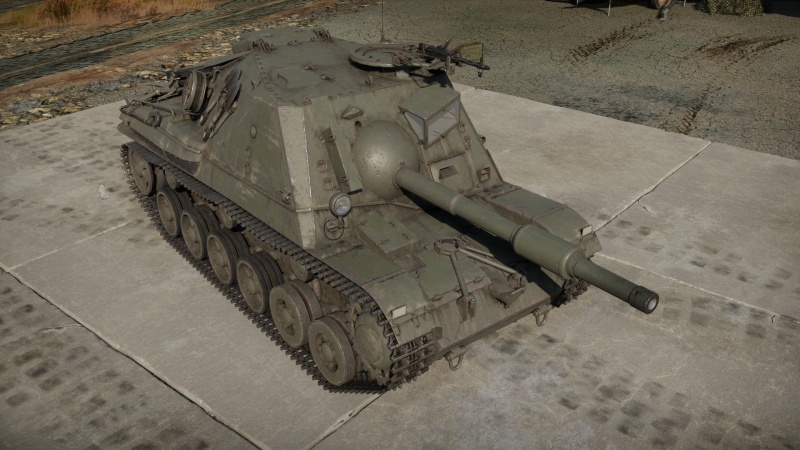
The Pansarvärnskanonvagn m/43 (1963) is a rank III Swedish tank destroyer with a battle rating of 4.7 (AB) and 5.0 (RB/SB). It was introduced in Update 1.97 "Viking Fury".
General info
Survivability and armour
Describe armour protection. Note the most well protected and key weak areas. Appreciate the layout of modules as well as the number and location of crew members. Is the level of armour protection sufficient, is the placement of modules helpful for survival in combat? If necessary use a visual template to indicate the most secure and weak zones of the armour.
Armour type:
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 70 mm RHA @ 30°
upper glacis 30 mm @ 80° lower glacis 70mm @ 32-69° |
30-25 mm Top 30 mm Bottom |
20 mm
25 mm on casemate |
9 mm |
| Turret | no turret 70 mm CHA mantlet |
no turret | no turret | no turret |
| Cupola | ___ mm | ___ mm | ___ mm | ___ mm |
Notes:
Mobility
Write about the mobility of the ground vehicle. Estimate the specific power and manoeuvrability, as well as the maximum speed forwards and backwards.
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 51 | 6 | 25 | 460 | 618 | 18.4 | 24.72 |
| Realistic | 47 | 6 | 287 | 324 | 11.48 | 12.96 | |
Modifications and economy
Armaments
Main armament
| 75 mm pvkan m/43 | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 43 | -15°/+20° | -13°/+20° | N/A | 7.0 | 9.8 | 11.8 | 13.1 | 13.9 | 8.71 | 7.70 | 7.10 | 6.70 |
| Realistic | 4.8 | 5.6 | 6.8 | 7.5 | 8.0 | ||||||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| slpgr m/43 | APCBC | 149 | 146 | 132 | 116 | 102 | 89 |
| sgr m/38 | HE | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 7,5 cm slpprj m/49 | APDS | 243 | 241 | 233 | 224 | 215 | 207 |
| Shell details | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile Mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive Mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
| slpgr m/43 | APCBC | 890 | 6 | 1.2 | 14 | 110 | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| sgr m/38 | HE | 840 | 6.43 | 0 | 0.1 | 690 | 79° | 80° | 81° |
| 7,5 cm slpprj m/49 | APDS | 1,110 | 3.7 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 75° | 78° | 80° |
Ammo racks
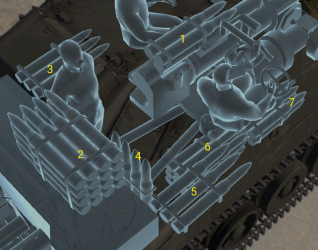
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
5th rack empty |
6th rack empty |
7th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | 42 (+1) | 26 (+17) | 23 (+20) | 19 (+24) | 16 (+27) | 7 (+36) | 1 (+42) | No |
Machine guns
| 8 mm ksp m/36 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Pintle | 2,000 (250) | 648 | -10°/+65° | ±180° |
Usage in battles
The Pvkv m/43 (1963) is a casemate TD, and as such, plays the role of sniper. With mediocre armour compared to its peers (will occasionally bounce a lucky front shot), it will depend on positioning or tank support in order to survive to deliver its shots. Move with tanks to your front, or find a long range sniping position in order to remain effective and support your team.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Starts with a stock APCBC found on the previous Pvkv m/43 (1946) and Strv m/42 DT
- Has access to a powerful APDS
- Great gun depression of -15°
- Relatively mobile
- Wide horizontal gun arc
Cons:
- APDS is a tier IV modification
- Outdated chassis - narrow tracks and light armour
- Casemated tank destroyer - dead engine = dead Pvkv
- Tall silhouette makes tank vulnerable at hull-down position
- Poor reverse
- Low survivability
- Thin roof armour - 20 mm shells can penetrate the top of the tank, knocking out the crew
History
During World War 2, the need for tank destroyers became evident, and Germany had great success with the StuG III and StuG IV. Because of the success of those platforms, Sweden decided to create a tank destroyer similar in concept to the StuG's. Landsverk created a design in 1942, based on the chassis of the Strv m/42. It was chosen by the Swedish military and was given the designation Pansarvärnskanonvagn m/43, or Pvkv m/43 for short.
The Pvkv m/43 used the chassis of the Strv m/42, but with a casemate superstructure replacing the turret. The superstructure was located at the front of the vehicle, and the glacis was sloped. It had an open tarp to keep the weight down, and used a tarp to protect the crew from the elements. The Pvkv m/43 had a crew of 4, and was initially armed with a 75mm luftvärnskanonen m/36 antiaircraft gun, modified with a longer barrel for increased armour penetration. The gun could traverse 15 degrees to the left and right. It had a Ksp m/39 machine gun as the secondary armament. It was powered by a Volvo A8B engine producing 360 hp. The gearbox was different than the gearbox of the Strv m/42, and the drive wheels had to be reinforced to handle the increased weight of the vehicle. The Swedish military ordered 87 Pvkv m/43 in 1942, but deliveries were delayed and the last vehicle was delivered in 1948.
In 1954, the vehicle was given an armoured roof to better protect the crew. Other improvements included a muzzle brake, a gun travel lock, and a bore evacuator/fume extractor. The Strv m/41 was retired from service in 1957, which allowed the two Scania-Vabis L603 engines per vehicle to be used in the Pvkv m/43. The two L603 engines produced less horsepower (320 hp) than the Volvo A8B, but were much more reliable. In 1970, the Pvkv m/43 was retired from service, and the guns were used in static fortifications until 1995.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
Bibliography
- Pansarvärnskanonvagn m/43. (2020, April 6). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Pansarv%C3%A4rnskanonvagn_m/43&oldid=949440407
| Sweden tank destroyers | |
|---|---|
| Strv m/41 derivatives | Spj fm/43-44 · Sav m/43 (1944) · Sav m/43 (1946) · Pvkv II · Pvkv III |
| Ikv 72/103 | Ikv 72 · Ikv 103 |
| Pvkv m/43 | Pvkv m/43 (1946) · Pvkv m/43 (1963) |
| ATGM | UDES 33 · Pbv 302 (BILL) · Pvrbv 551 |
| Other | SAV 20.12.48 · Bkan 1C |
| Norway | VIDAR |





