Difference between revisions of "F4U (Family)"
CobraKingII (talk | contribs) (→Service) (Tag: Visual edit) |
CobraKingII (talk | contribs) (→Service) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
Early in World War 2, the Royal Navy only had access to large, two seat planes with bad maneuverability. They quickly moved to replace them with newer designs, including naval variants of the Hawker Hurricane and the Supermarine Spitfire. These designs did not have the range necessary to operate from an aircraft carrier. The F4U Corsair was seen as an alternative. The Royal Navy received 95 F4U-1 Corsairs in November of 1943, and dubbed them Corsair Mk I. The squadrons were trained on the East Coast of the United States and then sent to Britain. The Royal Navy quickly learned of the Corsairs many flaws. There were multiple fatal crashes, as the Corsair was not yet optimized for carrier operations. | Early in World War 2, the Royal Navy only had access to large, two seat planes with bad maneuverability. They quickly moved to replace them with newer designs, including naval variants of the Hawker Hurricane and the Supermarine Spitfire. These designs did not have the range necessary to operate from an aircraft carrier. The F4U Corsair was seen as an alternative. The Royal Navy received 95 F4U-1 Corsairs in November of 1943, and dubbed them Corsair Mk I. The squadrons were trained on the East Coast of the United States and then sent to Britain. The Royal Navy quickly learned of the Corsairs many flaws. There were multiple fatal crashes, as the Corsair was not yet optimized for carrier operations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to clear the smaller bulkhead of their carriers, many Royal Navy Corsairs had their wings clipped by eight inches. The Royal Navy used a different landing approach than the US Navy. They would approach the carrier in a left-hand turn, in order to keep the deck in sight of the pilot. This approach was later adopted by the US Navy and Marine Corps, solving some of the problems of carrier landings. In addition, the Royal Navy was the first to add a number of modifications that further improved carrier landings. They raised the pilots seat by seven inches, gave the Corsair a new canopy with increased visibility, and permanently shut the cowl flaps on the engine. | ||
== US World War 2 Statistics == | == US World War 2 Statistics == | ||
Revision as of 03:06, 1 April 2020
Contents
Development
Origin
In 1938 the Navy wanted to find a design for a carrier-based fighter with more performance than the Brewster F2A and Grumman F4F. The design contract was given to Vought, based on their proposal, which featured a plane dependent on the Pratt and Whitney R-2800 engine. The design included an inverted gull wing shape. This was necessary because the engine required a large propeller, which needed a large ground clearance. This would require very long landing gear, except the inverted gull wing shape allowed shorter landing gear, while maintaining the necessary ground clearance. The prototype, named XF4U-1 was armed with 4 machine guns, two .50 caliber machine guns in the wings and 2 .30 caliber machine guns on the engine cowling. The XF4U-1 first flew on May 29, 1940, and became the first single engine plane to fly over 400 mph. Before Vought was allowed to produce the plane though, they had to increase its armament, as it was deemed insufficient based on data from Europe. Its armament was changed to six .50 machine guns, and it was ordered into production. A self-sealing fuel tank in the fuselage above the wings caused the cockpit to be moved aft as well. The Navy ordered 584 F4U-1's on April 2, 1941.
In-Game Aircraft
Rank II - Aircraft
- Corsair F Mk II (Great Britain) (British variant of F4U-1A)
- F4U-1A
- F4U-1A (USMC)
- F4U-1A (Japan) (Japanese captured American aircraft)
Rank III - Aircraft
Rank IV - Aircraft
Design
Powerplant
The F4U was powered by a Pratt and Whitney R-2800 engine. This was the most powerful and largest engine available when the F4U was being developed. An engine that powerful required a large propeller, 13 feet and 4 inches in diameter. The propeller was 3 bladed for all versions up until the F4U-4 when it got a 4 bladed propeller.
Wings and Landing Gear
Since the F4U was designed as a carrier-based fighter, the wings needed to be foldable, so the plane would take up less room on an aircraft carrier. In order to allow for the aircraft's wings to fold, the landing gear could not fold into the wings like many aircraft of the day, but would instead need to fold rearward. Unfortunately, due to the humongous 13-foot Hamilton Standard four-bladed propeller, the rearward folding landing gear would need itself to be extremely long in order to maintain propeller arc clearance, threatening the structural stability of the landing gear. To solve all of these problems, the aircraft's wing design was given inverted gull wings, which allowed the length of the landing gear to be reduced.
The F4U was very aerodynamic for its time. It utilized spot welding instead of rivets to decrease drag. It was also the first U.S. Navy aircraft to have landing gear that retracted into a fully enclosed wheel well, and the supercharger air intakes were located in the wings, instead of using scoops that protrude from the aircraft. The Corsair also used fabric to cover the parts of the wing aft of the main spar, the ailerons, rudder, and elevators. All of these factors significantly reduced drag, increasing the aerodynamics of the aircraft. Despite this, when using the flaps, the Corsair could still perform carrier landings, as the flaps could be angled at 60° to decrease speed while still maintaining enough lift to properly land.
Technical Issues
The F4U was not without its problems. Many of the issues it faced were related to its ability to be used on aircraft carriers such as having an aft placed cockpit and long "nose" at the front of the aircraft. This configuration reduced the pilot's visibility, which was important during carrier landings. In fact, the pilot could not see the Landing Signal Officer (LSO) for much of the landing approach. In addition, the hydraulically powered cowl flaps could potentially splatter hydraulic fluid onto the windscreen, limiting visibility even further. To prevent fluid splattering the solution was to affix the cowl flaps down permanently. The low visibility upon landing was later solved by the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy.
In addition to the visibility issues, there were other issues involved with landing on a carrier. During a carrier landing, the right-wing would unexpectedly stall and send the aircraft into a spin. When the throttle was quickly turned up the left-wing would drop very quickly, also causing a spin or causing the pilot to lose control. This issue was fixed by adding a stall strip to the right-wing just outboard of the main armament. This strip was added to the leading edge of the wing and allowed the right-wing to stall at the same point as the left-wing. The hydraulic landing gear would also tend to bounce upon landing. This was solved by adding a "bleeder valve" that released hydraulic pressure gradually, allowing the landing gear to absorb some of the contact with the runway and to prevent bouncing upon landing.
Performance Against Contemporary Designs
The F4U Corsair performed very well against its contemporary rivals. Compared to the Grumman F6F Hellcat, the F4U was significantly faster. Compared to the Republic P-47 Thunderbolt, the F4U was 13 mph slower, but reached its maximum speed at a lower altitude, giving the F4U an advantage at lower altitudes. All three of these planes used the Pratt and Whitney R-2800 engine.
Service
World War 2
United States
On July 31 1942, the Navy received its first F4U-1. The framed canopy, the long nose, and the angle of the nose made it very hard to taxi on a carrier deck, as forward visibility was low. Despite all of the problems with the design, it was found that the Corsair could land on a carrier during carrier qualification on USS Wolverine, USS Core, and USS Charger. Navy squadron VF-12 soon completed deck landing qualification, in April of 1943. By this point the F6F Hellcat had entered service, and it was preferred over the F4U because it was much easier to land on a carrier. In 1942, the Corsair was sent to the Marine Corps to be used as a land-based fighter, since it still had issues landing on carriers.
Marine Corps
Combat
In 1943, the Corsair started to be used by the Marine Corps, operating out of the Solomon Islands, notably, Guadalcanal. The first combat action was on 14 February 1943, when Corsairs of VMF-124 were escorting B-24 Liberator bombers, along with P-40 Warhawks and P-38 Lightnings. The Japanese launched an attack, and four P-38s, two P-40s, two F4Us, and two B-24s were lost. The Japanese lost four A6M Zeros, one of which was knocked out by an F4U, although it was because of an aerial collision, not combat.
On 26 March 1944, Corsairs recorded their first real kills. They shot down eight A6M Zeros while escorting B-25 bombers over Ponape. VMF-113 covered the landings at Ujelang, but quickly began striking targets in the Marshall Islands for the rest of 1944, since the landings were unopposed. One notable kill by a Corsair was when Marine Lieutenant R. R. Klingman of VMF-312 knocked out a Japanese aircraft by ramming its tail with his propeller, since his guns had jammed. He still managed to land safely, even though his propeller was missing five inches on the blades. At the Battle of Okinawa, a number of Corsair squadrons saw success, such as VMF-312, VMF-323, and VMF-224.
Modifications for Use as a Land-Based Fighter
965 F4U-1As were built as land-based fighters, since they had not yet been cleared for carrier operations. These models had the hydraulic mechanisms for folding the wings removed. In addition, many had their arrestor wire hooks removed in the field. The modifications simplified the design and reduced unnecessary weight.
Fighter-Bomber
The Corsair had the ability to be used as a fighter-bomber, which was utilized by the Marine Corps, starting in 1944. Charles Lindbergh, working with the Marines as a civilian adviser, flew Corsairs in attempts to increase their payload. In the process, he flew missions against Japanese positions in the Marshall Islands, and got a Corsair in the air with 4,000 lbs of bombs. By 1945, the Corsair was performing missions with bombs, rockets, napalm, tiny tim rockets, and even Bat glide bombs. It fought over Iwo Jima, Peleliu, and Okinawa.
In the Solomon Islands, VF-17 reinstalled the tail hooks on their Corsairs, so they could land on the carriers they would be providing air cover for during the raid on Rabaul. The Navy finally cleared the Corsair for carrier operations in April of 1944 when the oleo struts were improved to eliminate bouncing on landing. VMF-124 became the first Corsair squadron to be based on an aircraft carrier in December 1944, along with VMF-213. The amount of Corsair squadrons operating from carriers increased over the course of the war, as they were necessary to help protect against kamikaze attacks.
Carrier Optimization
Early in World War 2, the Royal Navy only had access to large, two seat planes with bad maneuverability. They quickly moved to replace them with newer designs, including naval variants of the Hawker Hurricane and the Supermarine Spitfire. These designs did not have the range necessary to operate from an aircraft carrier. The F4U Corsair was seen as an alternative. The Royal Navy received 95 F4U-1 Corsairs in November of 1943, and dubbed them Corsair Mk I. The squadrons were trained on the East Coast of the United States and then sent to Britain. The Royal Navy quickly learned of the Corsairs many flaws. There were multiple fatal crashes, as the Corsair was not yet optimized for carrier operations.
In order to clear the smaller bulkhead of their carriers, many Royal Navy Corsairs had their wings clipped by eight inches. The Royal Navy used a different landing approach than the US Navy. They would approach the carrier in a left-hand turn, in order to keep the deck in sight of the pilot. This approach was later adopted by the US Navy and Marine Corps, solving some of the problems of carrier landings. In addition, the Royal Navy was the first to add a number of modifications that further improved carrier landings. They raised the pilots seat by seven inches, gave the Corsair a new canopy with increased visibility, and permanently shut the cowl flaps on the engine.
US World War 2 Statistics
General
- Total Operational Sorties: 64,051
- Percentage of Total USMC and USN Sorties: 44%
- Sorties from Carrier Decks: 9,581 (15%)
- Air Victories (Kills): 2,140
- Total Air Combat Losses: 189
- Total Ratio of Victories to Losses: 11:1
- Ratio of Kills to Losses Against A6M Zeros: 12:1
- Ratio of Kills to Losses Against Ki-84's, N1K-J's and J2M's: 6:1
- Amount of Bombs Dropped: 15,621 Short Tons (14,171 Metric Tons)
- Percentage of Bombs Dropped by US Fighters: 70%
Losses
- By Aerial Combat: 189
- By Anti-Aircraft Fire: 349
- During Combat Missions: 230
- During Non-Combat Missions: 692
- While on the Ground or Aboard Ships: 164
Aces
Ira C. Kepford
A member of the famed VF-17 "Jolly Rogers" squadron, Kepford achieved a total of 16 confirmed kills in his F4U-1A.
Roger R. Hedrick
A member of VF-17, and later the Commanding Officer of VF-84, he got 12 confirmed kills in an F4U-1A and F4U-1D.
John T. Blackburn
He was the first Commanding Officer of VF-17, credited with 11 kills in his F4U-1A.
Thomas H. Reidy
A member of VBF-83, he was credited with 10 kills.
US Marine Corps
Gregory "Pappy" Boyington
The Marine Corp's top scoring ace, achieving 22 confirmed kills in an F4U-1A as part of VMF-214.
Kenneth A. Walsh
He had 21 confirmed kills in an F4U-1 and F4U-4, as part of VMF-124. He later was the Operations Officer of VMF-222.
James E. Swett
Serving in VMF-221 he was credited with 8.5 kills in an F4U, sharing one A6M "Zero" kill with another pilot. Before he flew the F4U he became an ace in a day by shooting down 7 planes in one action.
Archie Donahue
He is credited with 12 kills in an F4U while serving in VMF-112.
Notable Squadrons
US Marine Corps
VMF-124
The squadron was declared fully operational on 28 December 1942, even though its pilots only had an average of 25 hours in the Corsair. The first Marine Corsair ace was Kenneth A. Walsh, who had achieved 20 out of his 21 aerial victories as part of VMF-124. The Squadron first fought in the Solomon Islands, and later became the first Marine squadron to be based on an aircraft carrier, along with VMF-213. VMF-124 and VMF-213 became the first Marine squadrons to launch a ground attack off of an aircraft carrier on 3 January 1945, when they struck Formosa and the Ryukyu Islands.
VMF-214 "Blacksheep"
In 1943 the squadron was reinstated under the command of Major Gregory "Pappy" Boyington. They called themselves the Black Sheep. During their combat under Boyington's command, the squadron destroyed or damaged 203 enemy planes, with an official tally of 97 aerial victories. They also destroyed multiple enemy auxiliary ships and enemy installations. The squadron produced nine aces during the war.
VF-17 "Jolly Rogers"
VF-17 was the second US Navy squadron to receive F4U-1 Corsair fighters, in 1943. The Corsair had not been cleared for carrier operations by the time VF-17 was equipped with it, and as a result, the squadron operated off of the ground in the Solomon Islands. They amassed 152 aerial victories, and produced 11 aces. The commander of the squadron was Lieutenant Commander John T. Blackburn. Other notable members of the squadron include Ira C. Kepford and Roger R. Hedrick.
Variants
- XF4U-1
- The prototype for the F4U-1. It had a Pratt and Whitney R-2800 engine.
- F4U-1 (Corsair Mk I)
- The first production F4U. It had the “bird cage” canopy and low seating position. It had a more powerful Pratt and Whitney R-2800-8 engine.
- FG-1
- F4U-1 built by Goodyear for the Marine Corps. They had wings that could not be folded.
- F4U-1A (Corsair Mk II)
- This is not an official designation, but was used post-war to differentiate late production F4U-1s from early production F4U-1s. Mid-to-late production Corsairs saw the canopy changed to a clear-view canopy with only 2 frames in order to increase field of vision, and also a new windscreen that was easier to see through. This allowed the rear-view windows to be removed from the design. The pilot’s seat was also raised, to allow better view over the long nose. This was the first design to incorporate the stall strip on the leading edge of the right wing and the improved landing gear oleo-struts. These changes allowed the Corsair to be used in carrier landings. F4U-1As later incorporated a new R-2800-8W water injected engine, which was more powerful. F4U-1As in FAA service were known as Corsair Mk II, and had 8 in clipped off their wings, in order to fit on the Royal Navy aircraft carriers.
- FG-1A
- F4U-1As built by Goodyear for the Marine Corps. They had wings that could not be folded.
- F3A-1 (Corsair Mk III)
- F4U-1 license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy. Known as the Corsair Mk III in FAA service. None of these Corsairs saw frontline service because of their production defects.
- F4U-1B
- F4U-1s modified for Fleet Air Arm usage. This designation was given post-war.
- F4U-1D (Corsair Mk II)
- An F4U-1 with an R-2800-8W water injected engine, which gave 250 hp more power. It could carry double the rockets of the F4U-1A, and as such had to have bomb pylons and rocket tabs bolted onto the plane, causing drag. Despite this, it still had a considerable range, as the ability to mount an additional belly drop tank. It had the “blown” canopy, with only a single piece.
- FG-1D (Corsair Mk IV)
- F4U-1D built by Goodyear. It had the wingtips clipped for FAA service.
- F3A-1D (Corsair Mk III)
- F4U-1D license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy. This version, although different than the F3A-1, was still known as the Corsair Mk III in FAA service. It had the wingtips clipped for FAA service.
- F4U-1C
- These were F4U-1Ds but had four 20 mm AN/M2 cannons, instead of six .50 in machine guns. Machine guns were preferred for aerial combat, but the 20 mm cannons were proven in a ground attack role.
- F4U-1P
- An F4U-1 but with photo reconnaissance equipment.
- XF4U-2
- A night fighter variant, with two auxiliary fuel tanks.
- F4U-2
- F4U-1s but with the outboard right machine gun removed and replaced with an Airborne Intercept radar on the outboard starboard wing. It was intended to be a night fighter.
- XF4U-3
- Experimental variant used to test different engines in the Corsair airframe.
- FG-3
- Airframes made by Brewster that were used for the XF4U-3 project.
- XF4U-3B
- Slight modifications were added to the XF4U-3.
- XF4U-4
- This variant incorporated a new engine and cowling.
- F4U-4
- This variant incorporated the new, more powerful, R-2800-18W dual-stage-supercharged engine. The power could be boosted by injecting an alcohol/water concentration to the engine. An air scoop was added to the nose of the plane, and the fuel tanks in the wings were removed. This version had a 4-bladed propeller, instead of a 3-bladed propeller. The windscreen was also changed to flat, bulletproof glass, to reduce distortion.
- F4U-4B
- A version of the F4U-4 modified for FAA use, but was never given to the FAA. Instead, it was used in US service.
- F4U-4C
- F4U-4s with four 20 mm AN/M2 cannons instead of six .50 in machine guns.
- F4U-4E
- Night fighter variant of the F4U-4 with an APS-4 search radar on the starboard wing tip. Many had four 20 mm AN/M2 cannons instead of six .50 in machine guns, but it was not standard.
- F4U-4N
- Night fighter variant of the F4U-4 with an APS-6 search radar on the starboard wing tip. Many had four 20 mm AN/M2 cannons instead of six .50 in machine guns, but it was not standard.
- F4U-4K
- Drone variant of the F4U-4.
- F4U-4P
- Photo reconnaissance variant of the F4U-4.
- XF4U-5
- Had a new engine cowling, among other modifications.
- F4U-5
- A modification of the F4U-4. It incorporated a new R-2800-32(E) engine, a modernized cockpit, all-metal wings, a completely retractable tail wheel, and other modifications.
- F4U-5N
- F4U-5 with a radar.
- F4U-5NL
- Variant of the -5 and -5N modified for operations in a winter environment. It had de-icing boots on the leading edges of the tail and wings.
- F4U-5P
- A long range photo reconnaissance variant of the -5.
- F4U-6/AU-1
- The F4U-6 was a variant designed for ground attack missions for the Marine Corps. It had extra armor for the fuel tank and pilot, and relocated the oil coolers. It also featured a simplified supercharger, in order to optimise it for low altitude flying. It could carry up to 8,200 lbs of bombs, much more than other variants. This caused its top speed to be much lower than other variants. It was later redesignated as the AU-1.
- F4U-7
- An AU-1 modified for use with the French Navy.
- FG-1E
- An FG-1 with radar equipment. Produced by Goodyear.
- FG-1K
- A drone variant of the FG-1.
- FG-3
- An FG-1D with a turbo supercharged engine.
- FG-4
- F4U-4 produced by Goodyear. Never delivered.
- F2G-1
- Goodyear modified F4U-1 with a Pratt and Whitney R-4360, Wasp Major 4-row 28-cylinder radial engine. It had manual-folding wings and a 14 ft propeller. Never entered service.
- F2G-2
- F2G-1 with hydraulically folding wings, a tailhook for carrier landings, and a 13 ft propeller. Never entered service.
Specifications (F4U-4)
General
- Crew: One
- Length: 33 ft 8 in (10.26)
- Height: 14 ft 9 in (4.5 m)
- Wingspan: 41 ft 0 in (12.5 m)
- Wing Area: 314 sq ft (29.17 m2)
- Empty Weight: 9,205 lb (4,238 kg)
- Max. Takeoff Weight: 14,533 lb (6,592 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt and Whitney R-2800-18W radial engine, 2,380 hp (1,770 kw)
- Propeller(s):
- 3 or 4-bladed
- 13 ft 4 in (4.06 m) diameter
Performance
- Maximum Speed: 446 mph (718 km/h, 388 kn)
- Stall Speed: 89 mph (143 km/h, 77 kn)
- Range: 1,005 mi (1,617 km, 873 nmi)
- Combat Range: 328 mi (528 km, 285 nmi)
- Service Ceiling: 41,500 ft (12,600 m)
- Rate of Climb: 4,360 ft/min (22.1 m/s)
Armament
- Guns:
- 6 × .50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns, 400 rounds per gun or
- 4 × .79 in (20 mm) AN/M3 cannons, 231 rounds per gun
- Bombs: Up to 4,000 pounds (1,800 kg) and/or
- Rockets: 8 × 5 in (12.7 cm) high velocity aircraft rockets (HVAR)
Operators
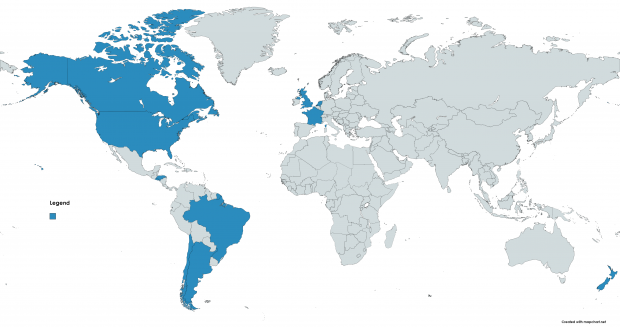
Argentina
Argentine Navy operated 26 F4U-5/5N/5NL Corsairs from 1956 to 1968.
Brazil
Brazilian Navy operated 30 F4U-1D from 1950 to 1976.
Canada
Royal Canadian Navy operated 130 F4U-1D from 1948 to 1960.
Chile
Chilean Navy operated 30 F4U-1D and 20 F4U-4 from 1953 to 1978.
El Salvador
Air Force of El Salvador operated 25 F4U/FG-1D from 1957 to 1976.
France
French Navy operated 69 AU-1 and 94 F4U-7 from 1954 to 1964.
Honduras
Honduran Air Force operated 19 from 1956 to 1979.
Netherlands
Royal Netherlands Navy operated 35 F4U-1D from 1943 to 1956.
New Zealand
Royal New Zealand Air Force operated 368 F4U-1 and 60 FG-1D from 1944 to 1949.
United Kingdom
Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm operated 2,012 Corsairs of all types during World War 2, including 95 Corsair I (F4U-1), 510 Corsair II (F4U-1A), 430 Corsair III (F3A-1D), and 977 Corsair IV (FG-1D).
United States
United States Navy and Marine Corps operated Corsairs of all production variants from 1942 to 1953.