Difference between revisions of "SA18 L/21 (37 mm)"
m (Edits.) |
m (→Historical part) |
||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
<!--''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of this weapon. If the historical reference turns out to be a big one, take it into a separate article and add a link to it by using the "main" template. In the end, be sure to include references to sources.''--> | <!--''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of this weapon. If the historical reference turns out to be a big one, take it into a separate article and add a link to it by using the "main" template. In the end, be sure to include references to sources.''--> | ||
| − | The 37 mm Puteaux SA18 cannon started life as a development of the ''Canon de 37 mm à tir rapide Modèle 1916'' (SA16), a small but powerful, portable infantry support gun designed by Eugène François Gilbert Garnier (1874-1964) on the instigation of the generals | + | The 37 mm Puteaux SA18 cannon started life as a development of the ''Canon de 37 mm à tir rapide Modèle 1916'' (SA16), a small but powerful, portable infantry support gun designed by Eugène François Gilbert Garnier (1874-1964) on the instigation of the generals Jean Estienne and Ferdinand Foch. The original purpose of the SA16 was a light gun capable of demolishing pillboxes and gunner nests, with a high rate of fire. Due to its intended use, its range was not considered a priority as part of the gun's design: the result was a relatively small and light weapon, with very high accuracy. When operated by an experienced crew, the gun could fire up to 15 shots per minute, although it had a practical firing rate of 10 shots per minute under normal circumstances. Despite its relatively small size, the original infantry gun would be operated by a crew of 8, consisting of commander, aimer, gunner, four ammunition handlers and one armourer. |
With the advent of the first tanks, a variant of the SA16 was developed which could be operated by a single crew member. This gun, the SA189, was technically similar to the SA16 and capable of firing the same ammunition. Crucially though, the gun was never intended as an anti-tank weapon: its primary goal remained that of infantry support gun tasked with destroying enemy machine gun emplacements, the only thing conceptually changing was the addition of a self-propelling function (''i.e. the Renault FT-17 tank built around it, allowing it to autonomously move on the battlefield rather than being fired from a static position''). | With the advent of the first tanks, a variant of the SA16 was developed which could be operated by a single crew member. This gun, the SA189, was technically similar to the SA16 and capable of firing the same ammunition. Crucially though, the gun was never intended as an anti-tank weapon: its primary goal remained that of infantry support gun tasked with destroying enemy machine gun emplacements, the only thing conceptually changing was the addition of a self-propelling function (''i.e. the Renault FT-17 tank built around it, allowing it to autonomously move on the battlefield rather than being fired from a static position''). | ||
Revision as of 22:42, 5 November 2019
Contents
Description
Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Make an air or ground vehicles list on which this weapon is installed in our game.
The SA18 L/21 was a World War I-vintage gun, originally intended to destroy pillboxes and machine gun nests. Adapted from the SA16 infantry support gun, it first appeared as the main armament of the revolutionary Renault FT series. Unfortunately, by the outbreak of World War II its penetration power had fallen well behind armour development.
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
General info
Available shells
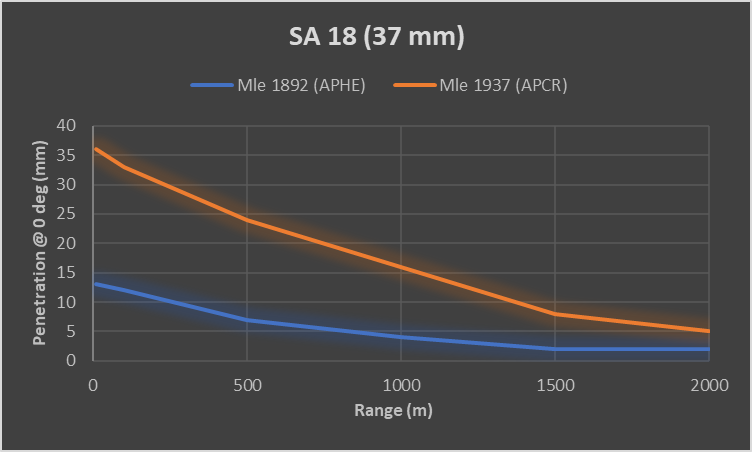
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of
warhead |
Penetration in mm @ 0° Angle of Attack | |||||
| 10m | 100m | 500m | 1000m | 1500m | 2000m | ||
| Mle1937 | APCR | 36 | 33 | 24 | 16 | 8 | 5 |
| Mle1892 | APHE | 13 | 12 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of
warhead |
Velocity
in m/s |
Projectile
Mass in kg |
Fuse delay
in m: |
Fuse sensitivity
in mm: |
Explosive Mass in g
(TNT equivalent): |
Normalization At 30°
from horizontal: |
Ricochet: | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||
| Mle1937 | APCR | 600 | 0.5 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ° | 66° | 70° | 72° |
| Mle1892 | APHE | 388 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 6.0 | 15 | ° | 47° | 60° | 65° |
Comparison with analogues
Give a comparative description of cannons/machine guns, that have firepower equal to these type of weapons.
Usage in the battles
The SA18 L/21 is, unfortunately, a gun in the wrong world war. Originally intended as a short-range support gun for easy transportation, it was designed as a basic, short-barrelled gun. While this meant it excelled in the role that it was intended for on the battlefields of the First World War, it also meant it quickly became obsolete in view of tank development on the eve of the Second World War. When used in combat against early World War II armour, it is only effective at very short range. If confronted with anything further than 100 yards with more than 30 mm or armour - hold fire if you don't want to attract the enemy's attention.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Very high firing rate
- Relatively accurate gun
Cons:
- Lack of penetration power (and that is an understatement)
- Light APCR round, doesn't do much damage upon penetration
- Low muzzle velocity, shell drops off very quickly, severely limiting its effective range
Historical part
The 37 mm Puteaux SA18 cannon started life as a development of the Canon de 37 mm à tir rapide Modèle 1916 (SA16), a small but powerful, portable infantry support gun designed by Eugène François Gilbert Garnier (1874-1964) on the instigation of the generals Jean Estienne and Ferdinand Foch. The original purpose of the SA16 was a light gun capable of demolishing pillboxes and gunner nests, with a high rate of fire. Due to its intended use, its range was not considered a priority as part of the gun's design: the result was a relatively small and light weapon, with very high accuracy. When operated by an experienced crew, the gun could fire up to 15 shots per minute, although it had a practical firing rate of 10 shots per minute under normal circumstances. Despite its relatively small size, the original infantry gun would be operated by a crew of 8, consisting of commander, aimer, gunner, four ammunition handlers and one armourer.
With the advent of the first tanks, a variant of the SA16 was developed which could be operated by a single crew member. This gun, the SA189, was technically similar to the SA16 and capable of firing the same ammunition. Crucially though, the gun was never intended as an anti-tank weapon: its primary goal remained that of infantry support gun tasked with destroying enemy machine gun emplacements, the only thing conceptually changing was the addition of a self-propelling function (i.e. the Renault FT-17 tank built around it, allowing it to autonomously move on the battlefield rather than being fired from a static position).
The end of the First World War more or less brought tank development to a halt in Europe. In the absence of any concrete threat and with French tank doctrine firmly based on experience during the First World War, the SA18 was seen as sufficient for the task of providing supporting fire for infantry against enemy troops and fixed gun emplacements. Added to this, the reconstruction of France after the destruction of the First World War and the worldwide economic crisis which erupted at the end of the 1920s, combined with a general anti-war sentiment reigning in politics meant there were little in the way of funds available for the development and replacement of the SA18. Even with a new generation of tanks which were developed at the beginning of the 1930s, these were armed by simply removing the SA18s from the Renault FTs they were supposed to replace and then installing them on the new tanks. As a result, this new generation of tanks, the Hotchkiss H.35, Forges & Chantiers de la Méditerrannée FCM.36 and the Renault R.35 entered production with the outdated gun, even though attempts were made to improve its capabilities by the development of new types of shells. The Obus de rupture Modèle 1935 APCR round offered a higher muzzle velocity than previous ammunition used on the gun, but as it was relatively light it could only do little damage even when if it by chance happened to penetrate.
By this time, the SA18 was seen as an interim solution: the FCM.36, for instance, had been designed with the SA38 in mind, and it received the SA18 with the intention of having it replaced at later date with the SA38. However, owing to a weak turret ring and other structural problems, this refit never came to be, and the FCM.36 entered battle in May of 1940 with a gun that was virtually incapable of penetrating any of the enemy armour it would oppose.
Despite being completely obsolete by the outbreak of World War II, the SA18 and its infantry counterpart, the SA16, were still widely in service and saw combat with several armies, such as France, Belgium, Poland, Yugoslavia and Finland.
Media
An excellent addition to the article would be a video guide, as well as screenshots from the game and photos.
Read also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example,
- reference to the article about the variant of the cannon/machine gun;
- references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.
ETC.
Sources
Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:
- topic on the official game forum
- page on the Wikipedia
- page on aircraft or gorund forces encyclopedia
- other literature
| France tank cannons | |
|---|---|
| 20 mm | 20F2 |
| 25 mm | SA35 L/72 |
| 37 mm | SA18 L/21 · SA38 L/33 |
| 47 mm | SA34 L/30 · SA35 L/32 · SA37 |
| 75 mm | APX · APX Canon de 75 mm modèle 1897 · SA35 L/17 · SA44 · SA49 · SA50 L/57 |
| 90 mm | D.911 APX · CN90 F2 · CN90 F3 · CN90 F4 · D915 · DEFA F1 · SA45 · SA47 |
| 100 mm | SA47 L/58 |
| 105 mm | CN-105-F1 · Giat 105 G2 · Modele F2 · PzK M57 |
| 120 mm | GIAT CN120-25 G1 · GIAT CN120-26 F1 · SA46 |
| 142 mm | ACRA |
| 155 mm | GCT F1 · Schneider 155 C · L'Obusier de 155 Modèle 1950 |
| Foreign: | |
| 15 mm | MG 151 (Germany) |
| 20 mm | MG 151 (Germany) |
| 30 mm | Bushmaster 2 Mk.44 (USA) |
| 37 mm | M6 (USA) |
| 40 mm | Bofors L/60 · QF 2-pounder (Britain) |
| 75 mm | KwK42 (Germany) · M3 (USA) · M6 (USA) |
| 76 mm | M7 (USA) |
| 90 mm | M3 (USA) |
| 105 mm | M4 (USA) |