Difference between revisions of "ZSU-57-2"
(Added In-game description.) |
SonOVickers (talk | contribs) m (→Survivability and armour) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 216: | Line 216: | ||
* 57 mm guns will destroy or cripple aircraft with one hit, and can heavily damage tanks if rounds penetrate | * 57 mm guns will destroy or cripple aircraft with one hit, and can heavily damage tanks if rounds penetrate | ||
* Very High Penetration for SPAA (approximately 122mm using default ammunition) | * Very High Penetration for SPAA (approximately 122mm using default ammunition) | ||
| − | * | + | * Very Effective against lightly armored German vehicles and other vehicles in general |
'''Cons:''' | '''Cons:''' | ||
| − | * Large vehicle size | + | * Large vehicle size and hull breakable to 105+ HEAT Munitions |
* Very vulnerable turret (ammo on all sides of turret+very thin armour) | * Very vulnerable turret (ammo on all sides of turret+very thin armour) | ||
* Crew is very crowded in the turret (1 shot has the potential to knock out 5 crew members with ease) | * Crew is very crowded in the turret (1 shot has the potential to knock out 5 crew members with ease) | ||
Revision as of 11:25, 16 January 2020
Contents
Description
The ZSU-57-2 is a Rank V Soviet self-propelled anti-aircraft vehicle
with a battle rating of 7.0 (AB/RB/SB). It was introduced in Update 1.43. Two 57 mm cannon placed in an anti-aircraft format on a T-54 chassis, the ZSU-57-2 has proven to be more of a menace to ground vehicles than aircraft with its high-velocity cannons, but the low sustained rate of fire.
General info
Survivability and armour
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour
| Armour | Front | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 13.5 mm (61°) Front glacis 15 mm (53°) Lower glacis |
15 mm | 10 mm (17-49°) Top 6 mm (73°) Bottom |
15 mm |
| Turret | 15 mm (14-57°) Turret front 15 mm (25-64°) Gun mantlet |
13.5 mm (9-61°) | 13.5 mm (4-59°) | N/A |
Notes:
- Suspension wheels and tracks are 20 mm thick.
- Belly armour is 13.5 mm thick.
- A 6 mm RHA plate separates the engine compartment from the crew.
- Hatches and air intake are 6 mm thick.
Mobility
| Mobility characteristic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Weight (tons) | Add-on Armor weight (tons) |
Max speed (km/h) |
| 28.0 | N/A | 54 (AB) |
| 50 (RB/SB) | ||
| Engine power (horsepower) | ||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded |
| Arcade | 739 | 821 |
| Realistic/Simulator | 460 | 520 |
| Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | ||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded |
| Arcade | 26.39 | 29.32 |
| Realistic/Simulator | 16.43 | 18.57 |
Armaments
| 57 mm S-68 (x2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity (Belt capacity each) | Fire rate (shots/minute) |
Vertical guidance |
Horizontal guidance |
Stabilizer | |
| 248 (4) | 120 | -5°/+85° | ±180° | N/A | |
| Turret rotation speed (°/s) | |||||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. |
| Arcade | 35.70 | 49.40 | 60.00 | 66.30 | 70.60 |
| Realistic | 35.70 | 42.00 | 51.00 | 56.40 | 60.00 |
| Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||
| Stock | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. | ||
| 2.6 | _._ | _._ | _._ | ||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration in mm @ 90° | ||||||
| 10m | 100m | 500m | 1000m | 1500m | 2000m | |||
| BR-281 | APHE | 121 | 119 | 106 | 91 | 78 | 68 | |
| BR-281U | AP-T | 142 | 140 | 116 | 91 | 72 | 56 | |
| OR-281U | HEFI-T | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Shell details | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity in m/s |
Projectile Mass in kg |
Fuse delay
in m: |
Fuse sensitivity
in mm: |
Explosive Mass in g (TNT equivalent): |
Normalization At 30° from horizontal: |
Ricochet: | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||
| BR-281 | APHE | 1000 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 15 | 22.1 | -1° | 47° | 60° | 65° |
| BR-281U | AP-T | 1000 | 2.8 | N/A | N/A | N/A | -1° | 47° | 60° | 65° |
| OR-281U | HEFI-T | 1000 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 153 | +0° | 79° | 80° | 81° |
Belt types
| Belts | Shell composition | Tips and usage |
| Default | APHE – HEFI-T | 50% of this belt are useless against tanks or planes. However, against other SPAA this belt can reliably take out crew, armament, ammo and engine. Having one belt in reserve does not hurt. |
| BR-281 | APHE | Intermediate usage until the better BR-281U rounds can be used. Decent enough versus light to medium tanks from the sides and rear. |
| BR-281U | AP-T – HEFI-T | Best penetrating rounds for the vehicle. At this Rank, the round is useful against moderately armoured tanks even from the front. |
| OR-281U | HEFI-T | Versus planes. One or two hits usually gets the job done. Heavy armoured attackers and bombers may require more thought. |
Ammo racks
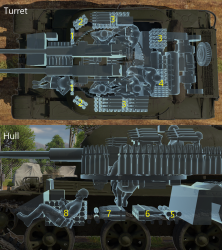
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
5th rack empty |
6th rack empty |
7th rack empty |
8th rack empty |
9th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62 | 56 (+6) | 50 (+12) | 42 (+20) | 36 (+26) | 28 (+34) | 22 (+40) | 14 (+48) | 8 (+54) | 1 (+61) | yes |
Usage in the battles
Versatile in the anti-aircraft and anti-tank role this heavily modified T-54 chassis delivers two heavy 57mm punches. The ZSU-57-2 can be used for two roles.
AAA
As an SPAA this should be the first course of action. Find a safe location from enemy ground vehicles, lay in wait and open fire on any enemies when they are in range. The powerful 57 mm cannons will tear apart any aircraft from the sky in 1-5 direct hits. The big downside is that the gunner crew are exposed to strafing aircraft and can easily be taken out by aircraft machine gun/cannon fire, so it is important to first prioritize aircraft which appear to be gunning for the ZSU-57-2.
Tank Destroyer
Using the 57 mm cannons on a ground attack role is possible and have been exploited by many players. Using BR-281U ammo, the guns can effectively pierce the side and rear of any tank (excluding the Maus). Remember the ZSU-57-2's armour does not compare to other tanks armour so one shot could be the end of the SPAA. Play cat-and-mouse and wait for the enemy to go into an engagement with another target and then jump out into the open and fire upon them while they are distracted. It is recommended to the first aim for their rear to disable their engine and cause a fire, they will have to stop what they are doing and put it out. During this time they won't be able to move or fire upon the ZSU-57-2, allowing a chance to finish off the crewmen inside by unloading the 57 mm cannons into the side of the enemy tank.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Effective Multi-role Weaponry (able to fight tanks)
- Excellent turret rotation speed
- 57 mm guns will destroy or cripple aircraft with one hit, and can heavily damage tanks if rounds penetrate
- Very High Penetration for SPAA (approximately 122mm using default ammunition)
- Very Effective against lightly armored German vehicles and other vehicles in general
Cons:
- Large vehicle size and hull breakable to 105+ HEAT Munitions
- Very vulnerable turret (ammo on all sides of turret+very thin armour)
- Crew is very crowded in the turret (1 shot has the potential to knock out 5 crew members with ease)
- Reverse is only decent
- Shells have bad accuracy in consecutive shots when "Adjustment of fire" modification is not researched
History
Development
The course of World War II revealed to the Soviets how dangerous the air power has become to their ground forces. It was determined that the best method of fighting these aircraft was to have ready vehicles in the front-lines with dedicated anti-aircraft roles to take out these assault aircraft. Experiences from other countries, such as the United States with their M3 half-tracks equipped with anti-aircraft armament and Germany with their Wirbelwind and Ostwind anti-aircraft vehicles showed that the role of the self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) makes a positive effect on the battlefield for the protection of the ground forces. The Soviet development of SPAAGs came as simple, truck-mounted weapons and armoured variants of SPAAG were scarce to begin. The first put into production was the ZSU-37, which did not see the majority of World War II as it was put into production on February 1945, with production lasted only until 1948 and retired not long after that. The single 37 mm gun on the ZSU-37 was also reported on no longer being efficient against aircraft, so a major development project was initiated for a new SPAAG in Soviet service.
Few projects were started on the SPAAG concept following right after World War II. One was just a BTR-152 armoured personnel carrier armed with two or four 14.5 mm KPV heavy machine guns. About two different vehicle development was made for the SPAAG role, designated the ZTPU-2 and ZTPU-4. Development, while slow at first, took up a large focus after the realization that the Soviet Union's enemy, the United States, posses a large air force power that could take the air supremacy of the battlefield anywhere. This causes the Soviets to begin investing in a SPAAG in order to fight against this. The first of such was in February 1946 where the design bureau at Works No. 174 at Omsk along with Research Institute No. 58 at Kaliningrad submitted their joint design of a SPAAG based off the T-34 chassis. The design had four 37 mm AA guns attached, but the design did not proceed as new tank production at the time had the High Command prioritize on the new tank chassis that was going to be produced.
Research Institute No. 58 during this time developed a twin 57 mm anti-aircraft gun under the guidance of Vasiliy G. Grabin. The 57 mm gun was based off the previous 57 mm S-60 gun from 1947 and the new one was called the S-68, which was ready by 1948. This armament is then chosen to be mounted onto the new SPAAG project currently known as Object 500, but the designation for such vehicle would be called ZSU-57-2 ("57" for the armament calibre and "2" for the twin armament). The project design finished in 1948 with the S-68 gun mounted onto the new T-54 tank chassis. The first prototype was completed in June 1950 and testings for the vehicle lasted from 27 January 1951 to 15 March 1951, which had the vehicle drive 1,500 km and fire 2,000 rounds. More prototypes were built for testings and had improvements built into their design such as more ammunition storage. Service update tests started in 1954 after much delays in deliveries of the S-68 guns and parts for it, but the ZSU-57-2 was finally put into service on 14 February 1955. First vehicles were completed by 1957 and a total of 2,023 ZSU-57-2s were completed by the time production ended at the end of the 1950s.
Design
The ZSU-57-2 used a modified T-54 chassis for its basis, the T-54 chassis uses four road wheels per side rather than five and uses thinner armour. However, the interior is nearly the same as the T-54, with more space due to the thinned armour. There are three crew compartments in the tank, the driver in the front, the fighting in the middle, and the engine in the back. The driver's position has been moved slightly forward and to the left and has accommodations for an infrared vision device. The vehicle has a maximum road speed of 50 km/h and is considerably much faster than the T-54 due to the lighter weight while still powered by the same V-54 4-stroke diesel V12 engine.
The fighting compartment uses an open-topped turret that mounted the dual 57 mm S-68 gun. The gun is aimed via a sighting system that is adjusted based on the target's speed, direction, and range by the sight adjuster crew member. While the speed and direction must be estimated, the range can be found via a rangefinder or estimated. Two loaders are needed to load the two gun and a gunner fires using a trigger that fires both barrels or one of the two-foot pedals that fire either barrel independently. The gun is able to reach a firing rate of 240 rounds per minute with, but the practical rate of fire is about 140 rpm to maximize the barrel cooling rate and firing sustainability. Shells available for the gun are fragmentation and armour-piercing tracer, the fragmentation comes with a safety-destructor that causes the shell to explode after a certain amount of time so the rounds do not come back to the surface and do harm. The 57 mm shells were considered to be the most powerful anti-aircraft armament at the time and can very quickly destroy an aircraft if a shell connects.
A huge disadvantage of the ZSU-57-2 was the lack of fire-control radar, so it must rely on optical vision in order to find and eliminate targets. A ZSU-57-2 battery of four vehicles was less effective than a battery of six towed 57 mm S-60 anti-aircraft guns due to the latter having a fire control radar. The reliance on radar has been due to the increased proficiency of jets, which makes an estimation of distance and speed a very difficult process. Other disadvantages were its low firing rate due to the manual loading by loaders per gun, the air-cooled barrels heated up too quickly, and the turret traverse could not keep up with the newer and faster jet aeroplanes as well.
Combat usage
Entering service in 1955, the ZSU-57-2 replaced the older BTR-40As and BTR-152As in 1957 and was revealed to the public in November 1958 during a military parade. The ZSU-57-2 was issued out to tank regiments in one battery, which contained four ZSU-57-2s. This was later changed to two batteries per regiment, increasing the number of SPAAGs available. Some ZSU-57-2s saw service in motor rifle regiments as well as one battery. Despite its superior armament, the ZSU-57-2's performance among the newer aircraft technology along with jets causes the ZSU-57-2 to be considered unsatisfactory and obsolete by early 1960s but stayed until early 1970s as it was replaced by the ZSU-23-4 Shikas, which has radar-guided abilities. The remaining ZSU-57-2s were put into reserves, storage, repurposed into other roles, or scrapped.
Like much of the Soviet hardware, the ZSU-57-2 was also given out to the Soviet allies in the Warsaw Pact. Countries that bought the ZSU-57-2 range from Poland, East Germany, Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Cuba, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Syria, North Korea, and North Vietnam. These countries used the ZSU-57-2 to a greater extent than the Soviets did. East Germany was the first foreign operator to own the ZSU-57-2, who received 129 vehicles. Poland also received 129 units as well. Yugoslavia ordered 100 units, Slovenia owned a few for the 44th Armoured-mechanized battalion, Finland imported 12 unit, and Cuba received 25 units during the missile crisis in 1962. Iraq, Iran, and Egypt ordered 100 units for deliveries, their use in conflicts would also end with the Israelis owning a few as well. North Korea developed its own units by using the Chinese Type 59 (copy of the Soviet T-54) tank chassis and bought the turrets to mount on them, about 250 were made like this. China attempted to make a copy of the ZSU-57-2 for Iraq by their request, which became the Type 80 SPAAG, though China is more well known for modernizing the S-68 ammunition.
The ZSU-57-2 saw use in many Cold-War conflicts in the hands of foreign operators. It saw action in the Vietnam War by the North Vietnamese and was used as air-defence for tank regiments and against ground targets. The ZSU-57-2 also saw conflicts in the Middle East such as in the Six Day War and Yom Kippur War against Israel by Syria and Egypt. These were used to defend the El-Arish airstrip, but they were not very successful and many were captured by the Israelis. Syria also used the vehicle again in the Lebanon War of 1982 against Israel, where they failed against the Israeli air force, but fair much better against ground targets. Iraq and Iran used the ZSU-57-2 against each other in the Iran-Iraq War, though Iraqi forces had access to Chinese copies and the benefit of radio information for their vehicles. Iraqi ZSU-57-2s also saw use in the Gulf War against the United States coalition where it manages to successfully shoot down a Tornado GR1 aircraft by the British, three more were reported to be heavily damaged as well. The Iraqi still used them up until the Second Gulf War. The ZSU-57-2s were used by many factions in the Yugoslav Wars and had air defence roles against the NATO air raids. The most recent usage of the ZSU-57-2 is in the Syrian Civil War, where 10 are still active in the Syrian Army, these are probably used exclusively against ground targets today.
In-game description
In 1947 at NII-58 research institute plans were made under the direction of B.G. Grabin to pair a 57mm automatic cannon with a C-68 anti-air cannon on the basis of the C-60. It was intended to be installed on either a track-based chassis or a body with wheels. The track-based chassis was based on aggregates of the T-54 medium tank. The self-propelled version of the vehicle received the factory designation of Object 500 and the military designation of ZSU-57-2.
The ZSU-57-2 underwent comprehensive testing from 1950-1954. In 1955 the ZSU-57-2 was accepted into the arsenal of the Soviet Army. It was produced at factory #174 in Omsk from 1955 to 1960. A total of 857 ZSU-57-2s were produced.
Media
Skins and camouflages for the ZSU-57-2: Search-terms "ZSU572", "ZSU57" and "ZSU_57_2" all from live.warthunder.com.
Videos
References
Read also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example,
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
ETC.
Sources
Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:
- topic on the official game forum;
- other literature.
| USSR anti-aircraft vehicles | |
|---|---|
| GAZ-AAA | GAZ-AAA (4M) · GAZ-AAA (DShK) |
| BTR-152 | BTR-152A · BTR-152D |
| Wheeled/Half-tracked | GAZ-MM (72-K) · ZiS-12 (94-KM) · ZiS-43 |
| Radar SPAAG | ZSU-23-4 · ZSU-37-2 |
| SAM | ZSU-23-4M4 · Strela-10M2 · 2S6 · Pantsir-S1 |
| Other | ZSU-23-4M2 · ZUT-37 · ZSU-37 · BTR-ZD · ZSU-57-2 |
| Czechoslovakia | M53/59 |
| North Vietnam | ▂Phòng không T-34 |





