Difference between revisions of "SPAA radars"
bangerland (talk | contribs) (After seeing Flame's data i realized what green field actually means on round radars. It's not passive FoV, it's tracking radar's maximum range. Also, i have no idea where to put this alternative radar view, or explanations to it, anyway.) |
bangerland (talk | contribs) (Tried to add a new section. Seems cringey to me, but that's about as much as i can do without going into RB, which i wont do anytime soon.) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
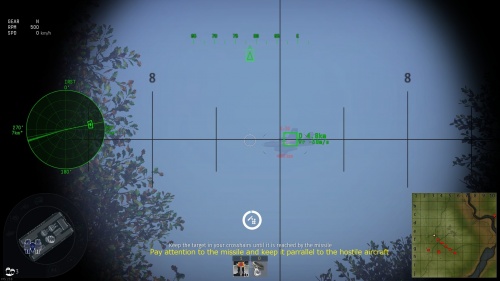
[[File:Radar_shot_marksman.jpg|none|thumb|500x400px|Enemy plane suffered a serious hit. Even if they somehow escape the rest of the volley, they're out of fighting capability and may crash soon.]] | [[File:Radar_shot_marksman.jpg|none|thumb|500x400px|Enemy plane suffered a serious hit. Even if they somehow escape the rest of the volley, they're out of fighting capability and may crash soon.]] | ||
For very long range sniper shots (~ 4-6 km engagements) it is best to change the radar from searching randomly and instead scan certain areas specifically. This is done by a key (Not set by default, name in settings is "change radar search mode"). This will stop the radar dish and force it to follow your turret's current direction. After that, you need to look into direction you think your enemy is going to come from (enemy airfield, for example). Since radar is static in this mode, it is advisable to move the turret a bit, just in case if the plane took a bit different route. You also should note, that smaller planes that fly near to ground are harder to detect, and even this trick might not work on them. | For very long range sniper shots (~ 4-6 km engagements) it is best to change the radar from searching randomly and instead scan certain areas specifically. This is done by a key (Not set by default, name in settings is "change radar search mode"). This will stop the radar dish and force it to follow your turret's current direction. After that, you need to look into direction you think your enemy is going to come from (enemy airfield, for example). Since radar is static in this mode, it is advisable to move the turret a bit, just in case if the plane took a bit different route. You also should note, that smaller planes that fly near to ground are harder to detect, and even this trick might not work on them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Passive optical system === | ||
| + | |||
| + | After a certain point, air forces realized the danger of radars to their ranks and started using specific radar-seeking missiles, which were able to guide straight onto SPAA and destroy it by itself. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a way to avoid a new threat entirely, new tracking system was adopted for some SPAA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Instead of using radars, an extremely advanced camera is constantly scanning air space around SPAA, and on lock-on it tries to provide you with approximate range and angular velocity of the target. The system has extremely short range by Radar standard, but it is capable of doing the job while being unnoticed by anti-radar detectors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Don't have your hopes too high up - this kind of tracking has a huge room for error, though it still provides user with enough information to get a successful manual hit on target, while it doesn't reveal your position to enemy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Using passive optical system ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | When it comes to tracking, it feels about the same as radar. The only visible difference is that power symbol is replaced by letters "IRST" - system still searches for targets, and you lock onto them. That's where the differences become more appearant: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Notice | ||
| + | |This example is modelled with [[Stormer HVM]] in mind. Aiming pattern and behaviour of system may be different for other SPAA. | ||
| + | |! | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Stormer HMV passive system lock on.jpg|none|thumb|500x400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | You no longer have a targeting reticle, meaning you have to aim at target yourself again, though you are supported with helpful tips from the guidance system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sometimes the optical system will become glitchy and give you less than coherent data, in which case you have to aim at target all by yourself, and all the system does for you is a little help with target tracking: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Stormer HVM hit with weird lock-on data.jpg|none|thumb|500x400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is why generally these kinds of systems use special Anti-Air missiles, which can hit enemy plane before it flew away from your targeting range and overcompensate for the lack of system accuracy - for example, [[Starstreak HVM]] is literally a triple missile, the only purpose of which is to chase enemy jet as fast as possible and try to hit it with at least one of them, as you check it's aim with your sniper scope. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Overall, these kinds of systems require very high level of "targeting" on crew and horizontal turret drive upgrades, as you have to track and catch extremely fast planes as fast as possible, and then guide very sensitive missiles at them as precisely, as you can. | ||
== Drawbacks of Using the Radar == | == Drawbacks of Using the Radar == | ||
Revision as of 21:01, 3 June 2019
War Thunder Update 1.87 "Locked On" introduced the capability of utilising radar units in a more active way in SPAA's and aircraft which historically had the use of early radars allowing for a more in-depth realism and a historic feel when utilising these vehicles.
Prior to this update, radars simply allowed SPAA to use a targeting reticle in realistic and simulator battle modes. While those targeting reticles tended to be extremely inaccurate, they were nonetheless helpful to the operator.
Post update, radars now have the capability to actively search, detect and lock onto an enemy's signal all the while providing a completely accurate firing solution, however, such battlefield benefit does come with its own share of risks when used.
Contents
SPAA Radar Types
At this time, War Thunder utilises two types of radar in SPAA vehicles, these radar units include the Rangefinder and the Active Radar:
Rangefinder
Rangefinders work by calculating the distance between two objects. There are two main components to a radio rangefinder which includes the transmitter unit and the receiver unit. The transmitter's job is to transmit a signal, usually, several hundred times a second and then waits. If an object such as an aircraft flies within the search area of the range finder, the transmitted signals from the rangefinder will bounce off of the aircraft and reflect back to to the SPAA which will then receive the transmitted signal into the receiver. The rangefinder then through a processing unit will calculate the time from when the signal was transmitted and then received and divide it by two, the time resultant is then converted into distance providing the SPAA with the distance to the vehicle being tracked. The more often the transmitters transmit, the more reflections are received giving the rangefinder an up-to-date distance to the moving aircraft. In some cases, with this data, the SPAA can set fuses for self-destroying ammo causing it to automatically explode near to where the tracked aircraft is showing to be, not requiring a direct hit, but close enough to cause damage through exploding shells. If target locking is an available function then the target will need to be manually locked.
How to use Rangefinders and Other Radar-Like Systems.
| This example is modelled with M163 in mind. Results may vary for SIDAM 25 and other SPAA vehicles. |
To use rangefinder substitute, you have to go to gunner (sniper) sight and direct the targeting crosshairs onto the target enemy aircraft, then press a lock-on key (default keybinding is alt+F, like with the rest of radars, is recommended to change to single key). As a result, lock on will occure:
All that is left is to aim the true targeting reticle and open fire on the enemy aircraft.
Active radar
When active radar units are operational, they search their surroundings for any flying aircraft. Active radars can lock onto targets and provide detailed information on the aircraft such as azimuth reading and distance. Active radars may employ a "sector" or "circular" radar view. One major drawback is that radars can easily be pinpointed through the use of counter-radar units and be targets of homing missiles as a result (not yet a feature in War Thunder).
-
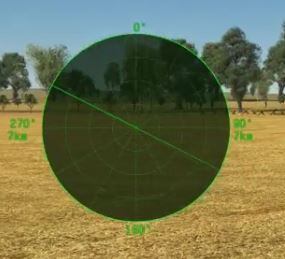
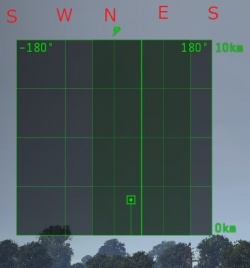 Sector view radar, alternative radar display. The default radar display is cut into 4 sectors (North,West,East,South) and is displayed as a square. Activated via "switch radar indicator type" keybinding. It helps to understand real distance from enemy to your SPAA easier. The bright line is your turret's direction, the dim one is your radar's direction.
Sector view radar, alternative radar display. The default radar display is cut into 4 sectors (North,West,East,South) and is displayed as a square. Activated via "switch radar indicator type" keybinding. It helps to understand real distance from enemy to your SPAA easier. The bright line is your turret's direction, the dim one is your radar's direction.
How to use Active Radars
When utilising any vehicle with a radar, two items will become visible on the view screen:
1) Radar screen
2) Radar-assisted compass
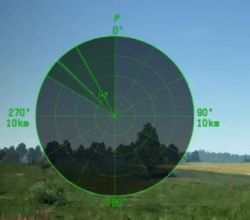
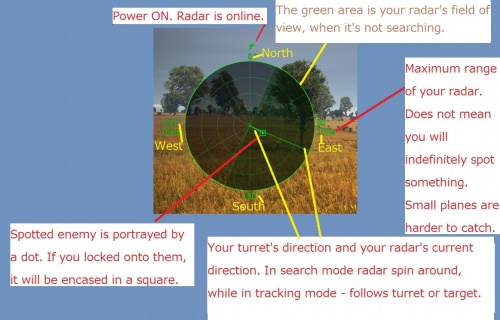
Whenever the radar unit is only in active search mode and does not have a lock on a target, it will scan on its own or if utilising a narrow scan field, will follow the vehicle turret. Its current direction is represented by a second line on the radar. This line must intersect with a target to "spot" it. Be aware, that small planes can avoid detection due to their small profile and obstacles such as trees and hills will obscure radar's field of view preventing tracking of objects on the other side of them. Even if the active radar fails to spot a target or is offline, generally SPAA gunner can still select and target an enemy aircraft and engage in manual targeting. The accuracy of this method is much lower when compared to utilising the active radar.
Whenever the active radar detects any target, a lock can be acquired by pressing a key (or pre-mapped controller button). Default keybinding is alt+F, unfortunately, this can cause problems due to the Alt key being used for other things and can incidentally deselect the target unintentionally and break target lock. Multiple targets (or even allied aircraft) within the field of the radar's search can cause tracking problems as multiple targets can cause the targeting system problems. In the event of multiple aircraft in the search area, it is recommended to switch to gunner view and manually attack targets to ensure not accidentally shooting down any friendly aircraft.
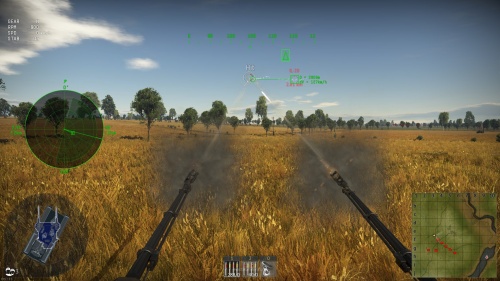
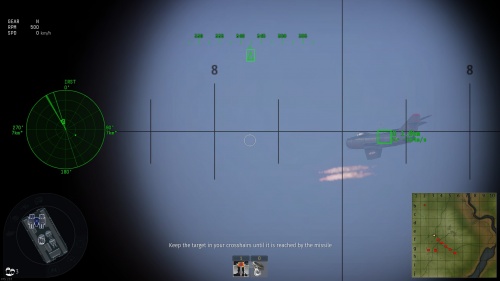
For active radars, the turret will receive the targeting information feed, adjust ammunition self-destruction fuse delays and follow the target automatically. When this happens, a "true" targeting reticle appears which 100% guarantees target destruction, only as long as the target maintains speed and bearing and does not alter its speed, course or direction.
At this point, the only concern now is preventing your opponent from dodging the incoming volley of ammunition. For this reason, conservation of ammunition is important and the gunner should not waste ammo firing in long continuous bursts in the same direction if your SPAA's accuracy is adequate.
For very long range sniper shots (~ 4-6 km engagements) it is best to change the radar from searching randomly and instead scan certain areas specifically. This is done by a key (Not set by default, name in settings is "change radar search mode"). This will stop the radar dish and force it to follow your turret's current direction. After that, you need to look into direction you think your enemy is going to come from (enemy airfield, for example). Since radar is static in this mode, it is advisable to move the turret a bit, just in case if the plane took a bit different route. You also should note, that smaller planes that fly near to ground are harder to detect, and even this trick might not work on them.
Passive optical system
After a certain point, air forces realized the danger of radars to their ranks and started using specific radar-seeking missiles, which were able to guide straight onto SPAA and destroy it by itself.
As a way to avoid a new threat entirely, new tracking system was adopted for some SPAA.
Instead of using radars, an extremely advanced camera is constantly scanning air space around SPAA, and on lock-on it tries to provide you with approximate range and angular velocity of the target. The system has extremely short range by Radar standard, but it is capable of doing the job while being unnoticed by anti-radar detectors.
Don't have your hopes too high up - this kind of tracking has a huge room for error, though it still provides user with enough information to get a successful manual hit on target, while it doesn't reveal your position to enemy.
Using passive optical system
When it comes to tracking, it feels about the same as radar. The only visible difference is that power symbol is replaced by letters "IRST" - system still searches for targets, and you lock onto them. That's where the differences become more appearant:
| This example is modelled with Stormer HVM in mind. Aiming pattern and behaviour of system may be different for other SPAA. |
You no longer have a targeting reticle, meaning you have to aim at target yourself again, though you are supported with helpful tips from the guidance system.
Sometimes the optical system will become glitchy and give you less than coherent data, in which case you have to aim at target all by yourself, and all the system does for you is a little help with target tracking:
This is why generally these kinds of systems use special Anti-Air missiles, which can hit enemy plane before it flew away from your targeting range and overcompensate for the lack of system accuracy - for example, Starstreak HVM is literally a triple missile, the only purpose of which is to chase enemy jet as fast as possible and try to hit it with at least one of them, as you check it's aim with your sniper scope.
Overall, these kinds of systems require very high level of "targeting" on crew and horizontal turret drive upgrades, as you have to track and catch extremely fast planes as fast as possible, and then guide very sensitive missiles at them as precisely, as you can.
Drawbacks of Using the Radar
Certain planes and helicopters have radar detection system, and as such, whenever your radar "hit" them, they see radar alerts.
Some aircraft have fully fledged out radars or counter-radars and will see SPAA clearly as soon as they try to track them.
Here is an example of what happens, when you got noticed by a helicopter:
Certain helicopters and planes may have no problems with carpet-bombing your position with rockets, just to make sure you aren't going to fire at them ever again. To avoid being bombed like this, you can turn the radar off with a key (default alt+R). This will shut down radar search, and you won't be able to lock on anymore. Certain SPAA's also hide their radar behind them, making their profile much smaller and harder to notice by tanks around them.
Despite losing Lock-on, you usually still retain your "fake" targeting reticle from rangefinders and can fire at enemy semi-precisely, however, in most SPAA's cases you can't hit targets that are too far away from you like this, because ammo will self-destruct at it's default range. (about 2.5 km away)
SPAA's Which Have Radars in Some Form
- Round view
- Gepard — Radar station for circular viewing and target tracking. Radar is pulled back, when offline
- Chieftain Marksman — Radar station for circular viewing and target tracking
- AMX-30 DCA — Radar station for circular viewing and target tracking
- M247 — Radar station for circular viewing and target tracking
- OTOMATIC — Radar station for circular viewing and target tracking
- Type 87 — Radar station for circular viewing and target tracking. Radar is pulled back, when offline
- ZPRK 2S6 - Radar station for circular viewing and target tracking. Radar is pulled back, when offline
- Sector view
- ZSU-23-4 — Radar station for sector search and target tracking
- Rangefinder Substitute