Difference between revisions of "Hotchkiss Mle 1930 (13.2 mm)"
(→Pros and cons) (Tag: Visual edit) |
Indo_Pilot (talk | contribs) (→See also) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | '' | + | <!-- ''Write an introduction to the article in 2-3 small paragraphs. Briefly tell us about the history of the development and combat using the weaponry and also about its features. Compile a list of air, ground, or naval vehicles that feature this weapon system in the game.'' --> |
| + | [[File:Hotchkiss Mle 1929.jpg|right|thumb|13.2mm Hotchkiss Mle 1929 in Naval quadmount]] | ||
| + | The '''13.2 mm Hotchkiss Mle 1930''' is a French-built heavy machine gun for multi-purpose use. Starting as the Hotchkiss Mle 1929, the Mle 1930 is a ground-based anti-aircraft designation of the machine gun. It is commonly used as close anti-air defence by the French Navy and also by the Army during the '30s until WW2. The guns was also adapted as main armament for tanks, armoured cars and anti-aircraft vehicles. The Hotchkiss was for France the equivalent of the [[M2HB_(12.7_mm)|M2 Browning]] heavy machine gun. | ||
=== Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | === Vehicles equipped with this weapon === | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| − | ''the 13. | + | <!-- ''Tell us about the tactical and technical characteristics of the cannon or machine gun.'' --> |
| + | |||
| + | The 13.2 mm Hotchkiss offers balanced performance against aircraft and soft targets, but has difficulty against vehicles with more than 20 mm of armour. It is fed by a 30-round magazine, which leads to the weapon's limited capacity to sustain suppressing fire. The gun has a fire-rate of 450 rounds per minute, but in practice it would seldom reach 200 rounds per minute due to the reload and recoil. | ||
=== Available ammunition === | === Available ammunition === | ||
| − | '' | + | <!-- ''Describe the shells that are available for the weapon and their features and purpose. If it concerns autocannons or machine guns, write about different ammo belts and what is inside (which types of shells).'' --> |
| + | Only one belt is currently available for the Hotchkiss in the game, the AP-T belt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''AP-T:''' {{Annotation|AP|M2 armour-piercing}}{{-}}{{Annotation|AP-T|Armour-piercing tracer}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{:{{PAGENAME}}/Ammunition|AP, AP-T}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Comparison with analogues === | ||
| + | <!-- ''Give a comparative description of cannons/machine guns that have firepower equal to this weapon.'' --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[M2HB (12.7 mm)]] - Similar gun in performance, but a lot more successful. It replaced the Hotchkiss 13.2 mm after WW2 for standardization purpose. | ||
| + | * [[Type 93 (13.2 mm)]] - Japanese licensed copy of the Hotchkiss | ||
| + | * [[Breda Model 31 (13.2 mm)]] - Italian licensed copy of the Hotchkiss | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Usage in battles == | ||
| + | <!-- ''Describe the cannon/machine gun in the game - its distinctive features, tactics of usage against notable opponents. Please don't write a "guide" - do not impose a single point of view, but give the reader food for thought.'' --> | ||
| + | This armament has a relatively small calibre which causes the post-penetration damage to be rather low. In many cases, even a direct hit to the crew might not be enough to knock them out. However, the 30-round magazine and fast fire-rate allow the user to place multiple hits in quick succession. Due to the low penetration, even reserve-level armoured vehicles might prove difficult targets. Anything with more than 20 mm of armour is better to avoid in combat. If you get close enough to a ground target, you might find this armament rather effective, but it is still strongly suggested to try to get your enemy from the side and rear where they are more vulnerable and pay less attention. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you have enough elevation and a traverse speed to follow an air target, this gun can prove pretty effective against aircraft. A couple of hits and the target is likely to be either set afire or lose some critical components. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Pros and cons === | ||
| + | <!-- ''Summarise and briefly evaluate the weaponry in terms of its characteristics and combat effectiveness. Mark pros and cons as a list.'' --> | ||
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | '''Pros:''' |
| − | ! colspan="8" |Penetration statistics | + | |
| + | * Good fire-rate | ||
| + | * Effective against soft targets | ||
| + | * Effective against aircraft | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Cons:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Penetration a bit lacking | ||
| + | * Magazine has only 30 rounds | ||
| + | |||
| + | == History == | ||
| + | <!-- ''Examine the history of the creation and combat usage of the weapon in more detail than in the introduction. If the historical reference turns out to be too long, take it to a separate article, taking a link to the article about the weapon and adding a block "/History" (example: <nowiki>https://wiki.warthunder.com/(Weapon-name)/History</nowiki>) and add a link to it here using the <code>main</code> template. Be sure to reference text and sources by using <code><nowiki><ref></ref></nowiki></code>, as well as adding them at the end of the article with <code><nowiki><references /></nowiki></code>.'' --> | ||
| + | Developed by Hotchkiss & Cie in the mid 1920s, the Hotckiss Mle 1929 was a multi-purpose heavy machine gun. First used by the French Navy, it served as close anti-air defence for ships with a range of up to 2,500 metres. The Army also adopted the gun, but in the Mle 1930 variants. The difference was that the Mle 1930 wasn't equipped with the sight and mount that allow the machine gun to be used against aircraft, as the French Army worried that the bullets might fall back on civilian areas and potentially kill someone. The Army strictly used this armament as anti-tank and anti-infantry weapons in their service. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the 1930s, the French cavalry mounted the 13.2 mm machine gun onto AMR.35 ZT1 reconnaissance vehicles to add some anti-tank capability to defend themselves during missions. This was also attempted on armoured cars such as the Laffly 80AM. Some machine guns were also presented for export, arming anti-aircraft trucks, though the export attempt as anti-aircraft had no success. As an independent heavy machine gun however, this armament was very successful, been exported notably to Brazil, Poland, and Romania, but also licensed to Italy and Japan, nearly all of which used the 13.2 mm intensively during WW2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{sp-begin|Hotchkiss Ammunition}} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" width="100%" | ||
| + | ! colspan="8" | Penetration statistics | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! rowspan="2" |Ammunition | + | ! rowspan="2" data-sort-type="text" | Ammunition |
| − | ! rowspan="2" |Type of | + | ! rowspan="2" | Type of<br>warhead |
| − | warhead | + | ! colspan="6" | Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) |
| − | ! colspan="6" |Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | !10 m | + | ! 10 m !! 100 m !! 500 m !! 1,000 m !! 1,500 m !! 2,000 m |
| − | !100 m | ||
| − | !500 m | ||
| − | !1,000 m | ||
| − | !1,500 m | ||
| − | !2,000 m | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''Type O''' | + | | '''Type O''' || AP || 24 || 23 || 14 || 10 || 7 || 4 |
| − | |AP | ||
| − | |24 | ||
| − | |23 | ||
| − | |14 | ||
| − | |10 | ||
| − | |7 | ||
| − | |4 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''Type OT''' | + | | '''Type OT''' || AP-T || 24 || 23 || 14 || 10 || 7 || 4 |
| − | |AP-T | ||
| − | |24 | ||
| − | |23 | ||
| − | |14 | ||
| − | |10 | ||
| − | |7 | ||
| − | |4 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''Type P''' | + | | '''Type P''' || APC || 28 || 27 || 20 || 15 || 11 || 9 |
| − | |APC | + | |- |
| − | |28 | + | | '''Type PT''' || APC-T || 28 || 27 || 20 || 15 || 11 || 9 |
| − | |27 | ||
| − | |20 | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" width="100%" |
| − | ! colspan="10" |Shell details | + | ! colspan="10" | Shell details |
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" data-sort-type="text" | Ammunition | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" | Type of<br>warhead | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" | Velocity<br>(m/s) | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" | Projectile<br>mass (kg) | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" | Fuse delay<br>(m) | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" | Fuse sensitivity<br>(mm) | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" | Explosive mass<br>(TNT equivalent) (g) | ||
| + | ! colspan="3" | Ricochet | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! 0% !! 50% !! 100% |
| − | ! | ||
| − | |||
| − | ! | ||
| − | |||
| − | ! | ||
| − | |||
| − | ! | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | '''Type O''' || AP || 810 || 0.051 || N/A || N/A || N/A || 66° || 70° || 72° | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''Type | + | | '''Type OT''' || AP-T || 810 || 0.051 || N/A || N/A || N/A || 66° || 70° || 72° |
| − | |AP-T | ||
| − | |810 | ||
| − | |0. | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |66° | ||
| − | |70° | ||
| − | |72° | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''Type | + | | '''Type P''' || APC || 810 || 0.052 || N/A || N/A || N/A || 66° || 70° || 72° |
| − | | | ||
| − | |810 | ||
| − | |0.052 | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |66° | ||
| − | |70° | ||
| − | |72° | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |'''Type | + | | '''Type PT''' || APC-T || 810 || 0.052 || N/A || N/A || N/A || 66° || 70° || 72° |
| − | |APC | ||
| − | |810 | ||
| − | |0.052 | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |N/A | ||
| − | |66° | ||
| − | |70° | ||
| − | |72° | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:13.2mm Ammunition.jpg|thumb|Main combat rounds for the 13.2 mm Hotchkiss]] | |
| + | <div style="text-align: left;"> | ||
| + | ;'''Cartouche à balle ordinaire O''' (AP type O) | ||
| − | + | The Type O was a standard armour-piercing round used against soft targets such as infantry, unarmoured vehicles, and aircraft. The projectile was made of carbon steel and was capped with lead. There was a brass cloak around the projectile. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The round can be identified by the primer seal painted either black or purple. | |
| − | + | * Projectile weight: 51.2 g | |
| + | * Velocity: 810 m/sec | ||
| − | + | ;'''Cartouche à balle traçante OT''' (AP-T type OT) | |
| − | |||
| − | '' | ||
| − | + | The Type OT was a standard round equipped with a tracer tail. It had the same ballistics as the Type O. | |
| − | + | The round can be identified by the primer seal painted green. | |
| − | + | ;'''Cartouche à balle perforante P''' (AP type P) | |
| − | '' | ||
| − | + | The Type P round was an armour-piercing hardened round used against armoured targets. The projectile was made of tungsten-steel alloy (3% tungsten, 97% steel) and was tempered. There was a lead cap and brass cloak on the rounds. | |
| − | + | The round can be identified by primer seal painted red. | |
| − | + | * Projectile weight: 52 g | |
| + | * Velocity: 810 m/sec | ||
| − | + | ;'''Cartouche à balle perforante traçante PT''' (AP-T type PT) | |
| − | + | The Type PT was an armour-piercing round equipped with a tracer tail. It had the same ballistics as the Type P. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | It can be identified by the primer seal painted yellow. | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | {{sp-end}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Media == | == Media == | ||
| Line 199: | Line 136: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| − | ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | + | <!-- ''Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' |
| + | * ''reference to the article about the variant of the cannon/machine gun;'' | ||
| + | * ''references to approximate analogues by other nations and research trees.'' --> | ||
| − | * | + | * [[Model 1929 Hotchkiss (13.2 mm)]] Original single mount version |
| − | * | + | * [[Hotchkiss (13.2 mm)]] German captured version |
| + | * [[Type 93 (13.2 mm)]] Japanese version built under licence | ||
| + | * [[Breda Model 31 (13.2 mm)]] Italian version built under licence | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' | + | <!-- ''Paste links to sources and external resources, such as:'' |
| + | * ''topic on the official game forum;'' | ||
| + | * ''other literature.'' --> | ||
| − | * | + | * [https://imgur.com/a/uSJrgKG French Manual of the Hotchkiss Mle 1929] |
| − | |||
{{France anti-aircraft guns}} | {{France anti-aircraft guns}} | ||
[[Category:Anti-aircraft guns]] | [[Category:Anti-aircraft guns]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:50, 10 August 2023
Contents
Description
The 13.2 mm Hotchkiss Mle 1930 is a French-built heavy machine gun for multi-purpose use. Starting as the Hotchkiss Mle 1929, the Mle 1930 is a ground-based anti-aircraft designation of the machine gun. It is commonly used as close anti-air defence by the French Navy and also by the Army during the '30s until WW2. The guns was also adapted as main armament for tanks, armoured cars and anti-aircraft vehicles. The Hotchkiss was for France the equivalent of the M2 Browning heavy machine gun.
Vehicles equipped with this weapon
General info
The 13.2 mm Hotchkiss offers balanced performance against aircraft and soft targets, but has difficulty against vehicles with more than 20 mm of armour. It is fed by a 30-round magazine, which leads to the weapon's limited capacity to sustain suppressing fire. The gun has a fire-rate of 450 rounds per minute, but in practice it would seldom reach 200 rounds per minute due to the reload and recoil.
Available ammunition
Only one belt is currently available for the Hotchkiss in the game, the AP-T belt.
- AP-T: AP · AP-T
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | ||||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| AP | 28 | 25 | 16 | 10 | 6 | 3 | |
| AP-T | 28 | 25 | 16 | 10 | 6 | 3 | |
| Shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay | Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | ||||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| AP | 800 | 0.05 | - | - | - | 47° | 56° | 65° | ||||
| AP-T | 800 | 0.05 | - | - | - | 47° | 56° | 65° | ||||
Comparison with analogues
- M2HB (12.7 mm) - Similar gun in performance, but a lot more successful. It replaced the Hotchkiss 13.2 mm after WW2 for standardization purpose.
- Type 93 (13.2 mm) - Japanese licensed copy of the Hotchkiss
- Breda Model 31 (13.2 mm) - Italian licensed copy of the Hotchkiss
Usage in battles
This armament has a relatively small calibre which causes the post-penetration damage to be rather low. In many cases, even a direct hit to the crew might not be enough to knock them out. However, the 30-round magazine and fast fire-rate allow the user to place multiple hits in quick succession. Due to the low penetration, even reserve-level armoured vehicles might prove difficult targets. Anything with more than 20 mm of armour is better to avoid in combat. If you get close enough to a ground target, you might find this armament rather effective, but it is still strongly suggested to try to get your enemy from the side and rear where they are more vulnerable and pay less attention.
If you have enough elevation and a traverse speed to follow an air target, this gun can prove pretty effective against aircraft. A couple of hits and the target is likely to be either set afire or lose some critical components.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Good fire-rate
- Effective against soft targets
- Effective against aircraft
Cons:
- Penetration a bit lacking
- Magazine has only 30 rounds
History
Developed by Hotchkiss & Cie in the mid 1920s, the Hotckiss Mle 1929 was a multi-purpose heavy machine gun. First used by the French Navy, it served as close anti-air defence for ships with a range of up to 2,500 metres. The Army also adopted the gun, but in the Mle 1930 variants. The difference was that the Mle 1930 wasn't equipped with the sight and mount that allow the machine gun to be used against aircraft, as the French Army worried that the bullets might fall back on civilian areas and potentially kill someone. The Army strictly used this armament as anti-tank and anti-infantry weapons in their service.
In the 1930s, the French cavalry mounted the 13.2 mm machine gun onto AMR.35 ZT1 reconnaissance vehicles to add some anti-tank capability to defend themselves during missions. This was also attempted on armoured cars such as the Laffly 80AM. Some machine guns were also presented for export, arming anti-aircraft trucks, though the export attempt as anti-aircraft had no success. As an independent heavy machine gun however, this armament was very successful, been exported notably to Brazil, Poland, and Romania, but also licensed to Italy and Japan, nearly all of which used the 13.2 mm intensively during WW2.
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| Type O | AP | 24 | 23 | 14 | 10 | 7 | 4 |
| Type OT | AP-T | 24 | 23 | 14 | 10 | 7 | 4 |
| Type P | APC | 28 | 27 | 20 | 15 | 11 | 9 |
| Type PT | APC-T | 28 | 27 | 20 | 15 | 11 | 9 |
| Shell details | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
| Type O | AP | 810 | 0.051 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 66° | 70° | 72° |
| Type OT | AP-T | 810 | 0.051 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 66° | 70° | 72° |
| Type P | APC | 810 | 0.052 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 66° | 70° | 72° |
| Type PT | APC-T | 810 | 0.052 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 66° | 70° | 72° |
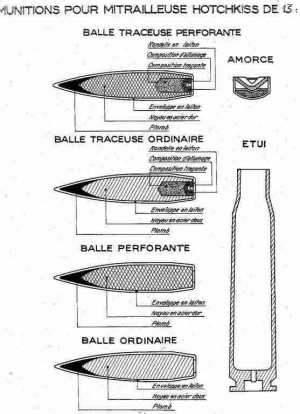
- Cartouche à balle ordinaire O (AP type O)
The Type O was a standard armour-piercing round used against soft targets such as infantry, unarmoured vehicles, and aircraft. The projectile was made of carbon steel and was capped with lead. There was a brass cloak around the projectile.
The round can be identified by the primer seal painted either black or purple.
- Projectile weight: 51.2 g
- Velocity: 810 m/sec
- Cartouche à balle traçante OT (AP-T type OT)
The Type OT was a standard round equipped with a tracer tail. It had the same ballistics as the Type O.
The round can be identified by the primer seal painted green.
- Cartouche à balle perforante P (AP type P)
The Type P round was an armour-piercing hardened round used against armoured targets. The projectile was made of tungsten-steel alloy (3% tungsten, 97% steel) and was tempered. There was a lead cap and brass cloak on the rounds.
The round can be identified by primer seal painted red.
- Projectile weight: 52 g
- Velocity: 810 m/sec
- Cartouche à balle perforante traçante PT (AP-T type PT)
The Type PT was an armour-piercing round equipped with a tracer tail. It had the same ballistics as the Type P.
It can be identified by the primer seal painted yellow.
Media
Excellent additions to the article would be video guides, screenshots from the game, and photos.
See also
- Model 1929 Hotchkiss (13.2 mm) Original single mount version
- Hotchkiss (13.2 mm) German captured version
- Type 93 (13.2 mm) Japanese version built under licence
- Breda Model 31 (13.2 mm) Italian version built under licence
External links
| France anti-aircraft guns | |
|---|---|
| 13.2 mm | Hotchkiss Mle 1930 |
| 20 mm | GIAT M693/mod F2 · Oerlikon KAD (Swiss) |
| 30 mm | HSS 831A |
| 40 mm | Bofors L/60 · Mle. 1951 T1 (Bofors L/70) |