Difference between revisions of "HMS Invincible"
(Updated format) |
(→Pros and cons) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
* Vulnerable to deep running torpedoes. | * Vulnerable to deep running torpedoes. | ||
* Underwater torpedoes have low range and a relatively small warhead in comparison to most deck mounted torpedoes aboard cruisers and destroyers. | * Underwater torpedoes have low range and a relatively small warhead in comparison to most deck mounted torpedoes aboard cruisers and destroyers. | ||
| + | * Isnt actually invincible | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| Line 131: | Line 132: | ||
* ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' --> | * ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' --> | ||
''Links to articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ''Links to articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:'' | ||
| + | |||
* ''reference to the series of the ship;'' | * ''reference to the series of the ship;'' | ||
* ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' | * ''links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.'' | ||
Revision as of 16:07, 23 June 2021
Contents
Description
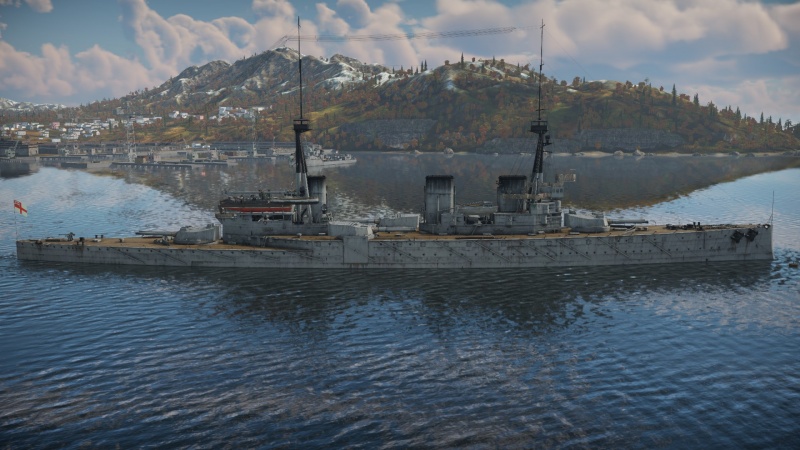
The Invincible-class, HMS Invincible (85), 1916 is a rank V British battlecruiser with a battle rating of 6.0 (AB/RB/SB). It was introduced in Update "Hot Tracks".
General info
Survivability and armour
Talk about the vehicle's armour. Note the most well-defended and most vulnerable zones, e.g. the ammo magazine. Evaluate the composition of components and assemblies responsible for movement and manoeuvrability. Evaluate the survivability of the primary and secondary armaments separately. Don't forget to mention the size of the crew, which plays an important role in fleet mechanics. Save tips on preserving survivability for the "Usage in battles" section. If necessary, use a graphical template to show the most well-protected or most vulnerable points in the armour.
Mobility
Write about the ship's mobility. Evaluate its power and manoeuvrability, rudder rerouting speed, stopping speed at full tilt, with its maximum forward and reverse speed.
| Mobility Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Game Mode | Upgrade Status | Maximum Speed (km/h) | |
| Forward | Reverse | ||
| AB | |||
| Upgraded | 58 | 28 | |
| RB/SB | |||
| Upgraded | 49 | 24 | |
Modifications and economy
Armament
Primary armament
Provide information about the characteristics of the primary armament. Evaluate their efficacy in battle based on their reload speed, ballistics and the capacity of their shells. Add a link to the main article about the weapon: {{main|Weapon name (calibre)}}. Broadly describe the ammunition available for the primary armament, and provide recommendations on how to use it and which ammunition to choose.
Secondary armament
Some ships are fitted with weapons of various calibres. Secondary armaments are defined as weapons chosen with the control Select secondary weapon. Evaluate the secondary armaments and give advice on how to use them. Describe the ammunition available for the secondary armament. Provide recommendations on how to use them and which ammunition to choose. Remember that any anti-air armament, even heavy calibre weapons, belong in the next section. If there is no secondary armament, remove this section.
Anti-aircraft armament
An important part of the ship's armament responsible for air defence. Anti-aircraft armament is defined by the weapon chosen with the control Select anti-aircraft weapons. Talk about the ship's anti-air cannons and machine guns, the number of guns and their positions, their effective range, and about their overall effectiveness – including against surface targets. If there are no anti-aircraft armaments, remove this section.
Additional armament
Describe the available additional armaments of the ship: depth charges, mines, torpedoes. Talk about their positions, available ammunition and launch features such as dead zones of torpedoes. If there is no additional armament, remove this section.
Usage in battles
Describe the technique of using this ship, the characteristics of her use in a team and tips on strategy. Abstain from writing an entire guide – don't try to provide a single point of view, but give the reader food for thought. Talk about the most dangerous opponents for this vehicle and provide recommendations on fighting them. If necessary, note the specifics of playing with this vehicle in various modes (AB, RB, SB).
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Main battery of eight 305 mm guns with access to SAP rounds can make short work of enemy cruisers, and APC can punish larger targets.
- Faster than the other 6.0 capital ships, inferior only to SMS Von der Tann in terms of top speed.
- Belt armour can shrug off medium calibre gunfire from cruisers and destroyers, and extends below the waterline to give protection against shallow torpedoes.
- Shell rooms are well below the waterline and hard to hit with gunfire.
- Numerous secondary battery guns with a high rate of fire that can easily deal with close range attacks from smaller unarmoured vessels.
- Has underwater torpedo launchers, which can potentially catch close targets unawares.
Cons:
- Vertical armour is very weak against large calibre guns from other capital ships; battleships can often cause crippling damage.
- Non-existent deck armour and extremely poor anti-aircraft armament makes Invincible highly vulnerable to bombers.
- 305 mm guns struggle to penetrate battleship belt armour beyond 10km, and the APC rounds suffer from poor post-penetration damage.
- Secondary battery SAP shells have low penetration; the guns will struggle to damage even most light cruisers.
- Main battery turret armour is thin on the roof, often resulting in disabled turrets or damage gun breeches.
- Vulnerable to deep running torpedoes.
- Underwater torpedoes have low range and a relatively small warhead in comparison to most deck mounted torpedoes aboard cruisers and destroyers.
- Isnt actually invincible
History
HMS Invincible was the lead ship of her class of three battlecruisers built for the Royal Navy. She was the first modern battlecruiser ever built, and pioneered the ship type, featuring less armour in exchange for more speed. Her construction led to a "battlecruiser arms race", including ships such as the German Von Der Tann and Derflingger classes as well as the Japanese Kongo class. During the First World War, Invincible participated in the Battle of the Heligoland Bight, as well as the Falklands Battle where she and her sister ship Inflexible sank the armoured cruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau. She ultimately met her demise at the Battle of Jutland, when her magazines detonated following hits from the German force.
Design and development
Invincible, as the first battlecruiser ever built, was the brainchild of First Sea Lord Jackie Fisher, who was responsible for a wide range of innovations including the Dreadnought. The ships were designed to be fast, with a top speed of 25 knots (46 km/h), but also extremely well armed, with a main battery of 12 inch (305 mm) guns. However, this came at the expense of armour, meaning that Invincible had a weaker armour protection compared to the dreadnoughts. The massive 41 000 horsepower engines that powered the Invincible took up a massive amount of space inside the hull, requiring a reduction in armour.
Invincible, being a larger vessel than her armoured-cruiser predecessors, displaced over 20 000 tons at full load. She had an armament of eight 12 inch (305 mm) guns in four twin turrets, with one fore, one aft, and two on beam positions. The turrets were placed in a position so that all four turrets could fire on a broadside. Invincible carried a secondary armament of twelve 4 inch 40 QF naval guns in single mounts, placed across the fore and rear superstructures. She carried a single 76 mm and 47 mm gun for anti-aircraft defence, as well as four 450 mm torpedoes. Invincible was laid down in April of 1906, and launched a year later in 1907. She was fully commissioned in 1909 and entered service with the 1st Cruiser Squadron of the British Grand Fleet.
Operational History
Invincible entered service with the British Grand Fleet and participated in fleet maneuvers along with the rest of the fleet. However, it was apparent during her early service that her main turrets were problematic as the faulty electric turret horizontal drives prevented them from turning properly. As a result, the battlecruiser spent much of late 1913 and early 1914 in dock, receiving new, hydraulic turret drives to replace her electric ones. She was also fitted with a new ranging fire director, but this had not been completed by the time of the outbreak of the First World War.
Heligoland Bight and the Falklands
Following the start of the First World War, Invincible saw her first action at the Battle of Heligoland Bight. There, she fired 18 rounds at the crippled cruiser Coln, but failed to obtain hits. Later, Invincible participated in a more important action, the Battle of the Falklands. As part of the British West Indies squadron commanded by Rear Admiral Christopher Cradock, she steamed from Port Stanley (in the Falklands) with her sister ship Inflexible to intercept the German squadron led by Admiral Von Spee; Spee's cruiser squadron, led by armoured cruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau, attempted to attack the British base at Port Stanley hours before. As the battlecruisers had a 5-knot advantage over the German armoured cruisers, they quickly caught up and began straddling the German cruisers with 12 inch shells. After a several hour long battle, both Scharnhorst and Gneisenau were sunk, the former with no survivors. Invincible was hit numerous times, but suffered no significant damage.
After the Falklands battle, Invincible returned to Port Stanley for repairs, followed by a more lengthy refit at Gibraltar. During this time, her ranging director was completed (it had been left unfinished with the outbreak of war) and her funnel was extended to reduce the amount of smoke entering the bridge and forward superstructure.
Battle of Jutland and sinking
Invincible ultimately met her demise at the Battle of Jutland in 1916, just a year after she sank the cruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau at the Falklands. In May of that year, she was assigned to Admiral Beatty's battlecruiser group and ordered to cruise into the north seas to intercept a potential breakout of the German fleet. Soon after, Invincible, along with her sister ships Inflexible and Indomitable, spotted a group of seven enemy ships including two armoured cruisers and promptly fired upon them. They succeeded in crippling the cruiser Wiesbaden with a hit to the engine room, as well as a similar heavy hit to the cruiser Pillau.
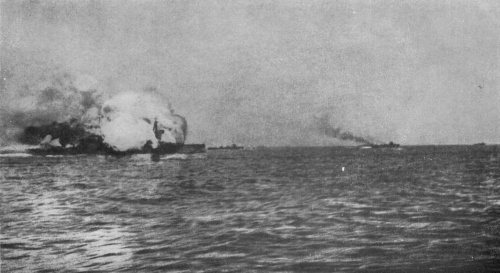
Soon after, Beatty's battlecruisers spotted the German battlecruiser line, and promptly opened fire on the battlecruisers Lutzow and Derfflinger. Invincible hit Lutzow twice beneath the waterline, which would eventually lead to her demise. However, she ended up directly in front of Lutzow and Derfllinger, who fired several salvoes at her. One of these shots hit the ship's midships 12 inch shell magazines, which exploded and blew the ship in half. Almost her entire crew of 1026 were killed, including her commanding officer Rear Admiral Horace Hood; six survivors were rescued by escorting destroyers. Hood's widow would later launch the battlecruiser HMS Hood, the most powerful battlecruiser ever launched by the Royal Navy.
Invincible lies at a depth of 55 metres in the North Sea, cut in half by the massive magazine explosion that doomed her. Her wreck is protected by the Protection of Military Remains act of 1986.
Devblog
HMS Invincible was laid down in April 1906 as the lead ship of her class of three new armoured cruisers, intended to replace the preceding Minotaur-class. The ship was launched a year later and completed in March 1909, subsequently being commissioned into service with the Royal Navy. Thereafter, HMS Invincible took part in fleet maneuvers and several reviews before being sent to drydock for refit. In 1911, the warship was officially redesignated into a battlecruiser, thus becoming the first ship of this kind.
In 1913, HMS Invincible was ordered to the dockyard once more to replace her electrically powered turret traverse mechanisms with hydraulic ones in order to fix ongoing problems and make the ship battle-worthy. However, while works were still being undertaken, the declaration of war on Germany in August 1914 signaled the start of WWI and HMS Invincible was quickly recommissioned.
Already at the outbreak of the conflict, HMS Invincible saw herself in the thick of the action, engaging German ships at the Battle of Heligoland Bight in late August 1914. Later that year, in December, HMS Invincible, along with her sister ship HMS Inflexible, took part in the Battle of the Falkland Islands, sinking the two German armoured cruisers, Gneisenau and Scharnhorst, during the engagement.
HMS Invincible also took part in what would become her last engagement - the well-known Battle of Jutland in May 1916. During the battle, HMS Invincible was struck by fire coming from the German battlecruisers Lützow and Derfflinger, detonating her midships magazine and causing the warship to break in half.
Media
- HMS Invincible Devblog Images
See also
Links to articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the ship;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
References
- Bowman, C. (2016, July 23). Dive on the wreck of HMS Invincible (Watch). Retrieved January 04, 2021, from https://www.warhistoryonline.com/featured/dive-wreck-hms-invincible.html
- Naval Encyclopedia. (2020, October 15). Invincible class battlecruisers (1907). Retrieved January 04, 2021, from https://www.naval-encyclopedia.com/ww1/UK/invincible-class-battlecruisers/
| Britain battlecruisers | |
|---|---|
| Invincible-class | HMS Invincible |
| HMS Queen Mary* | |
| Renown-class | HMS Renown · HMS Repulse |
| Courageous-class | HMS Glorious |
| Admiral-class | HMS Hood |
| * Unique ship | |