Difference between revisions of "USS New Orleans"
(→Scout plane) |
(→Description) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Specs-Card | {{Specs-Card | ||
|code=us_cruiser_new_orleans_class | |code=us_cruiser_new_orleans_class | ||
| − | |images={{Specs-Card-Image|GarageImage_{{PAGENAME}}.jpg}} | + | |images={{Specs-Card-Image|GarageImage_{{PAGENAME}}.jpg|ArtImage_{{PAGENAME}}.png}} |
}} | }} | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
<!-- ''In the first part of the description, cover the history of the ship's creation and military application. In the second part, tell the reader about using this ship in the game. Add a screenshot: if a beginner player has a hard time remembering vehicles by name, a picture will help them identify the ship in question.'' --> | <!-- ''In the first part of the description, cover the history of the ship's creation and military application. In the second part, tell the reader about using this ship in the game. Add a screenshot: if a beginner player has a hard time remembering vehicles by name, a picture will help them identify the ship in question.'' --> | ||
| − | The '''{{Specs|name}}''' | + | The '''{{Specs|name}}''' was the lead ship of the New Orleans class of heavy cruisers, the last of the American heavy cruisers to be built under the regulations of the Washington naval treaty, limiting her to 10,000 tons displacement. Laid down in 1931, she would enter service in 1934 and serve through World War Two, notably being at Pearl Harbour during the infamous attack. She would also take part in the Battle of the Coral Sea, Midway, and Tassafaronga, along with many others. After assisting with bringing troops home postwar, she was decommissioned in 1947. |
| + | |||
| + | New Orleans was introduced in [[Update "New Power"]], and has similar firepower to other American pre-war heavy cruisers with her main battery of 3 triple {{Annotation|8-inch|203 mm}}. As she is a treaty-era cruiser, she had to make some sacrifices to maintain the 10,000 ton limit, and thus has rather thin armour for a heavy cruiser, lacking even in comparison to WW2-era light cruisers. In exchange she has good main battery firepower for the rank and a healthy secondary and anti-aircraft battery. | ||
== General info == | == General info == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
{{Specs-Fleet-Armour}} | {{Specs-Fleet-Armour}} | ||
<!-- ''Talk about the vehicle's armour. Note the most well-defended and most vulnerable zones, e.g. the ammo magazine. Evaluate the composition of components and assemblies responsible for movement and manoeuvrability. Evaluate the survivability of the primary and secondary armaments separately. Don't forget to mention the size of the crew, which plays an important role in fleet mechanics. Save tips on preserving survivability for the "Usage in battles" section. If necessary, use a graphical template to show the most well-protected or most vulnerable points in the armour.'' --> | <!-- ''Talk about the vehicle's armour. Note the most well-defended and most vulnerable zones, e.g. the ammo magazine. Evaluate the composition of components and assemblies responsible for movement and manoeuvrability. Evaluate the survivability of the primary and secondary armaments separately. Don't forget to mention the size of the crew, which plays an important role in fleet mechanics. Save tips on preserving survivability for the "Usage in battles" section. If necessary, use a graphical template to show the most well-protected or most vulnerable points in the armour.'' --> | ||
| − | The USS Orleans is quite a survivable ship, and a quantum leap in protection over its other American treaty heavy predecessors. Chief among these changes is an increase in barbette protection from 37 mm to 127 mm and turret front armour from 63.5 mm to 203 mm. This resolves the biggest weakness of earlier US heavy cruisers, which was a tendency have their shell rooms and turrets ripped apart early in a fight, causing devastating fires, significant crew losses, and leaving them completely defenseless. Its turrets are still not as resistant as those on the Brooklyns and Clevelands, owing to the 38 mm sides curving around to form its cheeks. | + | The USS New Orleans is quite a survivable ship, and a quantum leap in protection over its other American treaty heavy predecessors. Chief among these changes is an increase in barbette protection from 37 mm to 127 mm and turret front armour from 63.5 mm to 203 mm. This resolves the biggest weakness of earlier US heavy cruisers, which was a tendency have their shell rooms and turrets ripped apart early in a fight, causing devastating fires, significant crew losses, and leaving them completely defenseless. Its turrets are still not as resistant as those on the Brooklyns and Clevelands, owing to the 38 mm sides curving around to form its cheeks. |
The same cannot be said of its secondary armament, which are still relatively dated open 5"/25 single mounts and as a result will be knocked out very early in a match and is prone to being set on fire. | The same cannot be said of its secondary armament, which are still relatively dated open 5"/25 single mounts and as a result will be knocked out very early in a match and is prone to being set on fire. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 60: | ||
The main guns have a slow rotation and reload speed, with 17 seconds with a spaded crew, and 20 seconds stock. the guns also have somewhat moderate shells, but with that, the ship's main armament is poor in reload and rotation speed. | The main guns have a slow rotation and reload speed, with 17 seconds with a spaded crew, and 20 seconds stock. the guns also have somewhat moderate shells, but with that, the ship's main armament is poor in reload and rotation speed. | ||
| − | { | + | |
| − | + | {{:8 inch/55 Mark 14 (203 mm)/Ammunition|8 inch Mk.14 Common, 8 inch Mk.19 APCBC, 8 inch Mk.25 HC, 8 inch Mk.17 SP Common}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | Mk.14 Common | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Secondary armament === | === Secondary armament === | ||
| Line 106: | Line 69: | ||
The 5-inch guns are highly effective at destroying aircraft at long range, and with the HE-VT shells unlocked, are even more effective at destroying aircraft at long range and killing unarmoured destroyers. However, the guns can't fire fast enough to kill destroyers or aircraft, and sometimes, the guns are targeted by stray shells, knocking them out. | The 5-inch guns are highly effective at destroying aircraft at long range, and with the HE-VT shells unlocked, are even more effective at destroying aircraft at long range and killing unarmoured destroyers. However, the guns can't fire fast enough to kill destroyers or aircraft, and sometimes, the guns are targeted by stray shells, knocking them out. | ||
| − | { | + | |
| − | + | {{:5 inch/25 Mk.13 AA (127 mm)/Ammunition|5 inch Mk.36 AAC, 5 inch Mk.28 AAC-VT}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | Mk.36 AAC | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Anti-aircraft armament === | === Anti-aircraft armament === | ||
Latest revision as of 22:21, 25 June 2023
Contents
Description
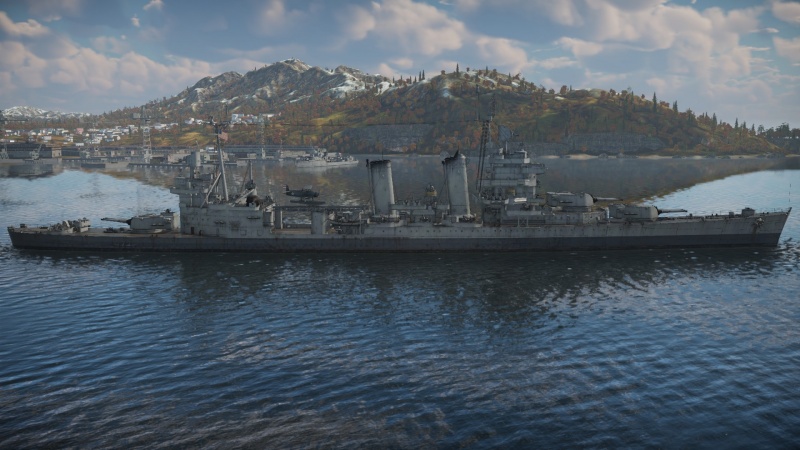
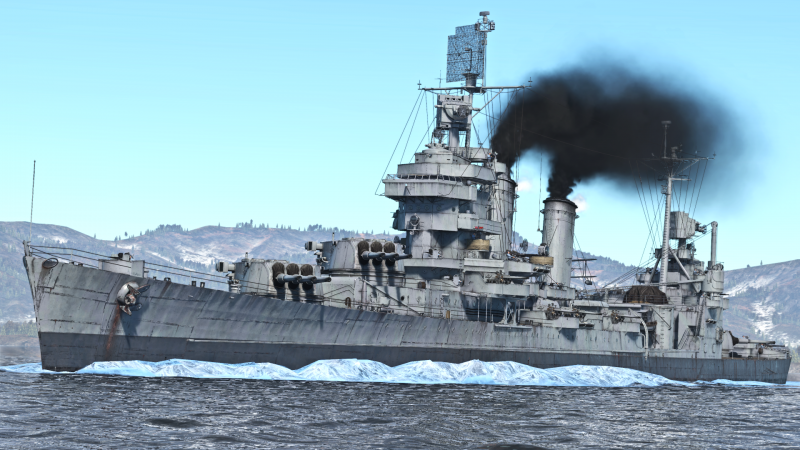
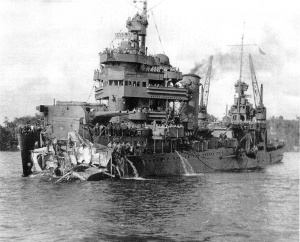
The New Orleans-class, USS New Orleans (CA-32), 1945 was the lead ship of the New Orleans class of heavy cruisers, the last of the American heavy cruisers to be built under the regulations of the Washington naval treaty, limiting her to 10,000 tons displacement. Laid down in 1931, she would enter service in 1934 and serve through World War Two, notably being at Pearl Harbour during the infamous attack. She would also take part in the Battle of the Coral Sea, Midway, and Tassafaronga, along with many others. After assisting with bringing troops home postwar, she was decommissioned in 1947.
New Orleans was introduced in Update "New Power", and has similar firepower to other American pre-war heavy cruisers with her main battery of 3 triple 8-inch. As she is a treaty-era cruiser, she had to make some sacrifices to maintain the 10,000 ton limit, and thus has rather thin armour for a heavy cruiser, lacking even in comparison to WW2-era light cruisers. In exchange she has good main battery firepower for the rank and a healthy secondary and anti-aircraft battery.
General info
Survivability and armour
The USS New Orleans is quite a survivable ship, and a quantum leap in protection over its other American treaty heavy predecessors. Chief among these changes is an increase in barbette protection from 37 mm to 127 mm and turret front armour from 63.5 mm to 203 mm. This resolves the biggest weakness of earlier US heavy cruisers, which was a tendency have their shell rooms and turrets ripped apart early in a fight, causing devastating fires, significant crew losses, and leaving them completely defenseless. Its turrets are still not as resistant as those on the Brooklyns and Clevelands, owing to the 38 mm sides curving around to form its cheeks.
The same cannot be said of its secondary armament, which are still relatively dated open 5"/25 single mounts and as a result will be knocked out very early in a match and is prone to being set on fire.
The New Orleans also has significantly improved protection for its engine room, which has the double effect of preventing engine room knock-outs (and associated crew losses and fires) and also making it more likely that you'll be able to turn around and escape from a sticky situation under your own power. Although main magazine protection is reduced somewhat, it is still strong enough and deep enough in the hull that ammo racks from cruiser calibre guns are extremely unlikely. As a nice little bonus, it maintains the strake of anti-fragmentation armour on its upper hull; a small plus compared to the Cleveland.
All in all, the USS New Orleans has everything in protection that the USS Portland, Northampton, and Pensacola lacked while keeping the same decent armament (and, an argument could be made for having better overall damage output due to the turrets spending less time blacked out in a game) and is comparable in durability to the USS Cleveland, making it a strong competitor on the high seas of War Thunder.
| Armour | Front | Side | Rear | Deck/Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turret | 203 mm | 38 mm | 38 mm | 70 mm |
| Front magazine | 38.1 mm | 101.6 mm Upper 76.2 mm Lower |
57.15 mm | |
| Citadel | 76 mm | 127 mm 82.55 mm |
76 mm | 57.15 mm |
| Rear magazine | 120.65 mm Upper 76.2 mm Lower |
38.1 mm | 57.15 mm | |
| Barbette | 127 mm | |||
Mobility
Write about the ship's mobility. Evaluate its power and manoeuvrability, rudder rerouting speed, stopping speed at full tilt, with its maximum forward and reverse speed.
| Mobility Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Game Mode | Upgrade Status | Maximum Speed (km/h) | |
| Forward | Reverse | ||
| AB | |||
| Upgraded | 71 | 25 | |
| RB/SB | |||
| Upgraded | 61 | 22 | |
Modifications and economy
Armament
Primary armament
The main guns have a slow rotation and reload speed, with 17 seconds with a spaded crew, and 20 seconds stock. the guns also have somewhat moderate shells, but with that, the ship's main armament is poor in reload and rotation speed.
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 1,000 m | 2,500 m | 5,000 m | 7,500 m | 10,000 m | 15,000 m | ||
| Mk.14 Common | Common | 116 | 102 | 83 | 69 | 57 | 43 |
| Mk.19 APCBC | APCBC | 383 | 339 | 277 | 228 | 190 | 143 |
| Mk.25 HC | HE | 61 | 61 | 61 | 61 | 61 | 61 |
| Mk.17 SP Common | SP Common | 137 | 121 | 99 | 81 | 68 | 51 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (s) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (kg) |
Ricochet | |||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| Mk.14 Common | Common | 853 | 117.9 | 0.035 | 9 | 4.84 | 47° | 60° | 65° | |||
| Mk.19 APCBC | APCBC | 853 | 117.9 | 0.035 | 9 | 1.62 | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
| Mk.25 HC | HE | 853 | 117.9 | 0 | 0.1 | 9.49 | 79° | 80° | 81° | |||
| Mk.17 SP Common | SP Common | 853 | 117.9 | 0.035 | 9 | 4.61 | 48° | 63° | 71° | |||
Secondary armament
The 5-inch guns are highly effective at destroying aircraft at long range, and with the HE-VT shells unlocked, are even more effective at destroying aircraft at long range and killing unarmoured destroyers. However, the guns can't fire fast enough to kill destroyers or aircraft, and sometimes, the guns are targeted by stray shells, knocking them out.
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 1,000 m | 2,500 m | 5,000 m | 7,500 m | 10,000 m | 15,000 m | ||
| Mk.36 AAC | HE-TF | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| Mk.28 AAC-VT | HE-VT | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (kg) |
Ricochet | |||||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| Mk.36 AAC | HE-TF | 657 | 24.42 | 0 | 0.1 | 3.16 | 79° | 80° | 81° | |||
| Proximity-fused shell details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Arming distance (m) |
Trigger radius (m) |
Explosive mass (TNT equivalent) (kg) |
Ricochet | |||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||||
| Mk.28 AAC-VT | HE-VT | 657 | 23.45 | 0 | 0.1 | 457 | 23 | 3.25 | 79° | 80° | 81° | |
Anti-aircraft armament
The anti-aircraft armament is the shining sword with the New Orleans. The 40 mm Bofors and 20 mm Oerlikon AA guns are very effective at close range. These guns can fight back against aircraft, pesky torpedo boats, and even, in some cases, lower battle-rating destroyers. The Oerlikon and Bofors AA guns can pressure aircraft to stay away, while hidden torpedo boats who come in the sights of the secondary and tertiary armament will have second thoughts about attacking USS New Orleans.
Scout plane
Located amidships is one catapult for a SOC-1 scout plane which provides unique offensive and defensive abilities, expanding tactical options. Ship-launched scout planes fly just like regular tree units but lack munition choices and cockpit views. Alongside the typical abilities of strafing, dropping 2 x 100 lb bombs, and capping zones, the SOC-1 and other scout planes have the added ability to lay down smoke cover (up to 3 times). Captains will be wise to remember to utilise the aircraft and consider when best to use it, for example to cap a point early or late in the match, to create a smoke screen to stymie enemy bombardment and repair, to attack enemy units directly, or perhaps something completely new!
Usage in battles
The USS New Orleans is a moderate top-tier ship. Being a step up from the three other heavy cruisers coming before it, the New Orleans is simply a USS Portland with much more anti-air capability. The downsides of the New Orleans are its below average shell dispersion, reload time, and rotation speed. The shells are somewhat moderate, and when the New Orleans is completely spaded, the heavy cruiser is a deadly force to be reckoned with. The silver lining about the ship is its huge anti-aircraft armament. In all, the ship has 28 Bofors and 24 Oerlikon AA guns, along with the eight 5"/25 guns that can act as dual-purpose weaponry.
When the enemy team starts spawning aircraft, most pilots will start heading towards the dreadnoughts on your team, so stay close to them and provide AA cover, pressuring aircraft to find different targets.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Very effective AA against aircraft and small targets
- The 5-inch guns with HE-VT shells are effective against destroyers when guns are knocked out
- 8-inch guns are useful in close combat
- Very high amount of crew
- Very good anti-aircraft capability
- Able to support dreadnoughts in AA role
- Has anti-fragmentation armour
- Can take hits before sinking
- Fast when spaded
- One scout seaplane
Cons:
- 8-inch guns have a slow reload speed
- Moderate speed when stock
- Stock time-fuzed Shells are poor against aircraft and naval targets
- Can't compete with fast-firing light cruisers
- Susceptible to torpedo damage
- No torpedo launchers
- Anti-fragmentation armour won't completely stop shells
- Guns rotate slowly
History
USS New Orleans (CA-32) was the lead ship of her class of heavy cruisers built for the United States Navy. As the last class of 10-thousand ton cruisers built for the US Navy (abiding by the conditions of the Washington Naval Treaty), she was initially classified as a light cruiser and subsequently reclassified due to her 8-inch calibre main armament. New Orleans had an extensive service history, and travelled abroad prior to the Second World War. During the war, she served extensively in the Pacific Theatre, surviving a crippling torpedo hit that almost sunk her. New Orleans was awarded 17 battle stars for her WWII service, making her one of the five most-decorated American vessels of WWII; her sister ships San Francisco and Minneapolis also made the list. She was decommissioned after the war, and scrapped in 1959.
Design and development
After the construction of the previous Portland, Northampton and Pensacola classes, the United States Navy (USN) began the construction of a new class of heavy cruiser - the New Orleans class. This was the last class of cruisers built to the 10-thousand-ton limit of the Washington naval treaty. The ships were intended to have a much heavier armour load than their predecessors, which were low in survivability. As a result, New Orleans' armour accounted for almost 15% of her total displacement, compared to 5-6% for the preceding ship classes. However, this resulted in a reduction in fuel stowage meaning that the New Orleans had a shorter range compared to her predecessors.
The ships themselves inherited the superstructure design of the preceding cruiser classes - however, the old tripod mast design was removed and replaced with a smoother forward superstructure. This change made the ships easily-distinguishable from their predecessors and was subsequently used on the Wichita, Cleveland and Baltimore classes of heavy cruisers. The ships, similar to the preceding Portland class, were built directly up to the 10 thousand ton limit; New Orleans herself displaced 9950 tons standard.
Technical specifications
New Orleans carried a main armament of nine 8-inch (203 mm) guns in three triple Mk 9 turrets, later upgraded to Mk 14 turrets during World War II. She also carried a secondary armament of eight single 5-inch 25 calibre guns for anti-aircraft defence. Rounding her armament off, New Orleans carried two 3-pounder (47 mm) saluting guns and eight 12.7 mm Browning machine guns for short-range Anti-aircraft armament. In the 1940s, her anti-aircraft armament was improved significantly with 24 x 40 mm Bofors guns in quad mounts and 28 x 20 mm Oerlikon guns in dual mounts.
Similar to other American cruisers, New Orleans didn't carry any torpedoes. Her engines developed 107 000 shaft horsepower giving her a top speed of 32.7 knots (60.6 km/h). Costing a total of 12 million dollars to build (non-inflation-adjusted), New Orleans was ordered in mid-1929 and laid down in March of 1931. She was eventually completed and commissioned on February 15th 1934.
Operational history
During her construction, New Orleans was reclassified as a heavy cruiser due to her 8-inch main armament. Thus, she was commissioned as CA-32. Following her commissioning, New Orleans sailed on a cruise to the United Kingdom and Scandinavia, followed by a trip to the Panama canal to escort the Northampton-class cruiser USS Houston as she carried President Franklin D. Roosevelt to Hawaii. She later participated in exercises off of California and in the Atlantic, and participated in the first "Fleet week" where civilians could tour the naval vessel.
New Orleans was docked in the inner harbour during the Pearl harbour attack, without power as she was being refueled. Her crewmen frantically tried to raise steam and sail her away while her gunners fired at the attacking aircraft with small arms. As she had no electrical power, New Orleans' ammunition hoists were inoperational making her 5-inch AA guns nearly useless. Despite this, her crew members attempted to lift shells manually using a rope hoist. New Orleans suffered a near miss from a Japanese HE bomb, but was otherwise unscathed.
In early 1942, New Orleans sailed back to port in San Francisco to repair damage and receive a search radar, along with several 20 mm Oerlikon guns. She then returned to the Pacific, and subsequently saw combat action during the battles of Coral Sea and Midway. During the Battle of the Coral Sea, she tried to save the crippled carrier USS Lexington; she was responsible for evacuating crew members once it was apparent the old carrier could not be saved. She later escorted Yorktown during the Midway battle, but was detached to join the Enterprise battlegroup, and was not present when the Yorktown was crippled by Japanese bombers.
Battle of Tassafaronga
In early November of 1942, New Orleans sailed for Fiji, and then returned to the Solomons for combat action. She was part of a heavy cruiser task force that engaged a Japanese transport squadron during the night of November 30th, in an engagement known as the Battle of Tassafaronga. During the battle, New Orleans, along with four heavy cruisers and six destroyers, spotted a Japanese troop convoy heading for the Solomons, escorted by eight destroyers. And thus began a short engagement limited by poor night-time visibility where the Japanese destroyer Takamani was sunk by gunfire. However, the rest of the Japanese destroyers were not fired upon, and launched a large number of Type 93 'Long Lance' heavy oxygen torpedoes.
At 23:27, Minneapolis was hit by two torpedoes in her engine rooms causing her to take heavy damage. New Orleans subsequently took evasive action, but was hit by a Type 93 that detonated her forward ammunition magazines. As a result, her bow was sheared off at the No. 1 turret and she was slowed to a speed of 2 knots. Subsequently, the cruisers Northampton and Pensacola were both hit, Northampton sinking and Pensacola taking severe damage.
Repairs and later service
New Orleans, with her entire bow sheared off, limped back to Cockatoo dockyard in Australia; in fact, she sailed backwards (stern first) to avoid flooding the ship's frontal section. There, temporary repairs were made including the fitting of a 'stub bow' to cover the blown-off bow section. In March of 1943, she sailed for Puget Naval Yard where she was given a complete repair, and had a new bow section fitted. She also received a large anti-aircraft armament boost of 24 Bofors guns (6 x 4) and numerous more double Oerlikon cannons. Repairs completed, she returned to service in August of 1943.
New Orleans spent the entirety of 1944 in the Pacific theatre, providing heavy fire support for troop landings in the Marshall Islands. She later escorted the Essex-class carrier Lexington (named after the carrier that she attempted to save at the Battle of the Coral Sea) back to Pearl Harbour after she was torpedoed. She later escorted the American carrier task force during the Battle of the Philippine Sea, and participated in the Battle of Leyte Gulf where she sank the light carrier Chiyoda with gunfire.
In early 1945, New Orleans returned to Mare Island for a refit, and then participated in the American invasion of Okinawa where she provided fire support for troops landing on the beaches. She returned to the Philippines in August of 1945, and was anchored at Subic Bay when the Japanese surrendered in Tokyo. She then served in various duties after the war, repatriating American soldiers from China, Japan and the Korean peninsula. She returned to the United States in 1947 and was laid up in reserve, to be scrapped starting in 1959.
New Orleans was awarded 17 stars for her service, making her one of the most decorated ships in American history. In fact, she is tied for third place with three other vessels, two of which are her sister ships: USS San Francisco and USS Minneapolis. The only ships with more stars are the legendary USS Enterprise (20 stars) and the cruiser USS San Diego (18 stars). As well, five ships are named after sailors who perished on USS New Orleans during the battle of Tassafaronga: the destroyer USS Rogers (DD-876), and the destroyer escorts USS Hayter, USS Foreman, USS Swenning, and USS Haines.
Media
- Skins
See also
Links to articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the ship;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
References
- Military Factory. (2017, May 30). USS New Orleans (CA-32). Retrieved January 10, 2021, from https://www.militaryfactory.com/ships/detail.asp?ship_id=uss-new-orleans-ca32-heavy-cruiser-united-states
- Naval History and Heritage Command. (2019, June 26). New Orleans II (CA-32). Retrieved January 10, 2021, from https://www.history.navy.mil/research/histories/ship-histories/danfs/n/new-orleans-ii.html
| New York Navy Yard | |
|---|---|
| Heavy Cruisers (CA) | |
| New Orleans-class | USS New Orleans |
| Battleships (BB) | |
| Tennessee-class | USS Tennessee |
| USA heavy cruisers | |
|---|---|
| Pensacola-class | USS Pensacola |
| Northampton-class | USS Northampton |
| Portland-class | USS Portland |
| New Orleans-class | USS New Orleans |
| Baltimore-class | USS Baltimore · USS Pittsburgh |
| Des Moines-class | USS Des Moines · USS Newport News |