Difference between revisions of "F4U Corsair (History)"
CobraKingII (talk | contribs) |
m (@CobraKingII, listed an optional way to display the variants, if you prefer the bullets, just swap the semi-colons for the asterisk. Looking forward to seeing how this page turns out.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Writing|CobraKingII}} | + | {{Writing|CobraKingII|24 March 2020}} |
== Development == | == Development == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Variants == | == Variants == | ||
| − | + | ; F4U-1 (Corsair Mk I): First production version of the Corsair. | |
| − | + | ; F4U-1A (Corsair Mk II): Had a simplified canopy, along with other minor improvements that allowed for easier carrier landings. | |
| − | + | ; F3A-1 (Corsair Mk III): F4U-1 license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy. | |
| − | + | ; F3A-1D (Corsair Mk III): F4U-1A license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy. | |
| − | + | ; FG-1A (Corsair Mk IV): F4U-1 license-built by Goodyear. | |
| − | + | ; FG-1D (Corsair Mk IV): F4U-1A license-built by Goodyear. | |
| − | + | ; F4U-1B: Post-war designation (unofficial) for F4U-1's modified for Fleet Air Arm (Royal Navy) service. | |
| − | * F4U-1C: An F4U-1D with four | + | * F4U-1C: An F4U-1D with four 20 mm cannons replacing the six .50 calibre machine guns. |
* F4U-1D (Corsair Mk II): Had a new R-2800-8W engine, which was more powerful, allowing for more payload and performance. | * F4U-1D (Corsair Mk II): Had a new R-2800-8W engine, which was more powerful, allowing for more payload and performance. | ||
* F4U-1P: Photo reconnaissance variant. | * F4U-1P: Photo reconnaissance variant. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
* F4U-4: Variant with a new 2100 hp dual-stage-supercharged 18-W engine, a four-bladed propeller, and other minor improvements. | * F4U-4: Variant with a new 2100 hp dual-stage-supercharged 18-W engine, a four-bladed propeller, and other minor improvements. | ||
* F4U-4B: F4U-4's with four 20mm cannons instead of machine guns. | * F4U-4B: F4U-4's with four 20mm cannons instead of machine guns. | ||
| − | * F4U-4E: Night fighter variant with the APS-4 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four | + | * F4U-4E: Night fighter variant with the APS-4 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four 20 mm cannons instead of machine guns. |
| − | * F4U-4N:Night fighter variant with the APS-6 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four | + | * F4U-4N: Night fighter variant with the APS-6 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four 20 mm cannons instead of machine guns. |
* F4U-4K: Experimental drone variant. | * F4U-4K: Experimental drone variant. | ||
* F4U-4P: Photo reconnaissance variant of the F4U-4. | * F4U-4P: Photo reconnaissance variant of the F4U-4. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
* F4U-5N: A variant of the F4U-5 with a radar. | * F4U-5N: A variant of the F4U-5 with a radar. | ||
* F4U-5NL: F4U-5N's equipped with rubber de-icing boots on the leading wing edge and leading tail edge. Made for cold temperatures of winter. | * F4U-5NL: F4U-5N's equipped with rubber de-icing boots on the leading wing edge and leading tail edge. Made for cold temperatures of winter. | ||
| − | * F4U-5P: Long range photo reconnaissance variant of the F4U-5. | + | * F4U-5P: Long-range photo-reconnaissance variant of the F4U-5. |
| − | * F4U-6: A variant made for the Marine Corps with extra | + | * F4U-6: A variant made for the Marine Corps with extra armour and oil coolers. It was designed for ground attack. |
| − | * AU-1: Later | + | * AU-1: Later redesignation of the F4U-6. |
* F4U-7: AU-1 in French service. | * F4U-7: AU-1 in French service. | ||
* FG-1E: A Goodyear FG-1 with radar equipment. | * FG-1E: A Goodyear FG-1 with radar equipment. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* FG-3: Turbo supercharged variant of the FG-1D. | * FG-3: Turbo supercharged variant of the FG-1D. | ||
* FG-4: Goodyear produced F4U-4. It was never delivered. | * FG-4: Goodyear produced F4U-4. It was never delivered. | ||
| − | * F2G-1: Goodyear modified F4U-1 with a Pratt and Whitney R-4360 , Wasp Major 4-row 28-cylinder radial engine. It had manual folding wings. Never entered service. | + | * F2G-1: Goodyear modified F4U-1 with a Pratt and Whitney R-4360, Wasp Major 4-row 28-cylinder radial engine. It had manual-folding wings. Never entered service. |
| − | * F2G-2: F2G-1 with hydraulically folding wings and a | + | * F2G-2: F2G-1 with hydraulically folding wings and a tailhook for carrier landings. Never entered service. |
== Operators == | == Operators == | ||
Revision as of 23:00, 24 March 2020
| Writing in process... This article is being edited by the member CobraKingII (start date). Other participants are requested to not make any changes while this warning is here. |
Contents
Development
Design
Service
Variants
- F4U-1 (Corsair Mk I)
- First production version of the Corsair.
- F4U-1A (Corsair Mk II)
- Had a simplified canopy, along with other minor improvements that allowed for easier carrier landings.
- F3A-1 (Corsair Mk III)
- F4U-1 license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy.
- F3A-1D (Corsair Mk III)
- F4U-1A license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy.
- FG-1A (Corsair Mk IV)
- F4U-1 license-built by Goodyear.
- FG-1D (Corsair Mk IV)
- F4U-1A license-built by Goodyear.
- F4U-1B
- Post-war designation (unofficial) for F4U-1's modified for Fleet Air Arm (Royal Navy) service.
- F4U-1C: An F4U-1D with four 20 mm cannons replacing the six .50 calibre machine guns.
- F4U-1D (Corsair Mk II): Had a new R-2800-8W engine, which was more powerful, allowing for more payload and performance.
- F4U-1P: Photo reconnaissance variant.
- XF4U-2: Night fighter variant with two auxiliary fuel tanks.
- F4U-2: Experimental night fighter based on the F4U-1. The outer right machine gun was removed, so it had a total of five. An airborne intercept (AI) radar was equipped on the outer starboard wing.
- XF4U-3: A variant designed for the testing of different engines in the F4U airframe.
- FG-3: XF4U-3 license-built by Goodyear.
- XF4U-3B: XF4U-3 with slight modifications, built for the FAA.
- XF4U-4: A variant with a new engine and cowling.
- F4U-4: Variant with a new 2100 hp dual-stage-supercharged 18-W engine, a four-bladed propeller, and other minor improvements.
- F4U-4B: F4U-4's with four 20mm cannons instead of machine guns.
- F4U-4E: Night fighter variant with the APS-4 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four 20 mm cannons instead of machine guns.
- F4U-4N: Night fighter variant with the APS-6 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four 20 mm cannons instead of machine guns.
- F4U-4K: Experimental drone variant.
- F4U-4P: Photo reconnaissance variant of the F4U-4.
- XF4U-5: A variant with a new engine cowling and other improvements.
- F4U-5: F4U-4 with a more powerful Pratt and Whitney R-2800-32(E) engine. Other improvements included all-metal wings, a modernized cockpit, and a fully retractable tail wheel.
- F4U-5N: A variant of the F4U-5 with a radar.
- F4U-5NL: F4U-5N's equipped with rubber de-icing boots on the leading wing edge and leading tail edge. Made for cold temperatures of winter.
- F4U-5P: Long-range photo-reconnaissance variant of the F4U-5.
- F4U-6: A variant made for the Marine Corps with extra armour and oil coolers. It was designed for ground attack.
- AU-1: Later redesignation of the F4U-6.
- F4U-7: AU-1 in French service.
- FG-1E: A Goodyear FG-1 with radar equipment.
- FG-1K: Drone variant of the Goodyear FG-1.
- FG-3: Turbo supercharged variant of the FG-1D.
- FG-4: Goodyear produced F4U-4. It was never delivered.
- F2G-1: Goodyear modified F4U-1 with a Pratt and Whitney R-4360, Wasp Major 4-row 28-cylinder radial engine. It had manual-folding wings. Never entered service.
- F2G-2: F2G-1 with hydraulically folding wings and a tailhook for carrier landings. Never entered service.
Operators
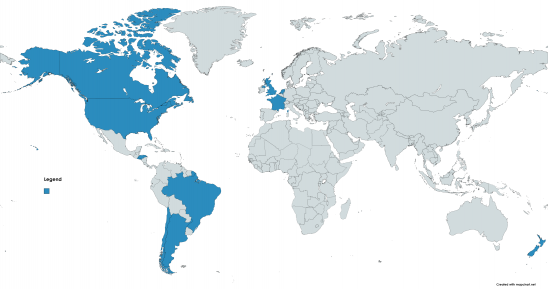
Argentina
Argentine Navy operated 26 F4U-5/5N/5NL Corsairs from 1956 to 1968
Brazil
Brazilian Navy operated 30 F4U-1D from 1950 to 1976
Canada
Royal Canadian Navy operated 130 F4U-1D from 1948 to 1960
Chile
Chilean Navy operated 30 F4U-1D and 20 F4U-4 from 1953 to 1978
El Salvador
Air Force of El Salvador operated 25 F4U/FG-1D from 1957 to 1976
France
French Navy operated 69 AU-1 and 94 F4U-7 from 1954 to 1964
Honduras
Honduran Air Force operated 19 from 1956 to 1979
Netherlands
Royal Netherlands Navy operated 35 F4U-1D from 1943 to 1956
New Zealand
Royal New Zealand Air Force operated 368 F4U-1 and 60 FG-1D from 1944 to 1949
United Kingdom
Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm operated 2,012 Corsairs of all types during World War 2, including 95 Corsair I (F4U-1), 510 Corsair II (F4U-1A), 430 Corsair III (F3A-1D), and 977 Corsair IV (FG-1D)
United States
United States Navy and Marine Corps operated Corsairs of all production variants from 1942 to 1953