




In 2009, shortly after the Mi-28N was formally accepted into service, multiple programs were already underway to upgrade the helicopter. The primary competitor, the Mi-28NM, represents the latest in Russian attack helicopter technology. Developed by Rostvertol, it features several improvements over its predecessor, such as advanced avionics, the N025 radar with enhanced capabilities for target detection and tracking, upgraded avionics, optics, powerplant, and weapons. The NM boasts a more powerful VK-2500 engine, increasing its payload capacity and operational range. This upgrade enables it to carry an array of weaponry, such as the Vikhr laser guided missiles and the Khrizantema radar-guided anti-tank missiles. Additionally, it incorporates advanced night vision and targeting systems for all-weather operations, significantly improving its combat effectiveness. The Mi-28NM first flew in 2016, and successfully completed state acceptance trials in 2020, with plans shortly after to upgrade the existing Mi-28N fleet as of 2022.
The Mi-28NM (NATO reporting name: Havoc) is a Soviet attack helicopter introduced in Update "Ground Breaking". The Mi-28NM is a further modernized version of the previous Mi-28N. While this Havoc may look more fashionable, it is meaner than ever in combat. The new sensor suite has excellent quality 3rd generation gunner thermals and the radar, MAWS, and new RWR improve situational awareness. The arsenal has been improved with the addition of two new ATGMs: the 9K127 Vikhr made famous by Kamov's Ka-50/52, and the radar-guided 9M123 Khrizantema previously only seen on the ground-based Khrizantema-S. The Mi-28NM still lacks some of the flexibility of its Kamov counterparts, but it can unleash a huge amount of destruction on enemy tanks thanks to its precise and advanced ordnance, great survivability and handling, and powerful avionics.
| Belt | Belt filling | Armor penetration (mm) at a distance: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1000 m | 1500 m | 2000 m | ||
| AP-T/HEF-I | 65 | 63 | 53 | 44 | 36 | 29 | |
| APDS/AP-T/HEF-I/HEF-I | 82 | 81 | 79 | 75 | 72 | 69 | |
| APDS | 82 | 81 | 79 | 75 | 72 | 69 | |
| HEF-T/AP-T/HEF-I/HEF-I | 65 | 63 | 53 | 44 | 36 | 29 | |
| Name | Weight | Slot | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 × | 42.4 kg |  |  |  |  | |
| 20 × | 326 kg |  |  |  |  | |
| 5 × | 505 kg |  |  |  |  | |
| 4 × | 216 kg | 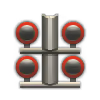 |  | |||
| 4 × | 195.6 kg | 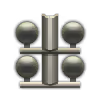 |  | |||
| 8 × | 391.2 kg | 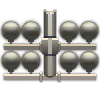 |  | |||
| 6 × | 354 kg | 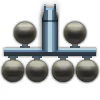 |  | |||
| 166.6 kg |  |  |  |  | ||
| 2 × | 271.6 kg |  |  |  |  | |
| 227 kg |  |  |  |  | ||
| 508.3 kg |  |  |  |  | ||
| 163.8 kg |  |  | ||||












Flight performance |
|---|
Survivability |
|---|
Weaponry | |||
|---|---|---|---|