Difference between revisions of "F4U Corsair (History)"
CobraKingII (talk | contribs) (I have added a little more to the development section.) (Tag: Visual edit) |
CobraKingII (talk | contribs) (I layed out what the article is going to look like when it is done, so I know what information to put where.) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Writing|CobraKingII|24 March 2020}} | {{Writing|CobraKingII|24 March 2020}} | ||
== Development == | == Development == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Origin === | ||
In 1938 the Navy wanted to find a design for a carrier-based fighter with more performance than the Brewster F2A and Grumman F4F. The design contract was given to Vought, based on their proposal, which featured a plane dependent on the Pratt and Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp engine. The design included an inverted gull wing shape. This was necessary because the engine required a large propeller, which needed a large ground clearance. This would require very long landing gear, except the inverted gull wing shape allowed shorter landing gear, while maintaining the necessary ground clearance. The prototype, named XF4U-1 was armed with 4 machine guns, two .50 caliber machine guns in the wings and 2 .30 caliber machine guns on the engine cowling. The XF4U-1 first flew on May 29, 1940, and became the first single engine plane to fly over 400 mph. Before Vought was allowed to produce the plane though, they had to increase its armament, as it was deemed insufficient based on data from Europe. Its armament was changed to six .50 machine guns, and it was ordered into production. A self-sealing fuel tank in the fuselage above the wings caused the cockpit to be moved aft as well. The Navy ordered 584 F4U-1's on April 2, 1941. | In 1938 the Navy wanted to find a design for a carrier-based fighter with more performance than the Brewster F2A and Grumman F4F. The design contract was given to Vought, based on their proposal, which featured a plane dependent on the Pratt and Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp engine. The design included an inverted gull wing shape. This was necessary because the engine required a large propeller, which needed a large ground clearance. This would require very long landing gear, except the inverted gull wing shape allowed shorter landing gear, while maintaining the necessary ground clearance. The prototype, named XF4U-1 was armed with 4 machine guns, two .50 caliber machine guns in the wings and 2 .30 caliber machine guns on the engine cowling. The XF4U-1 first flew on May 29, 1940, and became the first single engine plane to fly over 400 mph. Before Vought was allowed to produce the plane though, they had to increase its armament, as it was deemed insufficient based on data from Europe. Its armament was changed to six .50 machine guns, and it was ordered into production. A self-sealing fuel tank in the fuselage above the wings caused the cockpit to be moved aft as well. The Navy ordered 584 F4U-1's on April 2, 1941. | ||
== Design == | == Design == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Powerplant === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Fuselage === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Wings and Landing Gear === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Technical Issues === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Design Modifications === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Performance === | ||
== Service == | == Service == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === World War 2 === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== United States ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Marine Corps ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== US Navy ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Royal Navy ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Royal New Zealand Air Force ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Captured Corsairs ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Korean War === | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== United States ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== French Navy ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Salvadoran Air Force and Honduran Air Force ==== | ||
== Variants == | == Variants == | ||
| Line 45: | Line 81: | ||
; F2G-1: Goodyear modified F4U-1 with a Pratt and Whitney R-4360, Wasp Major 4-row 28-cylinder radial engine. It had manual-folding wings. Never entered service. | ; F2G-1: Goodyear modified F4U-1 with a Pratt and Whitney R-4360, Wasp Major 4-row 28-cylinder radial engine. It had manual-folding wings. Never entered service. | ||
; F2G-2: F2G-1 with hydraulically folding wings and a tailhook for carrier landings. Never entered service. | ; F2G-2: F2G-1 with hydraulically folding wings and a tailhook for carrier landings. Never entered service. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Specifications == | ||
== Operators == | == Operators == | ||
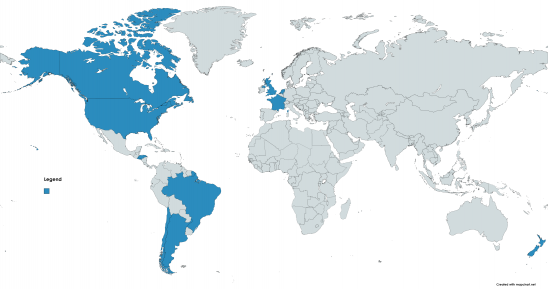
| − | + | '''Argentina'''[[File:F4U Corsair Operators (2).png|thumb|548x548px|F4U Corsair Operators]] | |
| − | [[File:F4U Corsair Operators (2).png|thumb|548x548px|F4U Corsair Operators]] | ||
Argentine Navy operated 26 F4U-5/5N/5NL Corsairs from 1956 to 1968 | Argentine Navy operated 26 F4U-5/5N/5NL Corsairs from 1956 to 1968 | ||
| − | + | '''Brazil''' | |
| + | |||
Brazilian Navy operated 30 F4U-1D from 1950 to 1976 | Brazilian Navy operated 30 F4U-1D from 1950 to 1976 | ||
| − | + | '''Canada''' | |
| + | |||
Royal Canadian Navy operated 130 F4U-1D from 1948 to 1960 | Royal Canadian Navy operated 130 F4U-1D from 1948 to 1960 | ||
| − | + | '''Chile''' | |
| + | |||
Chilean Navy operated 30 F4U-1D and 20 F4U-4 from 1953 to 1978 | Chilean Navy operated 30 F4U-1D and 20 F4U-4 from 1953 to 1978 | ||
| − | + | '''El Salvador''' | |
| + | |||
Air Force of El Salvador operated 25 F4U/FG-1D from 1957 to 1976 | Air Force of El Salvador operated 25 F4U/FG-1D from 1957 to 1976 | ||
| − | + | '''France''' | |
| + | |||
French Navy operated 69 AU-1 and 94 F4U-7 from 1954 to 1964 | French Navy operated 69 AU-1 and 94 F4U-7 from 1954 to 1964 | ||
| − | + | '''Honduras''' | |
| + | |||
Honduran Air Force operated 19 from 1956 to 1979 | Honduran Air Force operated 19 from 1956 to 1979 | ||
| − | + | '''Netherlands''' | |
| + | |||
Royal Netherlands Navy operated 35 F4U-1D from 1943 to 1956 | Royal Netherlands Navy operated 35 F4U-1D from 1943 to 1956 | ||
| − | + | '''New Zealand''' | |
| + | |||
Royal New Zealand Air Force operated 368 F4U-1 and 60 FG-1D from 1944 to 1949 | Royal New Zealand Air Force operated 368 F4U-1 and 60 FG-1D from 1944 to 1949 | ||
| − | + | '''United Kingdom''' | |
| + | |||
Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm operated 2,012 Corsairs of all types during World War 2, including 95 Corsair I (F4U-1), 510 Corsair II (F4U-1A), 430 Corsair III (F3A-1D), and 977 Corsair IV (FG-1D) | Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm operated 2,012 Corsairs of all types during World War 2, including 95 Corsair I (F4U-1), 510 Corsair II (F4U-1A), 430 Corsair III (F3A-1D), and 977 Corsair IV (FG-1D) | ||
| − | + | '''United States''' | |
| + | |||
United States Navy and Marine Corps operated Corsairs of all production variants from 1942 to 1953 | United States Navy and Marine Corps operated Corsairs of all production variants from 1942 to 1953 | ||
Revision as of 23:22, 25 March 2020
| Writing in process... This article is being edited by the member CobraKingII (start date). Other participants are requested to not make any changes while this warning is here. |
Development
Origin
In 1938 the Navy wanted to find a design for a carrier-based fighter with more performance than the Brewster F2A and Grumman F4F. The design contract was given to Vought, based on their proposal, which featured a plane dependent on the Pratt and Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp engine. The design included an inverted gull wing shape. This was necessary because the engine required a large propeller, which needed a large ground clearance. This would require very long landing gear, except the inverted gull wing shape allowed shorter landing gear, while maintaining the necessary ground clearance. The prototype, named XF4U-1 was armed with 4 machine guns, two .50 caliber machine guns in the wings and 2 .30 caliber machine guns on the engine cowling. The XF4U-1 first flew on May 29, 1940, and became the first single engine plane to fly over 400 mph. Before Vought was allowed to produce the plane though, they had to increase its armament, as it was deemed insufficient based on data from Europe. Its armament was changed to six .50 machine guns, and it was ordered into production. A self-sealing fuel tank in the fuselage above the wings caused the cockpit to be moved aft as well. The Navy ordered 584 F4U-1's on April 2, 1941.
Design
Powerplant
Fuselage
Wings and Landing Gear
Technical Issues
Design Modifications
Performance
Service
World War 2
United States
Marine Corps
Royal New Zealand Air Force
Captured Corsairs
Korean War
United States
Salvadoran Air Force and Honduran Air Force
Variants
- F4U-1 (Corsair Mk I)
- First production version of the Corsair.
- F4U-1A (Corsair Mk II)
- Had a simplified canopy, along with other minor improvements that allowed for easier carrier landings.
- F3A-1 (Corsair Mk III)
- F4U-1 license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy.
- F3A-1D (Corsair Mk III)
- F4U-1A license-built by Brewster. Poor quality caused the contract to be terminated by the Navy.
- FG-1A (Corsair Mk IV)
- F4U-1 license-built by Goodyear.
- FG-1D (Corsair Mk IV)
- F4U-1A license-built by Goodyear.
- F4U-1B
- Post-war designation (unofficial) for F4U-1's modified for Fleet Air Arm (Royal Navy) service.
- F4U-1C
- An F4U-1D with four 20 mm cannons replacing the six .50 calibre machine guns.
- F4U-1D (Corsair Mk II)
- Had a new R-2800-8W engine, which was more powerful, allowing for more payload and performance.
- F4U-1P
- Photo reconnaissance variant.
- XF4U-2
- Night fighter variant with two auxiliary fuel tanks.
- F4U-2
- Experimental night fighter based on the F4U-1. The outer right machine gun was removed, so it had a total of five. An airborne intercept (AI) radar was equipped on the outer starboard wing.
- XF4U-3
- A variant designed for the testing of different engines in the F4U airframe.
- FG-3
- XF4U-3 license-built by Goodyear.
- XF4U-3B
- XF4U-3 with slight modifications, built for the FAA.
- XF4U-4
- A variant with a new engine and cowling.
- F4U-4
- Variant with a new 2100 hp dual-stage-supercharged 18-W engine, a four-bladed propeller, and other minor improvements.
- F4U-4B
- F4U-4's with four 20mm cannons instead of machine guns.
- F4U-4E
- Night fighter variant with the APS-4 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four 20 mm cannons instead of machine guns.
- F4U-4N
- Night fighter variant with the APS-6 search radar on the right wingtip. It had four 20 mm cannons instead of machine guns.
- F4U-4K
- Experimental drone variant.
- F4U-4P
- Photo reconnaissance variant of the F4U-4.
- XF4U-5
- A variant with a new engine cowling and other improvements.
- F4U-5
- F4U-4 with a more powerful Pratt and Whitney R-2800-32(E) engine. Other improvements included all-metal wings, a modernized cockpit, and a fully retractable tail wheel.
- F4U-5N
- A variant of the F4U-5 with a radar.
- F4U-5NL
- F4U-5N's equipped with rubber de-icing boots on the leading wing edge and leading tail edge. Made for cold temperatures of winter.
- F4U-5P
- Long-range photo-reconnaissance variant of the F4U-5.
- F4U-6
- A variant made for the Marine Corps with extra armour and oil coolers. It was designed for ground attack.
- AU-1
- Later redesignation of the F4U-6.
- F4U-7
- AU-1 in French service.
- FG-1E
- A Goodyear FG-1 with radar equipment.
- FG-1K
- Drone variant of the Goodyear FG-1.
- FG-3
- Turbo supercharged variant of the FG-1D.
- FG-4
- Goodyear produced F4U-4. It was never delivered.
- F2G-1
- Goodyear modified F4U-1 with a Pratt and Whitney R-4360, Wasp Major 4-row 28-cylinder radial engine. It had manual-folding wings. Never entered service.
- F2G-2
- F2G-1 with hydraulically folding wings and a tailhook for carrier landings. Never entered service.
Specifications
Operators
ArgentinaArgentine Navy operated 26 F4U-5/5N/5NL Corsairs from 1956 to 1968
Brazil
Brazilian Navy operated 30 F4U-1D from 1950 to 1976
Canada
Royal Canadian Navy operated 130 F4U-1D from 1948 to 1960
Chile
Chilean Navy operated 30 F4U-1D and 20 F4U-4 from 1953 to 1978
El Salvador
Air Force of El Salvador operated 25 F4U/FG-1D from 1957 to 1976
France
French Navy operated 69 AU-1 and 94 F4U-7 from 1954 to 1964
Honduras
Honduran Air Force operated 19 from 1956 to 1979
Netherlands
Royal Netherlands Navy operated 35 F4U-1D from 1943 to 1956
New Zealand
Royal New Zealand Air Force operated 368 F4U-1 and 60 FG-1D from 1944 to 1949
United Kingdom
Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm operated 2,012 Corsairs of all types during World War 2, including 95 Corsair I (F4U-1), 510 Corsair II (F4U-1A), 430 Corsair III (F3A-1D), and 977 Corsair IV (FG-1D)
United States
United States Navy and Marine Corps operated Corsairs of all production variants from 1942 to 1953