Difference between revisions of "T-10M"
Inceptor57 (talk | contribs) (Restored page, Updated template w/ new design) |
Inceptor57 (talk | contribs) m (→Machine guns) |
||
| Line 198: | Line 198: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! colspan="7" | [[ | + | ! colspan="7" | [[KPVT (14.5 mm)|14.5 mm KPVT]] |
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="7" | ''Pintle mount'' | ! colspan="7" | ''Pintle mount'' | ||
Revision as of 16:59, 26 February 2019
Contents
Description
The T-10M is a Rank VI Soviet heavy tank
with a battle rating of 8.0 (AB) and 8.3 (RB/SB). It was introduced in Update 1.51 "Cold Steel".
General info
Survivability and armour
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour (Hull, Turret roof)
- Cast homogeneous armour (Turret)
| Armour | Front | Sides | Rear | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 120 mm (57°) Front glacis 120 mm (49°) Lower glacis 40,60 mm (78-79°) Driver's port |
120 mm (50°) Top 80 mm (0-64°) Middle 30 mm (60°) Bottom |
50 mm (53°) Top 60 mm (21°) Bottom |
30 mm |
| Turret | 120-250 mm (26-60°) Turret front 100 + 250 mm (0-75°) Gun mantlet |
130-190 mm (3-55°) | 102 mm (21-47°) | 30 mm |
| Armour | Sides | Roof | ||
| Cupola | 40 mm | 40 mm |
Notes:
- Suspension wheels are 20 mm thick while tracks are 30 mm thick.
- Turret side armour is not equally thick, ranging from 130 mm to 190 mm in some areas.
Mobility
| Mobility characteristic | ||
|---|---|---|
| Weight (tons) | Add-on Armour weight (tons) |
Max speed (km/h) |
| 50.0 | N/A | 53 (AB) |
| 50 (RB/SB) | ||
| Engine power (horsepower) | ||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded |
| Arcade | 968 | ___ |
| Realistic/Simulator | 663 | 750 |
| Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | ||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded |
| Arcade | 19.36 | __.__ |
| Realistic/Simulator | 13.26 | 15.00 |
Armaments
Main armament
| 122 mm M-62-T2S | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Vertical guidance |
Horizontal guidance |
Stabilizer | ||
| 30 | -4°/+15° | ±180° | Two-plane | ||
| Turret rotation speed (°/s) | |||||
| Mode | Stock | Upgraded | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. |
| Arcade | 13.8 | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ |
| Realistic | 10.1 | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ |
| Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||
| Stock | Prior + Full crew | Prior + Expert qualif. | Prior + Ace qualif. | ||
| 20.00 | __.__ | __.__ | __.__ | ||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration in mm @ 90° | |||||
| 10m | 100m | 500m | 1000m | 1500m | 2000m | ||
| BR-472 | APCBC | 282 | 276 | 262 | 246 | 230 | 215 |
| OF-472 | HE | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| 3BM-11 | APDS | 361 | 360 | 358 | 353 | 338 | 320 |
| 3BK-9 | HEATFS | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Shell details | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity in m/s |
Projectile Mass in kg |
Fuse delay
in m: |
Fuse sensitivity
in mm: |
Explosive Mass in g (TNT equivalent): |
Normalization At 30° from horizontal: |
Ricochet: | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | ||||||||
| BR-472 | APCBC | 950 | 25 | 1.2 | 15 | 204 | +4° | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| OF-472 | HE | 865 | 27 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 3,000 | +0° | 79° | 80° | 81° |
| 3BM-11 | APDS | 1620 | 7.4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | +1.5° | 75° | 78° | 80° |
| 3BK-9 | HEATFS | 920 | 18 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 2,890 | +0° | 65° | 72° | 75° |
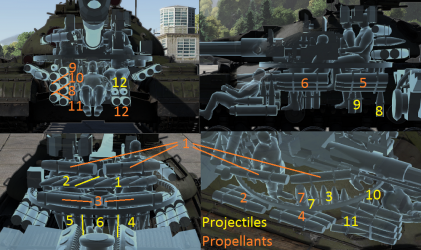
Ammo racks
| Full ammo |
Ammo Part |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
4th rack empty |
5th rack empty |
6th rack empty |
7th rack empty |
8th rack empty |
9th rack empty |
10th rack empty |
11th rack empty |
12th rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | Projectiles Propellants |
27 (+3) 27 (+3) |
24 (+6) 24 (+6) |
20 (+10) 20 (+10) |
17 (+13) 17 (+13) |
14 (+16) 14 (+16) |
11 (+19) 11 (+19) |
10 (+20) 10 (+20) |
9 (+21) 9 (+21) |
7 (+23) 7 (+23) |
5 (+25) 5 (+25) |
3 (+27) 3 (+27) |
1 (+29) 1 (+29) |
No |
Machine guns
| 14.5 mm KPVT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pintle mount | ||||||
| Capacity (Belt capacity) | Fire rate (shots/minute) |
Vertical guidance |
Horizontal guidance | |||
| 250 (50) | 600 | -5°/+60° | ±180° | |||
| Coaxial mount | ||||||
| Capacity (Belt capacity) | Fire rate (shots/minute) |
Vertical guidance |
Horizontal guidance | |||
| 200 (50) | 600 | N/A | N/A | |||
Usage in battles
Describe the tactics of playing in the vehicle, the features of using vehicles in the team and advice on tactics. Refrain from creating a "guide" - do not impose a single point of view but give the reader food for thought. Describe the most dangerous enemies and give recommendations on fighting them. If necessary, note the specifics of the game in different modes (AB, RB, SB).
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Decent top speed for a heavy tank
- Good reverse speed, as with many late Russian heavy tanks
- Can fire a wider range of ammunition than the IS-series heavy tanks (notably HEAT-FS)
- 14.5mm machine guns are effective at deterring strafing aircraft and can shred lightly-armored vehicles.
- Good frontal armor; can take a hit or two thanks to the "pike"
Cons:
- Has ammo in the back of the turret; a shell strike there can end your game if you get flanked
- Can and will be prioritized by the enemy team
- Due to the "pike" of the frontal armor, angling is not a good idea, especially against enemies with HEAT or Sabot rounds.
History
Development
The desire for the successor of the IS-3 heavy tank with a more lenient weight and cost requirement brought forth a start in development in 1948. The tank, labeled the IS-8, used many characteristics from the previous experimental heavy tanks, with the engine of the IS-4 and IS-6, road wheels and tracks of the IS-4, the turret traverse mechanism and suspension system from the IS-7. The IS-8 also used an improved 122 mm gun from the IS-2 and IS-3 models. The armour on the IS-8 and IS-3 were quite similar in format, but was thickened on the IS-8 for improved protection. The hull was extended to make room for an engine cooling system, necessitating another road wheel set on the suspension. The IS-8 was deemed ready for production between late 1950 to early 1951, with production to begin at the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant (ChTZ), with reports that some IS-8 were also produced at a tank plant in Omsk as well.[1]
Stalin's death in 1953 brought forth a political situation of De-Stalinization to eradicate the influence of the late Soviet leader. Due to this, the IS-8 heavy tanks that take its first two letters from the name of Joseph (Iosef) Stalin was renamed to the T-10. Production of the tank continued, but with implemented improvements. The T-10A model introduced a newer 122 mm D-25TS gun with a vertical stabilization system and a bore evacuator, with a rammer implemented inside the tank to ease with the loading process by helping the loaders push the rounds into the breech. The T-10's sole telescopic sight was replaced with two new sights, one periscopic and one telescopic. There was also a night-vision device and gyrocompass installed for the gunner. The next upgrade was the T-10B in the mid-1950s, which introduced a two-axis stabilization for the gun and new fire control sight inside with little changes outside. The final revision was with the T-10M in 1957, with the most notable difference being the new M-62-TS gun, which was longer than its previous iterations and presents a very unique multi-slotted muzzle brake and bore evacuator along with having a stabilization system. DShK heavy machine guns were also replaced with the newer KPVT machine guns, which benefited by being similar in ballistic characteristics with the M-62-TS gun to double as a range-finder. Another change in the T-10M was the improved 750 hp engine. The last reported change to the T-10 design was in the 1960s when the tanks went through a rebuild with a new transmission and main clutch.[1]
By the time the T-10's production ended in 1962, a total of 8,000 of all types of T-10 heavy tanks had been manufactured, making the T-10 the most numerous Soviet heavy tank produced.[1]
Usage
The T-10s were organized in heavy tank regiments in the same way as the IS-3s. When first introduced, the Soviet heavy tank regiments were a composite unit organized in 1947 that were made of between 44-46 heavy tanks bolstered by 21 heavy assault guns. In between 1958 and 1959, the heavy tank regiments were reorganized to consist of only heavy tanks, 100 IS-3 or T-10 tanks that made the formation quite powerful. These regiments would help make up heavy tank divisions, which would consist of two heavy tank regiments and one medium tank regiment. These heavy tank divisions, intended to drive an offensive operation, were stationed along the borders of Soviet Union against the Western forces.[1]
The T-10, like the IS-3, were a concern to the Western forces whose only response were the heavy M103 and Conqueror heavy tanks. The T-10 never saw combat against a Western force, but was deemed invulnerable in frontal engagements against medium tanks of the time like the M48 Pattons, even when they used HEAT rounds. However, in a contest against the heavy tanks, the M103 and Conqueror presented better fire-control systems and range-finders that would benefit a well-trained and emplaced crew against an offensive force. The contest between the two sides with their heavy tanks reached a disparity with the introduction of newer tanks like the M60 and Chieftain, both which have guns able to penetrate straight through the T-10's front armour at standard ranges.[1]
Decline and discontinuation
Though the T-10 and the Soviet heavy tank family gave a formidable opponent to the Western forces, their fame and glory became short-lived in the 1960s. The new premier of the Soviet Union, Nikita Khrushchev, began cut backs in the military with a new strategic goal of missiles and nuclear armament rather than with conventional forces. The heavy tanks, considered outdated, was ordered to have their production halted in 1960 by Khrushchev.[1] His orders are not without reason, heavy tanks are difficult to maintain and transport across the huge Soviet Union, which also did not have many bridges that could support a heavy tank. Another reason was the changing anti-tank technology that made tank armour extremely vulnerable, especially against the new anti-tank missiles that are becoming more and more efficient at their task in destroying tanks. Still, the order did not mean the dissolution of heavy tank units as by 1978, there were still up to 2,300 heavy tanks in the Far East. To this day, many heavy tanks are still either in inactive reserves or dug in as pillboxes along the borders of the Soviet Union. The heavy tank's place in the Soviet Union's military was replaced by the main battle tanks (MBT) like the T-64, which presented a much better firepower, armour, and mobility for only a weight of 35 tons, a technological sign on the rising prevalence of the MBT.[1]
Media
An excellent addition to the article will be video guides, as well as screenshots from the game and photos.
References
See also
Links to the articles on the War Thunder Wiki that you think will be useful for the reader, for example:
- reference to the series of the vehicles;
- links to approximate analogues of other nations and research trees.
External links
| USSR heavy tanks | |
|---|---|
| KV-1 | KV-1 (L-11) · KV-1 (ZiS-5) · KV-1E · KV-1S |
| KV-2 | KV-2 (1939) · KV-2 (1940) · KV-2 (ZiS-6) · KV-220 |
| Other KVs | KV-85 · KV-122 |
| IS-1/2 | IS-1 · IS-2 · IS-2 (1944) · IS-2 No.321 · IS-2 "Revenge" · Object 248 |
| Other IS tanks | IS-3 · IS-4M · IS-6 · IS-7 |
| T-10 | T-10A · T-10M |
| Multi-turreted | T-35 · SMK |
| Other | Object 279 |
| Lend-Lease | ▂MK-II "Matilda" |