Difference between revisions of "Pz.38(t) A"
(→Armaments: Added data, updated format) |
CobraKingII (talk | contribs) m (→Pros and cons) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 188: | Line 188: | ||
* Compact size allows great use of terrain as a cover | * Compact size allows great use of terrain as a cover | ||
* Vertical stabilizer | * Vertical stabilizer | ||
| + | * 10 degrees of gun depression allow you to hide your hull effectively | ||
'''Cons:''' | '''Cons:''' | ||
| − | |||
* Weak armour | * Weak armour | ||
| + | * Average mobility for a light tank | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
Revision as of 20:08, 23 May 2020
Contents
| This page is about the German light tank Pz.38(t) A. For other uses, see LT-38 (Family). |
Description
The Pz.Kpfw. 38(t) Ausf. A is a rank I German light tank
with a battle rating of 1.3 (AB/RB/SB). It was introduced during the Closed Beta Test for Ground Forces before Update 1.41.
The Panzerkampfwagen 38(t) Ausf. A is a small nimble beginners tank. It boasts a decent 37 mm cannon, which can easily get through most armour at its rank. The tank is primarily a support tank, helping the larger tanks push forward. The armour is not very heavy, and most cannons and autocannons can get through it. Always try to make use of your gun depression, hiding your hull behind terrain and obstacles, while exposing only your turret to the enemy.
General info
Survivability and armour
Armour type:
- Rolled homogeneous armour
- Cast homogeneous armour (Gun mantlet)
| Armour | Front (Slope angle) | Sides (Slope angle) | Rear (Slope angle) | Roof |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 25 mm (18-23°) Front plate 12 mm (74°) Front glacis 25 mm (14°), 8 mm (65°) Lower glacis |
15 mm | 15 mm (11-14°) | 10 mm |
| Turret | 25 mm (10°), 15 mm (9-10°) Turret front 25 mm (0-90°) Gun mantlet |
15 mm (0-9°) | 15 mm (8°) | 8 mm |
| Armour | Sides | Roof | ||
| Cupola | 15 mm | 8 mm |
Notes:
- Suspension wheels and tracks are 15 mm thick.
- Belly armour is 8 mm thick.
Mobility
| Game Mode | Max Speed (km/h) | Weight (tons) | Engine power (horsepower) | Power-to-weight ratio (hp/ton) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Stock | Upgraded | Stock | Upgraded | ||
| Arcade | 47 | 7 | 9.7 | 194 | 238 | 20 | 24.54 |
| Realistic | 43 | 7 | 111 | 125 | 11.44 | 12.89 | |
Armaments
Main armament
| 37 mm KwK38(t) | Turret rotation speed (°/s) | Reloading rate (seconds) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Capacity | Vertical | Horizontal | Stabilizer | Stock | Upgraded | Full | Expert | Aced | Stock | Full | Expert | Aced |
| Arcade | 90 | -10°/+25° | ±180° | Vertical | 13.33 | 18.45 | 22.40 | 24.77 | 26.35 | 4.29 | 3.80 | 3.50 | 3.30 |
| Realistic | 8.33 | 9.80 | 11.90 | 13.16 | 14.00 | ||||||||
Ammunition
| Penetration statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Penetration @ 0° Angle of Attack (mm) | |||||
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1,000 m | 1,500 m | 2,000 m | ||
| Pzgr. 34(t) | APC | 62 | 59 | 45 | 32 | 23 | 17 |
| PzGr. 40 | APCR | 86 | 77 | 47 | 26 | 14 | 8 |
| Pzgr.(t) umg. | APC | 61 | 58 | 44 | 31 | 22 | 15 |
| Shell details | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammunition | Type of warhead |
Velocity (m/s) |
Projectile Mass (kg) |
Fuse delay (m) |
Fuse sensitivity (mm) |
Explosive Mass (TNT equivalent) (g) |
Ricochet | ||
| 0% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
| Pzgr. 34(t) | APC | 741 | 0.85 | 1.2 | 9.0 | 22.1 | 48° | 63° | 71° |
| PzGr. 40 | APCR | 1,020 | 0.368 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 66° | 70° | 72° |
| Pzgr.(t) umg. | APC | 750 | 0.815 | 1.2 | 9.0 | 22.1 | 48° | 63° | 71° |
Ammo racks
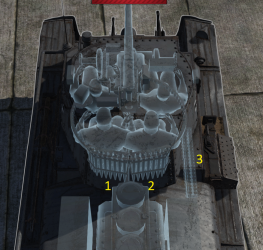
| Full ammo |
1st rack empty |
2nd rack empty |
3rd rack empty |
Visual discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 61 (+29) | 31 (+59) | 1 (+89) | Yes |
Center empty: 31 (+59)
Machine guns
| t) (7.92 mm MG37(t) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount | Capacity (Belt) | Fire rate | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Coaixal | 5,500 (200) | 768 | N/A | N/A |
Usage in battles
The Pz.38(t) A is used in much the same way as the Pz.35(t). It is lighter than and better-engined than its predecessor, so it can get to ambush positions quicker. The gun is the same, but the higher battle rating pits it against B1 ters and and other armored threats that it cannot deal with easily, even with its APCR shell.
Modules
| Tier | Mobility | Protection | Firepower | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Tracks | Parts | Horizontal Drive | Pzgr.(t) umg. | ||
| II | Suspension | Brake System | FPE | Adjustment of Fire | PzGr. 40 | |
| III | Filters | Crew Replenishment | Elevation Mechanism | |||
| IV | Transmission | Engine | Artillery Support | |||
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Good firepower
- Pzgr. 34(t) round has no tracer
- Decent mobility
- Compact size allows great use of terrain as a cover
- Vertical stabilizer
- 10 degrees of gun depression allow you to hide your hull effectively
Cons:
- Weak armour
- Average mobility for a light tank
History
Development
In 1935, ČKD (Českomoravská Kolben-Daněk), the tank manufacturer in Czechoslovakia wanted to find a replacement to the LT vz.35 (Also known as the Panzer 35(t) in German service). The reason being is that the vz.35 was complex and had its faults that impeded its efficiency and orders for new tanks would be coming from the gradually growing Czechoslovak army and other countries. They work jointly with Škoda Works in the development of this new tank.
The next tank design, designated in Czechoslovakia as the LT vz.38, fitted a conventional design for the interwar period. The armour was riveted with about 25 mm thick in the front hull and was not sloped. The engine was placed in the rear, with a two-man turret in the centre, and the driving compartment in the front with a front transmission. Perhaps the biggest distinction for this tank design was the use of a leaf-spring unit suspension consisting of four large wheels. The turret housed the 37 mm Skoda A7 armament with about 90 rounds of ammunition stored in the vehicle. Unlike traditional designs, the coaxial machine gun is mounted on a ball mount allowing it to be aimed independently on targets, yet could be fixed for coaxial usage. There is another machine gun in front used by the assistant driver, who also doubled as the radio operator placed on the left of the operator as the driver was on the right side of the tank. The LT vz.38 was a very reliable design.
The LT vz.38 was successfully exported under the name "TNH" and was given to Iran, Peru, Switzerland, and Lithuania, all under different names, but done in small quantities (Iran bought the most at 50 units). The British Royal Armoured Corps ordered one trial model out in an evaluation, but their evaluations came that the vehicle was uncomfortable for the crew and was impossible to lay the gun when the vehicle is in motion, thus the British did not order any and returned the trial model. Then in 1937, the Czechoslovak armed forces started a contest for a new tank to be put into service. Three companies, Škoda, ČKD and Tatra, were involved and submitted their various designs with Škoda a variant of the LT vz.38, ČKD a prototype model different from the LT vz.38, and Tatra a very different design concept altogether. The army then chose the LT vz.38 model and ordered 150 units in July 1938, but these were never put to service in Czech usage when the German-occupied Czechoslovakia in March 1939.
German adoption
When Germany took control of Czechoslovakia, they ordered the LT vz.38 production to continue as its firepower, armour, and mobility was considerably better than the Panzer I and Panzer II, which made up most of the German armoured forces in 1939. At first, it was used under the designation LTM 38, but this was changed in January 1940 to the Panzerkampfwagen 38(t), or the Panzer 38(t) for short. The Panzer 38(t) was used as a substitute for the Panzer III due to the similarity in armour and armament. The 37 mm Skoda A7 cannon was renamed the 37mm KwK38 (t). The Germans would gradually upgrade the design in its production life and have seven different variants (A-G) of the normal production model, but are divided into one with 25 mm of frontal riveted armour originally, and the other with a total frontal armour thickness of 50 mm by bolting on another 25 mm of armour to the hull. Production under Germany control continued from 1939 to 1942 with a total of 1,414 tank units built (excluding export models and other vehicles built with the chassis).
Combat usage
The Panzer 38(t) served well in the initial campaigns for Germany in World War II, performing well in the invasion of Poland and France in 1939 and 1940 respectively. Some notable German tank aces would start their careers with this tank; such as Otto Carius, who would become one of Germany's well known Tiger Ace. Though unable to deal with the heavier tanks in Allied service, it was able to engage the armour of most light tank designs at the time. It wasn't until the initiation of Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union, where the Panzer 38(t) has become outclassed in all ways by the Soviet T-34s and KV-1 tanks. Due to the small two-man turret, it could not be modified to accept a larger gun capable of defeating these tanks. Not only that, but the Panzer 38(t) was also vulnerable to the Soviet 47 mm anti-tank gun due to the lower armour quality on the tank. These two drawbacks of the Panzer 38(t) caused it to be retired from front-line services for better tanks such as the Panzer IV. Despite its retirement, the chassis was found to be a very adaptable design, so it would continue to be used in a variety of roles such as the Marder III and Jagdpanzer 38(t) tank destroyer, Flakpanzer 38(t) anti-aircraft gun, and the Grille self-propelled artillery piece. A dedicated reconnaissance variant is known as the Aufklärungspanzer 38(t) was also built to supplement the need for reconnaissance vehicles.
Despite its retirement as a front-line weapon, the Panzer 38(t) tank still saw usage as a reconnaissance vehicle and an anti-partisan vehicle in German-controlled territory. The usage of the chassis in different roles freed up many turrets to serve as fortifications to be used in a variety of locations, such as the Atlantic Wall, which proved well in against infantry attacks as it's small 37 mm cannon was inadequate against the increasing armour of Allied tanks.
Other countries
The Panzer 38(t), as a widely exported tank model, also saw service with Romania, Kingdom of Bulgaria, Hungary, Slovak Republic, Sweden, Switzerland, Peru, and Iran. Sweden was one of the few countries that were granted a license to construct the Panzer 38(t) under their designation as the Stridsvagn m/41 after their initial batch were seized by the Germans with the takeover of Czechoslovakia. Deliveries of the first batch of the initial tank model started in December 1942 and ended in August 1943. Then the second batch of 122 units was ordered in mid-1942 for more of these tanks due to urgent demand, the second batch would have the 50 mm armour plate thickness and with a redesigned interior and better engine to compensate the weight increase. 104 of the second batch was delivered before production ended in March 1944. Some of these tanks would be converted into sav M/43 assault guns or armoured personnel carriers during and after the war. Peru was also another prolific user of the Panzer 38(t), using them in the Ecuadorian-Peruvian War in 1941 as the mainstay of their tank battalions. The tanks added with the lack of capable anti-tank weapons in Ecuadorian forces made the Panzer 38(t) proved very well in the war and even stayed in service for more than 50 years before being retired.
In-game description
The Pz.Kpfw. 38(t) Ausf. A light tank was developed by the company ČKD in 1938 for the Czechoslovakian Army, under the designation LT vz.38. Serial production of the tank in 1939 manufactured 150 machines. After the German occupation began, they entered the service of the German Army, under the designation Pz.Kpfw. 38(t) Ausf. A.
8 rollers were installed in place of the multi-wheel suspension chassis typical of Czechoslovakian tank construction. The front and rear pairs of wheels were joined with a balancer using a leaf spring unit for shock absorption. The suspension's design coped well with the full 8,500 kg of the tank's weight and allowed designers to save a couple hundred kilograms. The tank had a forward mechanical transmission with a 5-speed Praga-Wilson gearbox, which later became the standard for all tanks of this type.
The PzKpfw. 38(t) Ausf. A tanks were completely identical to those intended for the Czechoslovakian Army, with the exception of some equipment. German engineers slightly increased the armor of the ball-mount machine gun in the tank's hull and replaced the vz.37 radio for their own Fu5 with the handle antenna. The tank had Praga ERA engines providing 125 horsepower. Its armament consisted of 37-мм Škoda A-7 3.7 cm KwK 38(t) L/47.8 cannons with 72 shells and two Zbrojovka Brno ZB vz.37 (MG.37(t)) machines guns with 2,400 rounds for both. The tank's armor thickness ranged from 8 to 25 millimeters.
These machines were used in German Panzer divisions in the Polish and French campaigns and in the attack on the USSR. The PzKpfw. 38(t) Ausf. A is considered the best Czech-made tank.\t The tank's main disadvantages were the riveted joints between its armor plates and the use of fragile, inflexible steel. A 45 mm projectile could fragment the armor plating and bolts, and these fragments would do more damage to the crew and the tank than the shrapnel from the projectile itself.
Media
Skins and camouflages for the 38(t) series from live.warthunder.com.
See also
- Pz.35(t) - Preceding Czech tank design.
- Pz.38(t) F - Succeeding version.
External links
| Germany light tanks | |
|---|---|
| Pz.II | Pz.II C · Pz.II C (DAK) · Pz.II C TD · Pz.II F · Pz.Sfl.Ic |
| Sd.Kfz.234 | Sd.Kfz.234/1 · Sd.Kfz.234/2 · Sd.Kfz.234/2 TD |
| Marder | Marder A1- · Marder 1A3 · Begleitpanzer 57 · DF105 |
| SPz PUMA | PUMA · PUMA VJTF |
| Wheeled | Sd.Kfz.221 (s.Pz.B.41) · Class 3 (P) · Radkampfwagen 90 · Boxer MGS |
| Other | Ru 251 · SPz 12-3 LGS |
| Argentina | TAM · TAM 2C · TAM 2IP · JaPz.K A2 |
| Czechoslovakia | Pz.35(t) · Pz.38(t) A · Pz.38(t) F · Pz.38(t) n.A. · Sd.Kfz. 140/1 |
| France | Pz.Sp.Wg.P204(f) KwK |
| Lithuania | Vilkas |
| USA | leKPz M41 |
| USSR | SPz BMP-1 |





